1:2. Orbit and the Eye Anatomy Flashcards
Name the bones (not the labels)

Beige = Frontal
Blue = Zygomatic
Purple = Maxilla
Red = Sphenoid
Yellow = Ethmoid
Dark Blue = Lacrimal
Green = Nasal
Name the labels (not the bones)
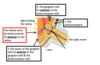
A –> F

A = Superior Orbital Fissue
B = Optic Canal
C = Orbital Plate of the Frontal Bone
D = Supraorbital Notch/Foramen
E = Orbital Plate of Ethmoid
F = Infraorbital Foramen
Name all the same labels on this skull?
Superior Orbital Fissure
Optic Canal
Orbital Plate of the Frontal Bone
Orbital Plate of the Ethmoid Bone
Supraorbital Notch
Infraorbital Foramen
Difference between a foramen and a notch?
Foramen is a complete circle
Notch is uncomplete - like a C shape
The bony orbit is described as a four sided pyramid
The apex is the orbital canal
What does the base make up?
What is it composed of?

The base makes up the orbital rim
Composed of superior, inferior, medial and lateral orbital margins
How is the eye protected from a direct blow?
Orbital Margins - superior orbital margin is further forward than inferior so eye is protected
Orbital rim - nothing bigger than the orbital rim will come into contact with the actual eye
Describe orbital blowout fractures?
The medial wall and orbit floor are very thin
In trauma, the orbital margins and rim don’t fracture as they are strong
The medial wall and floor are very thin though and can break
Can cause an orbital blowout fracture
Complications of orbital blowout fracture?
Orbital contents can become trapped
Infraorbital neurovascular bundle can be damaged
If the infraorbital neurovascular bundle was damaged in a blowout fracture, what would happen?
Loss of sensation to face
The external eyelid is split into two parts:
Name them
Identify them
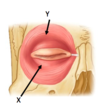
Orbital Part
Palpebral Part
X = Palpebral
Y = Orbital
Name the muscle that surronds the eye in the external layer?

Obicularis Oculi
What is the orbital septum?
This is a sheet of fascia below the eyelid
Found in the middle layer
This separates the superficial part of the eye from the deep part to prevent the spread of infection

Label these parts of the eyelid
Which layer is this?
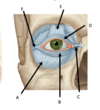
A = Orbital Septum
B = Inferior Tarsus
C = Medial Palpebral Ligament
D = Superior Tarsus
E = Tendon of Levator Palpebrae Superioris
F = Lateral Palpebral Ligmanent
Internal Layer
What is the Tarsal gland?
Where is it found?
These secrete an oily/waxy substance that prevents the eyelids from sticking together and prevents tears from overflowing and streaming constantly
Found in the tarsal plates of the tarsi
Describe the Tarsi?
Found above and below the eye
Plates of fibrous connective tissue that give the eyelid its half moon shape
Give protection to eye and attachment for muscles
Where does the Levator Palpebrae superioris attach?
The superior Tarsi
Name the surface anatomy of the eye
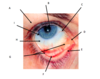
A = Location of the lacrimal duct
B = Pupil
C = Blood Vessel (Conjuctival vessel)
D = Lacrimal Lake
E = Puncta
F = Lower eyelid, lined with Conjuctiva
G= Conjunctival Fornix
H = Sclera, covered by conjuctiva
I = Limbus/Corneoscleral Junction
What innervates the lacrimal gland?
CN VII (Facial Nerve)
Parasympathetic
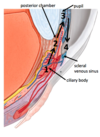
Describe how the lacrimal apparatus works?
CN VII Parasympathetic innervation
Lacrimal gland produces lacrimal fluid
Washes across eye
Collects in lacrimal lake
Drains out of Puncta
Drains into lacrimal sac
Drains along nasolacrimal duct
Eventually reaches inferior meatus
Where does the lacrimal fluid end?
Inferior Meatus
Coloured bit in the centre of the eye?
Black bit in the very centre of the eye?
White bit in the eye?
Clear, transparent bit that covers the coloured bit?
Iris
Pupil
Sclera
Cornea
What control is the pupil under?
Autonomic
Describe the layers of the eye?
Fibrous, Outer Part
Uvea = Middle Layer
Retina (Inner Layer)
Describe the outer layer of the eye
Tough and fibrous
Composed of two parts
Sclera - the white part where extra-ocular muscles attach. Makes up about 5/6ths of the eye
Cornea = Clear, colourless, front of the eye. Makes up most of the refractive power - the ability to focus light
Describe the middle layer of the eye
The Uvea
This is the vascular layer
Has three parts:
- Iris
- Ciliary Body
- Choroid
Describe the function of the three parts of the middle layer of the eye (the uvea)
Iris = Changes size of pupil
Ciliary Body = Attaches to iris. Changes shape of lens and secretes aqueous humour
Choroid = Provides nutrition and gas exchange