10/15- Malabsorption Flashcards
Effects of Billroth II (gastric surgery)?
- Loss of antrum -> poor grinding
- Loss of pylorus
- Asynchronous bile and pancreatic secretions
- Poor mixing
- Blind loop
- Abnormal motility and poor mixing
- Gastrojejunostomy
What are the different classes of nutrients?
- Fats
- Carbohydrates
- Proteins
- Vitamins
- Minerals
- Water
What is the most energy dense nutrient?
Fat
- 9 kcal/g
- Intake 60-100 g/day
Are TGs water soluble or insoluble?
TGs are NOT water soluble
- Absorption takes the most steps:
- Pancreatic
- Biliary
- Intestinal
- Intracellular

What is the structure of a TG? Common fatty acids?
H2C-O-CO-R (3) + fatty acid
90% of the fatty acids are:
- Palmitic (16)
- Stearic (18:0)
- Oleic (18:1)
- Linoleci (18:2)
Describe the pancreatic phase of fat absorption
TG degraded by lipase into 2-monoglyceride + 2 fatty acids
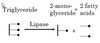
Describe the hepato-biliary phase of fat absorption
Solubilization
- Bile acid monomers can form micelles
- Can complex with cholesterol (and phospholipid)
1. Micelle Formation
- Physical chemical complex - spherical ~3 mm, related to detergent property of bile acids
2. Bile acids
- Detergents (polar and non-polar ends) made from cholesterol
(Critical micellar concentration 2 - 4 mM spontaneously orient into spheres)
What substances can micelles carry/bind?
- Fatty acids
- Monoglycerides
- Cholesterol
- Fat soluble vitamins
Describe the mucosal/absorptive (intestinal) phase of fat absorption
- Micelles disaggregate at mucosal cell surface
- Monoglycerides and fatty acids are absorbed
- Bile acids reform micelles
- Bile acids absorbed in ileum and recycled (entero-hepatic circulation) for reuse (4-6 times per meal)
Describe the intercellular/lymphatic phase of fat absorption
- Re-esterification of long-chair fatty acids and monoglycerides
- Packaged into chylomicrons (protein-cholesterol-phospholipids)
- Transported via lymph
T/F: Micelle formation is essential for fat absorption
False
- Medium chain TGs do not require micelles
- Re-esterification is not essential
When could one benefit from the alternate fat absorption method involving medium chain TGs
- Re-esterification is not essential
- Transported via portal vein
- Useful in diseases associated with lymph blockage (e.g. lymphoma)
What enzyme breaks down starch?
- Percentage of carb intake
Amylase (in the brush border)
- Starch = 60% of carbs in diet (sucrose 30%, and lactose, 10%)
What enzymes break down disaccharides?
- Breakdown products?
- Maltase (maltose, maltotriose) -> glucose
- Dextrinase (dextrins) -> glucose
- Lactase (lactose) -> galactose + glucose
- Sucrase (sucrose) -> glucose + fructose
Where does major protein absorption occur?
- Jejunum (major)
- Ileum (final absorption touches)
Where does protein degradation occur?
- Saliva
- Stomach: gastric acid, mixing
- Duodenum: bile and pancreatic secretions
What are the typical presenting features of malabsorption?
- Weight loss
- Steatorrhea
- Vitamin deficiencies
- Malnutrition
- Watery diarrhea is NOT a usual presentation
What is steatorrhea?
- Creatorrhea?
- Steatorrhea = fat malabsorption with large, bulky, paste-like, very foul stools
- Creatorrhea = nitrogen malabsorption (typically fixed when fat malabsorption problem fixed)
Causes of weight loss (broadly)?
- Inadequate intake
- Excess loss
- Excess need
What conditions fall under the category of weight loss: inadequate intake (or mal-ingestion)?
- Anorexia
- Depression
- Inability to chew
- No food
- No money
- Dysphagia, etc.
What conditions fall under the category of weight loss: excess loss?
- GI = malabsorption
- Urinary = diabetes
What conditions fall under the category of weight loss: excess need?
Thyrotoxicosis
What are tests for malabsorption?
- Fecal fat excretion
- Quantitative or qualitative
- Measure of total intestinal function
- D-xylose absorption
- Measure of proximal* intestinal function
- No digestion required
- Can measure in blood, urine, breath
- B12 absorption tests
- Measure of distal* intestinal function
- Small bowel biopsy
- Diagnose mucosal diseases, parasites, tumors
- Small bowel x-ray
- Breath tests (e.g., bile salt)
- Screening tests for malabsorption (e.g. carbs, bile salts)
- Pancreatic function
- Lundh test meal
- Secretin test
- Response to enzyme therapy
Tests that are not of great value for malabsorption?
- Serum carotene
- Qualitative fecal fat
Describe fecal fat test
- 72 hr duration test
- Measure amt of fat ingested (% of intake)
- Fat intake influences fat excretion (?)
- Evaluate effect of bowel resection
What are the effects of ileal resection on fecal fat?
If > 100 cm (fixed) of ileum resected, will have increased fecal fat excretion
Describe the bile acid breath test
- Breath collected (drying tube, rubber tubing, transfer pipette) into scintillation counting vial
- Measure breath radioactive CO2 specific activity
- Indicates exposure of bile acids to bacteria
What are causes of B12 absorption?
- Describe Schilling’s test
Schilling’s used radioactive B12 (not done anymore)
- Stage 1: no addition = normal IF and ileum
- Stage 2: add intrinsic factor => pernicious anemia
- Stage 3: add antibiotics => bacterial overgrowth
- Stage 4: add tryspin => pancreatic insufficiency
What are some causes of insufficient pancreatic enzyme activity?
- Chronic pancreatitis
- Pancreatic resection
- Pancreatic carcinoma
- Cystic fibrosis
- Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
What is the treatment for insufficient pancreatic enzyme activity?
- Replace enzymes
- Fix pH problems
Describe the different protective substances that bind B12 and aid in absorptive process
- R protein binds B12 in stomach
- Trypsin in pancreatic secretions digests R protein
- B12 binds intrinsic factor
What are some causes of insufficient bile salt activity?
- Biliary obstruction (jaundice)
- Blind loop syndrome
- Ileal disease or resection
- Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
How could you help diagnose pernicious anemia is you suspect it as the cause of B12 malabsorption?
Measure gastrin (should be low)
Treatment for insufficient bile salt activity?
- Remove obstruction
- Eliminate bacteria
- Give ox bile
- Fix pH problems
List of small bowel diseases (contributing to malabsorption)
- Resection
- Celiac sprue (gluten enteropathy)
- Whipple’s disease
- Amyloid
- Lymphoma
- Crohn’s disease
- Many more
What causes Celiac Sprue?
- Histological finding
- Results in
- Caused by ingested toxin (gluten)
- Loss of intestinal villi
- Results in malabsorption
What is seen here?

