18.1 - Enzymes Flashcards
2
A molecule being acted upon by an enzyme.

substrate

A substance needed for enzyme functioning, not protein based.

coenzymes

A substance needed for enzyme functioning, other than substrates.

cofactors

Most enzyme end with this suffix.
–ase (Suffix)
Example: kinase or carboxylase.
Molecules sugars end with this suffix.
–ose (suffix)
(Examples: sucrose and glucose.)
This class of enzymes oxidizes or reduces reactions.

oxidoreductases
This subclass enzyme oxidizes a substance.

oxidase
This subclass enzyme reduces substances.

reductase
This subclass enzyme forms a double bond on a molecule by removing dihydrogen (H2).
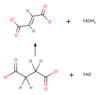
dehydrogenase
(Dihydrogen, H2, HH)
The two pairs of cofactors that are found in the body, they oxidize and reduce cofactors.
NAD+/NAD
FAD/FADH2
This class of enzymes transfers a functional group from one substrate to another.

transferase
This subclass enzyme transfers amine groups on molecules.

transaminase
This subclass enzyme transfers phosphate groups on molecules, with the cofactor of ATP/ADP or analog thereof.

kinase
This class of enzymes breaks bonds in molecules with water (HOH).

hydrolase
This enzyme is commonly found in Chymotrypsin (a protease).
The amino acids C-term and N-term are peptide chains and charged at psychological pH
This subclass enzyme breaks glycosidic bonds by hydrolysis.

glycosidase
(sugar)
This subclass enzyme breaks ester bonds by hydrolysis.

lipase
(lipids).
This subclass enzyme breaks peptide bonds by hydrolysis.

peptidase
(or protease)
peptide/amide/protien
This subclass enzyme breaks phosphate ester bonds by hydrolysis.

nuclease
(nucleic acids).
This class of enzymes Joins or breaks and adds or removes groups or substrates on molecules with no energy.

lyase
Not to confuse with ligase, which does use energy.
This subclass enzyme adds water (HOH).

hydrase
This subclass enzyme removes carbon dioxide (CO₂).

decarboxylase
Carbon dioxide: CO2 \ COO- \ Carboxylic Acids
This subclass enzyme removes water (H2O).

dehydrase
Water: H2O \ HOH
This subclass enzyme removes ammonia (NH3)-.

deaminase
Ammonia: (NH3) \ (NHHH)-
This subclass enzyme adds small molecules to doubled bonds on a molecule.

synthase















