Week 4 Flashcards
(89 cards)
Name structures
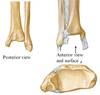
Tibia: Medial malleolus, Inferior articular surface (for trochlea of talus), Fibular notch
Fibula: Lateral malleolus, Ligaments Interosseous membrane, Anterior and posterior tibiofibular ligament
Muscle that pass in the front of malleolus?
Muscules that pass in the back of malleolus?
Dorsiflexion
Plantar flexors
Name compartments

Anterior
Lateral
Posterior deep
Posterior superficial
Posterior superficial compartment muscles?
Gastrocenmius
Soleus
Plantaris
Deep posterior compartment muscles?
Function?
Tibialis posterior
Flexor digitorum longus
Flexor Hallucis Longus
Popliteus
Invertors and plantarflexors / unlocking the knee

Anterior compartment?
Function?
Extensor digitorum longus, extensor hallucis longus, Tibialis anterior
dorsiflexion, Tibialis anterior - inversion

Lateral Compartment muscles?
Fibularis (peroneus) lonugs
Fibularis ()peroneus) brevis
Plantar flexors and everters
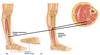
Nerve supply to the leg?
Posterior?
Anterior?
Lateral?
Tibial n
Fibular n
Fibular n
What is the continuation of anterior tibial?
What artery supplies lateral muscles in a leg?
Dorsalis pedis
Perforating branches of fibular
Tendon Sheaths and Retinacula

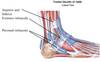
Name the vessels in flexor retinaclum

Tibialis posterior
Flexor digitorum longus
Posterior tibial atery and nerve
Flexor hallucis longus
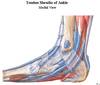
Name structures in dorsal side of the foot

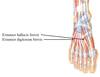
What innervates dorsal side of the foot (muscles)?
What supplies dorsal compartment of the foot?
What supplies plantar compartment of the foot?
Fibular nervew
Dorsalis pedis (anterior tibial)
LKateral plantar artery forms arch

Cutaneous nerve supply to leg
Lateral sural cutaneous nerve
Superficial fibular (peroneal) nerve
Sural never via lateral dorsal cutaneous branch
Deep fibular (peroneal) nerve

First layer of the plantar comparment
Plantar aponeurosis
Abductor digiti minimi
Flexor digitorum brevis
Abductor hallucis

Second layer of foot muscles on plantar side
Lumbricals
Flexor hallucis longus
Flexor digitorum longus
Quadratus plantae (flexor accessorius)
Third layer muscles

Flexors
Adductor hallucis transverse and/oblique head

Fourth layers of foot

Plantar and dorsal interossi

Innervation of the plantar foot
Lateral Plantar Nerve?
Medial Plantar Nerve?
Lateral Plantar Nerve-(like the ulnar) All intrinsic muscles except the thenar equivalents, the lumbrical to the functional midline on the medial side, and the flexor digitorum brevis (like the flexor digitorum superficialis)
Medial Plantar Nerve innervates the above named exceptions -(like the median)
Nerve innervation to foot


Bone is the foot
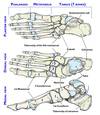

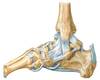
Ligaments

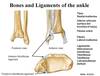
Posterior ligaments
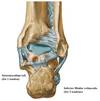

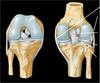
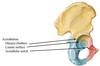
Joints in the foot?

Subtalar joint
Transverse tarsal joint
Tarsometatarsal joint