Viral Immunity Flashcards
What receptors on the cell membrane recognize viral infection?
Viral capsid proteins : TLR2/6 and TLR4
Viral RNA: TLR3
Cytoplasmic RNA receptors - RIG-I
With a viral infection, what response to you want to produce?
Type 1 interferons
What happens after a receptor recognizes viral RNA or the virus capsule?
it activates IRF 3/7 which then binds to the DNA and promotes synthesis of the antiviral cytokines, another cascade makes inflammatory cytokines
What is the responsibility of the Type 1 IFNS?
they are antiviral cytokines that create a hostile environment for the virus- works on the neighborhood and the infected cells themselves too.
- it shuts everything down
How does IFN shut down viral replication?
Viruses use host machinery to replicate, synthesize genes and make proteins
IFN inhibits the host transcription and translation machinery
Are Interferons the same thing as cytokines?
_Cytokines i_s the umbrella term for
interferons
chemokines and
interleukins
What is the effect of type 1 IFN on immune cells?
it upregulates the MHC class 1 (so cytotoxic T cells can target the cell)
- it activates DC and macrophages
- Activates cytotoxic T cells - directly kill infected cell
- B cell activation - antibodies
- Activate NK cells - directly kill infected cells
How does the complement system play a role in fighting viral infections?
when an antibody meets and antigen- it causes a cleave of C3- wihch recruits the inflammatory cells, opsonisation of pathogens, and membrane attack complex
How do Viruses avoid our immune response?
- some viruses can antagonize the normallly cellular response to make transcription factors for anti-viral cytokines
- some viruses express membrane CD59 - which is a protein that our cells express to inhibit complement activation against our own cells

how are antibodies used against viral infections?
- B cells encounter the virus coating
- BCR binds to epitope on viral coating and internalize it
- Viral coating segment is degraded into peptides within the B cell
- Peptides form the internal protiens of the virus are presented to the T cell- which activates B cells to make antibodies agains viral coat protein
What are the three activities of Antibodies agains the virus?
neutralization - prevents viral adherence to cells (IgG, IgA)
opsonization - promotes phagocytosis (IgG)
and complement activation - activates complement which enhances opsonization (IgG, IgM)
What is ADCC- antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity ?
you use antibodies to invoke a process that kills cells that you don’t want - so once you have an antibody/antigen interaction = it will perturb the membrane and make it release the toxic granules into the cytoplasm - driving cell apoptosis
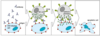
- Antibody driven
- Effector cell – Natural Killer Cell, Eosinophil,
Macrophage and Neutrophils
- Antibody binds virus/bacteria/tumour cell
- Fc region binds FcR on effector cell
- Induce cell death
What is the principle mechanism of disposing of virally infected cells?
Cytotoxic T cell activation
- virally infected cell will display viral antigens on MHC class 1 molecule
- vill be activated to upregulate MHC class 1
- infected cell decorated with MHC class 1 bound to viral antigens
- Cytotoxic T cells are pre-programmed to kill if they recognize an antigen on MHC Class 1

How do viruses use MHC class 1 to their advantage?
- The viruses can mutate genes so they aren’t recognized by MHC class 1
- they can interfere with antigen processing (epstein barr virus does)
- they can down regulate MHC class 1 and prevent it from getting to the surface- but our body still attacks these cells
What are NK cells?
Natural killer cells = lymphoid cells that detect altered self cells -
What do Natural Killer cells do?
Innate immune cells – no Ag receptor
- Key in anti-viral and anti-tumour immunity
- Recognise altered ‘self’ cells – viruses trigger down regulation of MHC
class I on cells to prevent Tc (CTL) discovery
- Cytotoxic activity
- Detected within 2 days of an infection
- Very active against Herpes viruses and cytomegalovirus
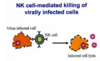
How do NK cells work?
NK cells have an inhibitory receptor (when bound inhibitis cell lysis) - and an activatory receptor (when bound it activates cel lysis)
- When the NK cells bind MHC class 1, it inhibits the cell lysis = normal cell, do not attack
- When the NK cell cannot find an MHC class 1 to bind to = activates itself and kills the cell
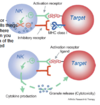
Do NK cells and cytotoxic T cells kill differently?
No, they kill the same way
1) perfornin
2) granzyme
3) cell death/apoptosis
*they also release the cytokine IFN gamma, which drives Th1 responses and CTL activity
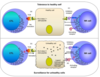
What causes activation of the NK cell?
the lack of MHC class 1 binding activates the NK cell
What is RSV and why is it so dangerous?
Respiratory Synctial Virus - RSV -
Major cause of lower respiratory tract infections
particularly affects newborns, elderly, immunocompromised
- virus infects respiratory cells, causes the cells to secrete mediators which accumulate an inflammatory response
- after that you get the specific immune response - ultimately this leads to an inflammatory status in patients- and brachial swelling making it difficult to breath
- RSV is sneaky - it can block the antiviral response by blocking interferon response factors blocking their upregulation of interferon transcription
What treatment do we have for RSV?
antiviral treatment and breathing aids -
antiviral = Ribarvirin
How do Cytoxic T cells and Natural Killer cells use MHC class1?
Cytotoxic T cells- if MHC 1 presents antigen = cell death
Natural Killer cells = if no MHC 1= cell death
*both are looking for abnormal cells, but both rely on differnt signals*


