1.4: Orbital Autonomics Flashcards
What holds the eyes in their vertical position?
The suspensory ligament
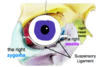
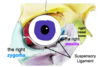
Where does the suspensory ligament attach?
Laterally, it attaches to the zygoma
Medially, it attaches to the maxilla
Describe what can happen during ocular trauma when the zygoma is damaged?
Zygoma is damaged
Suspensory ligament lowers the eye on one side
Can lead to diplopia
What is diplopia?
Double Vision
Orbital trauma can lead to damage to the XXXX
This results in a general sensory deficit of the YYYYY
Orbital trauma can lead to damage to the neurovascular bundle
This results in a general sensosry deficit of the facial skin
What supplies
Purple
Blue
Pink?

CN V1 Opthalmic Nerve
CN V2 Maxillary Nerve
CN V3 Mandibular Nerve
What nerve is supplying the skin? (Purple)
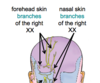
CN V1
Opthalmic Nerve
What supplies the:
- Forehead
- Upper Eyelid
- Cornea
- Conjunctiva
- Skin of the top of the nose
CN V1
Opthalmic
What nerve is supplying the skin?
(Blue)

CN V2
Maxillary
What supplies the:
- Skin of the lower eyelid
- Skin over the maxilla
- Skin over the ala of the nose
- Skin/mucosa of the upper lip?
CN V2
Maxillary
What nerve is supplying the skin?
(Pink)

CN V3
Mandibular
What supplies the skin over the TMJs and the mandible?
CN V3
Mandibular
What supplies the angle of the mandible?
C2,C3 Spinal Nerves
Describe the blink reflex
- Action potentials conducted centrally via CN V1 to the trigeminal ganglion
- Then conducted in CN V to the Pons
- CNS connections between CN V and CN VII
- Action potentials are conducted peripherally via CN VII to the eyelid part of the orbicularis oculi
What are the two nerves involved in the blink reflex?
CN V (Specificially CN V1)
CN VII
Briefly describe the path of sympathetic axons from the CNS to the organs of the head region?
- Cell body of the presynaptic neurone in the CNS
- Presynaptic Axon
- Ganglion
- Postsynaptic Axon
- Organ

SYMPATHETIC
What is released by the presynpatic axon?
What is released by the postsynaptic axon?
Presynaptic axon releases acetylcholine
Postsynaptic axon releases noradrenaline
Describe the pathway presynpatic sympathetic axons from the CNS?
Descend in the spinal cord
Exit spinal cord at T1 spinal nerve
Ascend within the sympathetic trunk
Synapse in the superior sympathetic ganglion
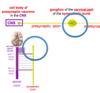
Descrieb the pathway of the post-synaptic axons from the CNS?
- Enter the internal and external carotid nerve
- Pass onto the surface of the internal and external carotid arteries
- Carried to the organs on the surface of the branches of these arteries