Week 1 Flashcards
How muscle can be affected after neural fibers are removed from the muscle?
Muscle atrophy
What is Spondylolisthesis?
Displacement of vertebra
What degeneration of cartilage between bones might lead to?
More bone rubbing leading to bone growth
Which part of vertebra are fused?
Coccygeal
Which vertebra do not have the intervertebral disk?
Atlas and axis
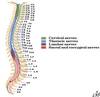
How many cervical nerves are there?
How many cervical vertebra are there?
8
7
What is the name of the hole that spinal cord is passing through?
Vertebral foramen
What forms neural arch?
Pedicle
Lamina
Body
What is the join between inferior and superior transverse proceeses of vertebra
azygoshypophyseal joint
Name the locations where nerves are exiting from spinal cord
Intravertebral foramen
What is the effect of anastetic injected in sacral hiatus?
Only affects spinal nerves not spinal cord
What artery passes through transverse foramen of cervical vertebra?
Exception?
Vertebral artery C1-6 not 7
Which vertebra can be felt on the back of the neck?
C7
What articular facets are connected to?
Which type of vertebra are they found in?
Ribs
Thoracic
Direction of superior/inferior articular proceses:
Cervical vertebra
Thoracic vertebra
Lumbar vertebra
Transverse plane
Frontal plane
Saggital plane
Would thicker or thinker disc allow more movement?
Thicker
What is found in all vertebra except atlas?
Body
What is the difference in shape of inferior vs. superior articular fovea?
What movement is allowed by superior articular fovea?
Superior is more concave
Front/back
Why spinal cord does not extend entire length of vertebral column?
It does not grow as much as vertrebral column
What is the special innervation of trapeizus muscle?
Innervated by CN XI
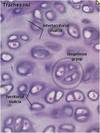
What is osteophytes?
a bony outgrowth associated with the degeneration of cartilage at joints
Components of axial skeleton
Skull
Vertebral column
Ribs
Sternum (not pelvis)
How many vertebra are there?
How many at each level?
7C, 12T, 5L, 5S, 4C

Which segment of vertebral colum belong to primary / secondary curvatures
Primary: thoracic & sacral
Secondary: cervical & lumbar

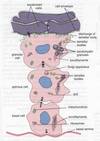
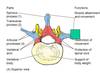
Name the parts of vertebra
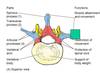
BOdy
Pedicle
Lamina
Transverse process
Spinous process
Articular process
What is intervertebral foramen made of?
Inferior and superior vertebral notches

What is present on the lateral surface of each superior articular facet (muscle attachement)? – name it
Mammillary prossess
Name these two structures:

Posterior sacral foramina (anterior is behind)
Sacral Hiatus

Name the characteristics structure for each group of vertebra


Name the structures


Complete the table


What are the restrictions on movement of vertebral column?
Thickness of the intervertebral discs
Orientation of the articular facets
Attachements of ribs
Size, elasticsity, and orientation of muscle of th back and abdominal wall
Definition of pain
An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage
Defintion of
Actute Pain
Chronic Pain
Paid due to injury of tissues and activation of nocioceptors
Pain that extends beoynd the expected period of healing
Three general types of pain
Nociceptive pain (somatic pain / visceral pain)
Neuropathic pain (lesion or disease affecting the somatosensory system)
Mixen pain (cancers e.g. lung)
Two types of nociceptive pain
Arthritis (most common) : mechanical-osteoarthiritis & inflammatory-rheumatoid arthiritis
Low Back Pain
Examples of neuropathic pain
Herpes Zoster dormant in DRG -> Shingles and Post Herpetic Neuralgia (pain that could last for years)
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS) - Involvement of sympathetic nervous system BPPS model (fire hand)
Central pain (pain associated with lesions of the CNS including spinal and central -opposite)
Phantom pain (stabbing, throbbing, burning)
Dependence vs. Addiction
Physical vs. Psychological
What fibers carry the pain signals?
Characteristics?
Location?
C-fiber and Ad-fiber
Heretogenous, unmylenated
Sking, muscle, joints, and viscera
Two types of sensitization
Location of central?
Primary / peripheral
Central (Lamina V)
What receptor triggers pain and exaple of molecule that binds to it?
How voltage gated sodium channels can be inhibited?
What voltage channels promote propagation of pain signals? Medications?
TRPV1 receptor / Capsaicin
Local Anasthetics and Lidoderm patches
N-type calcium channels

