04-06 - Bacterial genomes & genomics, growth & cell division Flashcards
Shape, growth pattern and cell division of bacteria are programmed…
Genetically
The nucleoid consists of…
a) highly condensed circular DNA
b) relaxed linear DNA
c) highly condensed linear RNA
d) all the genetic material within a bacterial cell
The nucleoid consists of…
a) highly condensed circular DNA
b) relaxed linear DNA
c) highly condensed linear RNA
d) all the genetic material within a bacterial cell (bacterial DNA may also be contained within plasmids)
Bacterial genomes are small in size and can vary between…
150kbp to as much as 10mbp
Although plasmids are extrachromosomal, they can be…
Integrated into the chromosome
A bacteriophage is a virus which infects bacterial cells. They can be used for gene…
Transduction (the transfer of genes)
State the difference between lytic and lysogenic bacteriophage…
Lytic = cell is killed
Lysogenic = stable insertion
Chromosomal DNA from bacteria can sometime enter a phage and subsequently be transfered to…
Other organisms
Bacterial chromosomes are mosaics of genes. The core genome represents…
Genes present in all members of a bacterial species
The pan genome represents…
The sum total of all the different genes present throughout a bacterial species
(core genome + variable genome)
Areas of the bacterial genome associated with virulence are known as…
Pathogenicity islands
The presence of what can interfere with the assembly of DNA sequences for human cells?
Abundance of repeat DNA sequences
Oxford nanopore is an example of what type of sequencing?
Long read
In bioinformatics, software can identify ribosomal binding sites, which usually correspond to a…
New start codon
SubtiList is a website which collates information about…
Genomes
Bacillus subtilis is a bacterium found in soil and the gastrointestinal tract.
Which of the following statements about B. subtilis is correct?
a) It can convert to an ‘L-form’ with no cell wall
b) It produces complex fruiting bodies which form spore-like cells
c) It produces PETase enzyme (can degrade plastic)
Bacillus subtilis is a bacterium found in soil and the gastrointestinal tract.
Which of the following statements about B. subtilis is correct?
a) It can convert to an ‘L-form’ with no cell wall
b) It produces complex fruiting bodies which form spore-like cells
c) It produces PETase enzyme (can degrade plastic)
Bioremediation is the use of microorganisms to…
Break down pollutants
Bioremediation
Sewage water can be purified using microorganisms in what is known as an…
Activated sludge

Bioremediation
Ideonella Sakaiensis bacteria produces which notable enzyme?
PETase (degrades plastic)
Biotechnology
Bacteria can be used as cell factories. For example (4)…
- Antibiotics
- Vitamin B12
- Expressing a mammalian gene
- Industrial enzymes
An engineering approach applied to synthetic biology may use standard parts, like a circuit board. Give an example of what some of these parts of a synthetic genome might be…
- Promoters
- Ribosome binding site
- Terminator

List the 4 phases of bacterial growth…
- Lag phase
- Exponential phase
- Stationary phase
- Death phase

Viable cell count represents the number of…
Living cells able to grow
(Whereas total cell count = all cells)
Name 4 methods for counting bacteia…
- Extrapolate back from CFU
- Turbidity (optical density)
- Direct counting
- Flow cytometry and FACS (fluorescent activated cell sorting)
Measuring turbidity is a commonly prefered method of counting bacteria. State 2 advantages and 2 disadvantages of this method.
Advantages
- Non-destructive (can be done continously)
- Simple/convenient
Disadvantages
- Low sensitivity
- Includes all particles, such as dead cells
Flow cytometry uses lasers to measure particles in a microfluidic flow in order to count bacteria. The advantage of this method is it is…

Highly automated
Which of the following statements regarding the bacterial cell division cycle is true?
a) SeqA initiates replication, DnaA blocks replication
b) DnaA intiates replicaiton, SeqA blocks replication
c) Replisomes bind to terC
d) Replication of new chromosome starts when previous round of replication has finished
Which of the following statements regarding the bacterial cell division cycle is true?
a) SeqA initiates replication, DnaA blocks replication
b) DnaA intiates replicaiton, SeqA blocks replication
c) Replisomes bind to terC replisomes bind to oriC
d) Replication of new chromosome starts when previous round of replication has finished
* replication of new chromsomes starts before previous replication has finished*
Circular bacterial chromosomes replicate…
Bidirectionally (from oriC to terC)
The divisome is a…
Complex contractile ring involve in bacterial cell division
In bacterial cell division, FtsZ protein assembles into a…
Z-ring structure
Bacterial cell division is regulated by…
Negative regulation
Bacterial cell division is regulated by two main mechanisms…
- the Min system (inhibits Z-ring formation at poles)
- Nucleoid occlusion (inhibits Z-ring formation near nucleiod)
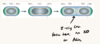
There are a variety of cell cycles in bacteria. For example cell is cyanobacteria, such as anabaena may…
Differentiate to form different types of cell (vegitative cells, heterocysts, akinetes) depending on conditions
Bacterial differentiation occurs via modification of the…
Cell cycle
Anabaena (a cyanobacteria) may form a symbiotic relationship with plants…
- Anabaena is protected from harsh conditions by the plant, which promotes formation of heterocyst cell types
- Heterocyst cell types engage in nitrogen fixation, which benefits the plant
Where does bdellovibrio bacteria grow?
Periplasmic space of gram-negative bacteria

Myxococcus
- eats other bacteria
- produces complex fruiting bodies in nutrient poor environments
- differentiation into spore-like cells to aid survival in harsh conditions



