Week 3 Flashcards
Groups of anteiror arm muscle
Thenar
Hypothenar
Lumbricals
Interossei
List thenar muscle
List hypothenar muscle
Innervation?
Thenar muscles - median
Opponens pollicis
Abductor pollicis brevis
Flexor pollicis brevis
Hypothenar muscles - ulnar
Opponens digiti minimi
Abductor digiti minimi
Flexor digiti minimi (brevis)
Ulnar nerve
What passes through the carpal tunnel
Medial nerve
Flexor pollicus longus
Flexor digitorum superficialis
Flexor digitorum profundus
Name the compartments


Dupuytren’s Contracture
A disease of the palmar fascia resulting in thickening and shortening of fibrous bands on the palmar surface of the hand and fingers.

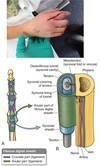
Arrangement of tendon sheats in palm
thenar (2)
midpalmar (3+4)

Fibrous Digital Sheaths
Attachement and their location?
Importance?
Bands A2 and A4 are on the proximal and middle phalanx respectively
A1,A3, and A5 are near the MP, PIP and DIP respectively
A2 and A4 Bands are most important to prevent bowstringing. A1 band is involved in trigger finger.

Lumbirical muscles
Origin?
Insertion?
Innervation?
Function
Originate from the flexor digitorum profundus tendons
Insert in the extensor hoods
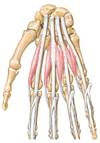
Interosseus Muscle
2 types?
Function
Origin?
Insertion?
Innervation
Dorsal and palmar
Originate from metacarpals
Insert on the extensor hoods
PaD / DaB
Ulnar

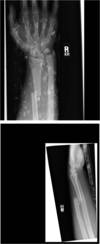
Fracture of Scapoid
Complications?
Most common wrist fracture
Non-union
Avascular necrosis

Dermatomes in the upper limb

Cutaneous Innervation of the Upper Limb
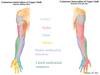
Segmental Innervation of the Upper Limb

Innervation to
Anterior arm?
Anterior forearm?
Shoulder?
Posterior arm?
Posterior forearm?
Anterior compartment
anterior arm-musculocutaneous
anterior forearm-all median except FCU+2 heads of FDP (ulnar)
anterior hand-all ulnar except thenar comp muscles + lumbricals to the functional midline on radial side (median)
Posterior compartment
Shoulder-axillary (deltoid and teres minor)
posterior arm & forearm-radial
Erb-Duchenne Paralysis
Cause?
Symptoms?
Damage to upper trunk of the brachial plexus
Shoulder movements are affected most dramatically

Klumpke’s Paralysis
Cause?
Symptoms?
Damage of lower trunk of the brachial plexus
Hand movements are affected most dramatically

Damage to
Axillary?
Musculocutaneous?
Radial?
Axillary nerve-severely weakened abduction, weakened lateral rotation
Musculocutaneous nerve- almost no forearm flexion, weakened arm flexion
Radial nerve-no forearm extension, arm may be slightly flexed
(note also has major effect on forearm and hand, see later)
Mid humeral shaft fracture damage to what?
Radial Nerve
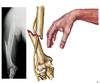
Elbow fracture damage to what?
Median Nerve Damage

Ulnar Nerve Damage
Location?
Phenotype?
Fracture of the medial epicondyle can cause trauma to the ulnar nerve.
Hyperextension with flexion

Jersey finger
Tendon injury Flexor Profundus vs. Superficialis?
Tear of the FDP off the distal phalanx
Profundus-passively extend MP and PIP while trying to flex the DIP
Superficialis-passively extend unaffected fingers while trying to flex

Extensor Tendon Injuries
Mallet finger?
Boutonniére deformity?