What is
Hyperalgesia
Allodynia
Hyperalgesia – heightened sense of pain to noxious stimuli
Allodynia – pain resulting from normally painless stimuli
What is the location when synapse of primary afferent neurons?
substantia gelatinosa
What tract carries pain signal?
Spinalthalamic tract (STT)
How pain is regulated?
Spinoreticular neurons have targets in medulla and brainstem
Spinomesencephalic neurons have targets midbrain and periaqueductal grey (PAG)
Where are all sensory system send to?
Thalamus
Two pathways of pain signals from thalamus to cerebrum
Lateral pain system -> Cerebral coretex (localization and intensity)
Medial pain system -> Limbic System
What is gate control theory (of melzack and wall)
Jamming pain signals (rubbin or massaging injured parts of body in order to achieve pain relief)
What can cause central sensitization
high intensity or prolonged stimuli such as occur with nonneuronal tissue injury and inflammation
Difference between:
Spondylolysis
Spondylolisthesis
Scotty Dog (Scotty Dog=fracture of pars interarticularis)
Displacement of vertebra
Ligaments that prevent flexion in spinal column?
Ligmanets that prevent extension in spinal column?
Importance?
Anteior Longitidinal Ligament = largest
Posterior Longitidinal Ligament = prevent disk herniation

What ligament on atlas surrounds dens?
What is the connection between skull and dens?
Cruciate ligament
Alar ligament

Parts of intervertebral disk
Annulus fibrosis = fibrocartilage thinner posteriorly
Nucleus pulposis= gelatinous fore

Where do spinal nerves exit in cervical region?
Where do spinal nerves exit in thoracic/lumbar/sacral region?
What nerve gets pinched?
Above same number vertebra
Below same number verebra
One number below
Spinal Meninges
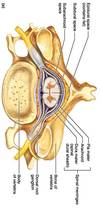
What is the name of collection of fibers below the spinal cord?
Where does the spinal cord end?
Cauda equina
L2

Artery that runs in back/front of spinal cord?
What supplies these arteries?
Posterior / Anterior spinal
Posterior radicular artery / anterior medullary artery

Where is the Adamkiewicz artery located (level)?
T8-L2
What is Anterior Spinal Artery Syndrome?
Loss of blood flow to a spinal cord

Importance about venous drainage in vertebral column?
Conntected to both brain and prostatic venous plexus (prostate cancer metastasize to the CNS).

On what level are the dimples?
On what level is the iliac crest?
On L4/L5
Dimples on S2

Back muscles

Three groups of intrinsic back muscles
Spinotransverse (superficial)
Erector spinae (intermediate)
Transversospinae (deep)

What innervates back muscle?
Dorsal rami
What is the relationship between the direction of the muscle and vertebra turn?
Oblique
Transversospinal
Same side
Opposite side
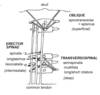
Another name for spinotransverse
Splenius (superficial)
What are the three erector spinae muscle?
Spinalis
Longissimus
Ileocostalis

Two components of splenius group
Capitis and Cervicis

Transversospinae muscle group members
Semispinalis spanning 6-8 vertebrae
Multifidus spanning 3-5 vertebrae
Long rotators spanning 2
Short rotators spanning 1

What is the most powerful extender of the head
Semispinalis capitis (transversospinae muscle)
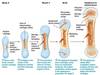
Microfailure

Yield Point
Failure Point
Elastic Region
Plastic Region

Isotropy
Anisotropy
Orthotropy
Mechanical properties independent of direction of stress
Mechanical properties different in all directions of loading
Mechanical properties symmetric within two planes
Hysteresis
The dependence of the output of a system not only on its current input, but also on its history of past inputs
Cyclic loading leads to smaller difference between loading and unloading curves

How multiple cycle of load affects failure strength?

Condition?
Stress Fracture