Normal small bowel biopsy
- Many villi with big absorptive surface area
What is seen here?

Celiac disease
- Big crypts; no villi
What is seen here?

Celiac disease: “scalloping”
What is seen here?

Celiac disease: “scalloping”
- Mosaic pattern (50% sensitive; 95% specific)
What is seen here?
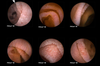
Characteristics of Celiac Sprue
- Absent villi
- Fissuring
- Scalloping
- Mosaic pattern
- Fissuring and ulcer
What causes celiac disease
- Pathogenesis
- Immune response centers on what
- Where is it most severe
Genetically determined, specific immune response to antigens present in the wheat protein, gluten
- Most severe in proximal bowel (because allergy)
Pathogenesis:
- Gluten -> deamidated gluten -> activates APC -> activates Th cell
- > activates plasma cell to produce antibodies
- IgA vs. TG2 and anti-deamidated gluten
- Immune response is focused on limited portion of alpha-gliadin
- Production of epitopes recognized by CD4 T cells
- Requires deamidation by tissue transpeptidase producing a 33 mer resistant to further digestion

How is celiac disease diagnosed?
- Stool fat
- D-xylose
- Serologic (antibody) tests
- Anti-gliadin
- Anti-endomysial (EMA) (EMA-IgA)
- Anti-tissue transglutaminase (tTG) (tTG-IgA)
- Small bowel biopsy***
Process of diagnosing/documenting celiac disease?
- Demonstrate impaired mucosal function
- Document mucosal lesion
- Improvement with gluten withdrawal
- Clinical - rapid
- Histologic - slower
What causes variability in celiac disease?
- Key = length of bowel involved
- Proximal only: selective iron deficiency anemia unresponsive to oral iron therapy
- Iron reabsorbed in duodenum!!
- Large amount: pan malabsorption
- Diarrhea, weakness, weight loss, anemia, tetany, bleeding (vitamin K deficiency), etc.
What key nutrients are absorbed in:
- Dudodenum
- Jejunum
- Ileum
- Duodenum: Iron (Fe)
- Jejunum: folate
- Ileum: Vit B6
(double check?)
Therapy for celiac disease?
- Gluten free diet
- No: wheat, rye, barley
- Yes: rice, oats, corn
- Replace vitamins
What causes lactase deficiency
- Mechanism
- Genetic?
- Lack of brush border disaccharidase
- Congenital
- Acquired
- Ethnic
- Mucosal disease (e.g., viral gastroenteritis)
How to diagnose lactase deficiency?
- History (e.g., can not drink milk)
- Lactose tolerance test
- Symptoms after large lactose drink: diarrhea, cramps, gas, borborygmi; no rise in blood glucose
- Breath hydrogen test
- Increase after lactose ingestion as lactose gets to colon
Lactose is normally broken down into what products?
- What about in lactase deficiency?
- Normally -> glucose + galactose and absorbed in small intestine
- In lactase deficiency, converted into lactic acid and other products (H2 and CO2) by bacteria in the colon; osmotic diarrhea as well (fluid pulled into colon)
What does someone have if they think they are allergic to mushrooms?
Trehalase (a disaccharidase) deficiency!
Bacterial overgrowth:
- Causes/predispositions
- Pathogenesis
- Result
Causes:
- Diverticula
- Motor abnormalities of the small bowel
- Surgical bypass, etc.
Pathogenesis
- Bacterial compete for luminal contents (Vitamin B12, bile acids [deconjugate])
Results in: Malabsorption
- Caused by abnormal populations of bacteria in the small intestine (stasis is implied)
Test for bacterial overgrowth?
- Schilling test before and after antibiotics
- Fecal fat before and after antibiotics
- Bile salt breath test
- D-xylose breath test
- Response to antibiotic therapy