Axis of Rotation for Upper Limb Joints
- *Glenohumeral**-AP (ab and adduction), vertical (rotation), transverse (flex and extend)
- *Humeroulnar**-transverse (flex and extend)
- *Humeroradial**-transverse (flex and extend), vertical, rotation (pronate and supinate)
- *Radioulnar**-vertical, rotation (pronate supinate)
- *Radiocarpal**-transverse (flex and extend), AP (ab and adduct
Axis of rotation
Fingers?
Thumb?
Often arthiritis where?
Thumb
Carpometacarpal multiaxi
MP uniaxial
Finger
MP biaxial
1st CMC
Join definition
UNION BETWEEN TWO OR MORE RIGID ELEMENTS OF THE SKELETON – BONE OR CARTILAGE
Two types of joints
SYNOVIAL: the skeletal elements are separated by a joint cavity or space that contains synovial fluid.
“freely movable”
NONSYNOVIAL: the skeletal elements are directly connected or continuous with each other.
“non-movable”
Types of non-synovial joints: fibrous joints
Connection by?
Types/Examples?
Movemement?
Connective tissue
Suture, tooth, interosseous membrane
No movement (except interosseus membrane)

Nonsynovial: Cartilaginous Joints
Connection by?
Types/Examples?
Movemement?
Cartilage
Pubic symphisis, intervertebral disks
Slight movements

Joint ligaments types
Extracapsular
Capsular
Intracapsular

Name the structure

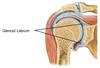
Name the sturcutre


Common of bursitis in glenohumeral cavity?
Name?
Bicipital tenosynovitis

Elbow joints parts
Humeroulnar
Humeroradial
Proximal radioulnar

Ligaments of Elbow
Name?
Function?

Radial collarteral - prevents adduction of forearm
Unlar collateral - prevents abduction
Annular ligaments - surrounds radius head

Disclocation of radius in elbow
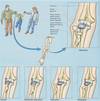
Three joints between radius and ulna
Does ulna articulates with carpals
No it is separated by a disc

Where does transverse carpal ligament attaches to?
Scaphoid and trapezium laterrall
pisiform and hamate medially

Carpals
Proximal Row
S scaphoid (oid first in the 1st row)
L lunate
T triquetrum
P pisiform
Distal Row
T trapezium (by the thumb)
T trapezoid (oid second in the 2nd row)
C capitate
H hamate

Function of transverse metacarpal ligaments
Transverse metacarpal ligaments stabilize the hand in single metacarpal fractures
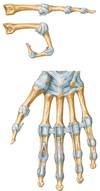
Mesoderm sublayers in embryo
paraxial - somites
intermediate - GU
lateral - splanchnic and sometic
Skeletal derivatives from:
Somites
Neural crest cells
Lateral plate mesoderm
Vertebra and ribs, skull behind prechordal plate (rostal end of notochord)
Skull in front of precordal plate
Long bones, pelvic and shoulder girdles

Which becomes bone sclerotome/dermotome?
What makes dermis?
What somtimes differentiate into?
Sclerotome
Dermatomyotome
Sclerotome/dermatomytome
Spina bifida

Genes that control limbs development?
The day of the formation of limb buds in lateral plate somatic mesorderm?
Direction of progression?
HOX genes
24 upper limb 28 lower limb
To caudal / distal

What is the type of bone formation of the gridles minus clavicle? From where?
Where does limb muscularture is derived from?
Endocondral ossification from lateral plate mesoderm
Somitic mesoderm
How is dermatomyotome divided?
Differentiations?
DML (drosomedial lip) => epimere => expasial musculature (back muscles)
Dermatome (intermediate)
VLL (ventrolateral lip) => hypomere => hypaxial muscules (limbs and anterior and lateral body wall)

How muscles become innervated? Why not simple?
Nerves follow the muscle
Signalling from adjacent connective tissue
AER (Apical Epidermal Ridge) gene function?
ZPA (only on caudal) gene function?
Regulates continued growth
Cephaic and caudal organization
Syndactyyl?
Meromelia?
Suspetible time to teratogens to limbs?
Associated symptoms?
Amniotic bands?
Fused fibers
Short limbs
4-5th week
Cardio, GI, cranio-facial
Can cause amputations
Limb abnormality


Prune-belly
Lateral and anterior muscle not migrating properly

Level of:
Femoral/Obturator
Sciatiatic
L2,3,4
L4,5+S1,2,3

Anteior (flexor) division nerves?
Posterior (extensor) division nerves?
tibial (thigh, leg, foot); obturator (thigh)
femoral (thigh); gluteals (hip); peroneal (fibular) (thigh, leg, foot)

Medial rotaiton of the limb

Nerves and compartments
Posterior vs. Anterior
Upper / Lower limb

Spinal cord segments estimates to upper and lower limb

Dermatome of the little toe
Dermatome of the big toe
S1
L4/5
Name the structures: