09 - Okta Policy Network Flashcards
What is Okta’s MFA enrollment policy
Demonstrate knowledge of the policy types available in Okta and their functionalities
Use the Multifactor Policies tab to create and enforce policies for your chosen MFA factors and the groups that are subject to them. Sign-on policies determine the types of authentication challenges these users receive.
An MFA policy can be based on a variety of factors, such as location, group definitions, and authentication type. It can also specify actions to take, such as allowing access or prompting for a challenge.
Add a new policy by navigating to Factor Enrollment and clicking Add Multifactor Policy.
Change the order of policies, except the Default Policy, by dragging the bar on the blue policy name, thereby rearranging the list.
The Default Policy: The default policy applies when no other policy has been set. It also immediately reflects the factors you chose under the Factor Type tab.

Demo 1: Multifactor Authentication
Demonstrate knowledge of the policy types available in Okta and their functionalities
Multifactor Authentication
Test Multifactor Authentication
3
c. The dialog box will refresh with the final step to set up Okta Verify.
d. On your mobile device, open the app store. Search for and install Okta Verify.
e. Open the Okta Verify app.
f. On the Welcome to Okta Verify screen, tap Add Account.
g. Hold your device up to the computer screen and scan the barcode.
h. Click Done.

Demo 1: Multifactor Authentication
Demonstrate knowledge of the policy types available in Okta and their functionalities
Multifactor Authentication
Test Multifactor Authentication
- Select and answer a forgot password question.
- Select a security image.
- Click Create My Account.
- In the top bar, click Faith > Sign out.

Demo 1A: Password Policy Types
Demonstrate knowledge of the policy types available in Okta and their functionalities
Password Policy Types
Create an Application Sign on Policy
- Under Location, leave the default Anywhere selection. Notice that if you select the other options this can trigger how this policy could be applied to the zones you defined earlier.

Demo 1A: Password Policy Types
Demonstrate knowledge of the policy types available in Okta and their functionalities
Password Policy Types
Create an Application Sign on Policy
- Under Location, leave the default Anywhere selection. Notice that if you select the other options this can trigger how this policy could be applied to the zones you defined earlier.

Demo 1A: Password Policy Types
Demonstrate knowledge of the policy types available in Okta and their functionalities
Password Policy Types
Test the Application Sign on Policy
- Log out of Okta as the Administrator 2. Login in as frank.molen.
Username: frank.molen
Password: Tra!nme4321
3. Click on the Salesforce app and you will be prompted to set up an MFA Factor.
- Did you get prompted for MFA?
- Enter your factor and login into Salesforce.
- Sign out of and close the Salesforce browser tab. 7. Log out as frank.molen.
Conclusion
Now that you have created an Okta password policy and configured MFA, you are now ready to learn about attribute mappings.

Demo 1A: Password Policy Types
Demonstrate knowledge of the policy types available in Okta and their functionalities
Password Policy Types
Create an Application Sign on Policy
Enable MFA
- Under Actions, select Prompt for factor and select Every sign on.
- Click Save.

Demo 2: Okta Essentials Module 5: Implement the Okta Policy Framework
Demonstrate knowledge of when to use each policy
Okta Essentials Module 5: Implement the Okta Policy Framework
Demo 3: Security Policies
Demonstrate understanding of how policies are applied based on the policy priority order
Security Policies
Demo 4: Password Policy Types
Demonstrate understanding of the importance of the default policies in Okta
Password Policy Types
What are the steps in creating an Okta-Mastered Password Policy
- Point to Security and click Authentication.
- You will land on the Password tab. Click Add New Password Policy. 3. In the Add Policy dialog box, perform the following:
In the Policy Name field, type the following: Okta Accounts
In the Policy description field, type the following: Okta-mastered user
password policy
IntheAddgroupfield,typeandselectthefollowing:Salesand
Marketing
Under Authentication Providers, in the Applies to list, verify that
Okta is selected.

What are the 4 types of Okta Policies
About app sign-on policies
About MFA enrollment policies
About Okta sign-on policies
About password policies
What is Okta’s App Sign-on policy
App sign-on policies allow or restrict access to applications. By default, all Client options in the App Sign On Rule dialog box are pre-selected. To configure more granular access to the app, selectively apply conditions as you create one or more prioritized rules based on:
Who users are and/or the groups to which they belong
Whether they are on or off network or within a defined network zone
The type of client running on their device (Office 365 apps only)
The platform of their mobile or desktop device
Whether or not their devices are Trusted
Important to know about the User-Agent
Okta’s Client Access Policies (CAPs) allow you to manage access to your enterprise apps based on the client type and device platform. Okta CAPs evaluate information included in the User-Agent request header sent from the users’ browser. Because the User-Agent can be spoofed by a malicious actor, you should consider using a whitelist approach when you create CAPs and require MFA or Device Trust as described in the following best practices:
Implement a whitelist consisting of one or more rules that specify the client type(s) + device platform(s) + trust posture combinations that will be allowed to access the app.
Require Device Trust or MFA for app access.
Include a final catch-all rule that denies access to anything that does not match any of the CAPs preceding rules.
MFA and legacy protocols
While you can configure your App Sign-On Policies to prompt end users for MFA, be aware that legacy protocols such as POP or IMAP do not support MFA even if MFA is configured for Okta sign-in.
To ensure that authentication to apps remains secure, Okta strongly recommends that you evaluate the following:
The use of legacy protocols with Microsoft Office 365 applications and whether to disable them if necessary
Whether to enable Modern Authentication on Microsoft Office 365 tenants for improved security
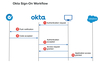
What is Okta’s Sign on Policy
Okta sign-on policies can specify actions to take, such as allowing access, prompting for a challenge, and setting the time before prompting for another challenge. You can specify the order in which policies are executed and add any number of policies. If a policy in the list does not apply to the user trying to sign in, the system moves to the next policy.
You can specify any number of policies and the order in which they are executed. There is one required policy named Default. By definition, the default policy applies to all users.
In addition to the default policy, which you cannot delete, there is another policy named Legacy that is present only if you have already configured MFA. This policy reflects the MFA settings that were in place when you enabled your sign-on policy, and ensures that no changes in MFA behavior occur unless you modify your policy. If needed, you can delete it.
When a policy is evaluated, the conditions in the policy are combined with the conditions in the associated rules. Rules are applied when all these conditions are met.
Note: A policy with no rules cannot be applied.
Policies can contain multiple rules, and the order of the rules determines their behavior.
What is Okta’s Password Policy
Password policies enables admins to define password policies and associated rules that enforce password settings at the group and authentication-provider level. Okta provides a default policy to enforce the use of strong passwords to better protect your organization’s assets. Admins can also create additional policies that are less or more restrictive and apply them to users based on group membership.
Group Password Policy is now enabled for all orgs:
The Password tab on the Authentication page displays all group password policies. Initially, only the Default Policy and the Default Rule appear.
If Group Password Policy was previously not enabled, the Password tab now displays the Legacy Policy and the new Default Policy. The Legacy Policy reflects the org settings present when Group Password Policy was enabled and includes the Legacy Rule and the additional Default Rule.
What is Okta’s Group Password Policy
Using Group Password Policy
With group password policies, you can:
Define password policies and associated rules to enforce password settings on the group and authentication-provider level.
Create multiple policies with more or less restrictive rules and apply them to different groups.
Use policies to enforce the use of strong passwords to better protect your organization’s assets.
An error can occur during provisioning when user’s Okta password meets the password policies requirements while the password policy itself does not. Ensure that the Okta password policy meets the application’s requirements, typically, eight characters with an upper and lower case character and either a symbol or number.
What is Okta’s Policy on AD and LDAP Mastered Users
Active Directory (AD) and LDAP mastered users
Group Password Policies are enforced only for Okta and Active Directory (AD) and LDAP mastered users.
For AD and LDAP mastered users, ensure that your AD and LDAP password policies don’t conflict with Okta policies. Passwords for AD and LDAP mastered users are still managed by the directory service. For example, some applications, such as Microsoft Office 365 and Google G Suite, check an Okta password policy when provisioning a user to ensure that the Okta policy meets the application’s password requirements.
Previous Group Password Policy options are not retained after the LDAP Group Password Policy feature is disabled.
When the LDAP Group Password Policy feature is enabled, a custom password policy message cannot be used and previous password policy messages are not applied.
When LDAP delegated authentication is disabled, the LDAP Group Password Policy no longer applies to LDAP mastered users.
What is Okta’s Password Policy Evaluation
Password Policy evaluation
A password policy is evaluated using the following criteria:
Complex requirements are evaluated when the password is set.
On the current policy and when the user last set their password, unless the user’s password is already expired in which case it remains expired.
For AD and LDAP mastered users, the AD and LDAP complexity requirements should match the AD and LDAP instances.
What is Okta’s Password Policy Types
Default policy: All Okta-mastered users are subject to the Default Policy unless another policy applies. The Default Policy cannot be deactivated or deleted, and always holds the lowest ranking within the policy list.
Legacy Policy: In previous versions of the platform, password policy settings were located on the Security > General page. For orgs that were created before Group Password Policy was enabled, the Legacy policy and associated Legacy rules are preserved. Existing password policy settings for an org are copied to the Legacy Policy. All Legacy policy and rule settings are configurable.
Active Directory Policy: If you currently have one or more Active Directory (AD) integrations, an AD policy is automatically created for you. You can customize the elements of the policy and its rules.
LDAP Policy: If you currently have one or more LDAP integrations, an LDAP policy is automatically created for you. You can customize the elements of the policy and its rules
- What is the advantage of configuring security within Okta?
Configuring security within Okta enables you to provide additional security layers on sensitive corporate data, while also enabling users to access data and applications securely. The Okta Policy Framework allows admins to configure password requirements, sign-on options, mobility requirements, and a lot more. The framework allows policies to be scoped to specific groups and can be applied to individual applications.
The Okta Policy Framework allows admins to configure what?
Password requirements,
sign-on options,
mobility requirements, and a lot more.
The framework allows policies to be scoped to specific groups and can be applied to individual applications.
How are policy applied?
Policies are assigned to any group type and are applied sequentially.
For example, if you have two policies mapped to the same group, the second policy will never be executed.
All policies have associated rules that follow the same principle.
How are policies different from rules?
While the specifics of policy rules are different for each policy type, rules are always context-scoped and policies are group-scoped.
What are the different types of Policy?
Password: Define password policies and associated rules to enforce password settings at the group and authentication-provider level.
Multifactor: Use the Multifactor Policies tab to create and enforce policies for your chosen MFA factors and the groups that are subject to them.
Okta Sign-on: Sign-on policies determine the types of authentication challenges users receive.
Application Sign-on: Define application-level access parameters.