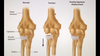
UWORLD 6 Flashcards
Management of shoulder dystocia?
BECALM
Breathe, do not push, lower head of the bed
Elevate legs into McRoberts position - sharp hip flexion while in supine position
Call for help
Apply suprapublic pressure - downward & lateral to release the anterior shoulder
L-enLarge vaglnal opening with episiotomy to facilate extra maneuvers
Maneuvers:
- delivery of the posterior arm
- pressure against baby’s posterior shoulder either anteriorly or posteriorly & anterior rotation (Woods corkscrew or Rubin maneuver)
- mother on hands & knees - “all fours” (gaskin maneuver)
- replacement of the baby’s head to vagina followed by cesarean delivery (Zavanelli maneuver)
what is the most common cause of acute non-traumatic mono-and oligoarthritis in young healthy adults?
Confirmation of suspected diagnosis is usually done by?
Gonococcal arthritis.
Should be strongly suspected in patients with a history of unprotected sexual relationship.
Confirmation of the suspected diagnosis is usually done by culturing the joint fluid and the mucosal surfaces, including the urethral, cervical, rectal and oral mucosal.
More than 80% of patients with diseminated gonococcal infection have positive cultures from at least one of the mucosal sites.
how does you distinguish gonococcal infection from other forms of infectious arthritis?
Tenosynovitis is a unique finding in patients with disseminated gonococcal infection; it is very unusual for other forms of infection.
Several tendons are usually simultaneously inflamed, particulary at the wrist, fingers, ankle and toes.
Another characteristic feature is pustular or vesiculo-pustular skin rash that is often transient and disappear spontaneously in several days.
Sausage digits (dactylitis) are commonly seen in patients with?
spondyloarthritis

What is usually the earliest manifestation of Cystic Fibrosis?
What does plain abdominal x-ray reveal?
Meconium ileus (is almost pathognomonic for the disease)
Uncompicated meconium ileus is characterized by distal intestional obstruction, wherein the terminal ielum is dilated and filled with thick, tar-like, inspissated meconium.
Plain abdominal x-ray findings (dilated, gas-filled loops of small bowel, absent air-fluid levels, and a meconium mass within the right side of the abdomen) are usually suggestive of the diagnosis.

Duodenal atresia is associated with?
Down’s syndrome and polyhydramnios
Inheritance pattern of cystic fibrosis?
Why is it important?
Since CF is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, a family history of recurrent respiratory infections (or other manifestation of CF) is an important clue to the diagnosis of the patient.
What is diagnostic of ectopic pregnancy?
Most common location for ectopic pregancy?
Treatment?
B-HCG levels >1,500, Transvaginal ultrasound revealing adnexal mass, empty uterus
*an early intrauterine pregnancy can be visualized by ultrasound when the B-hCG level is above the discriminatory zone (>1500 IU/L)
Most common location - ampulla of the fallopian tube
Treatment: Stable: medical (methotrexate) or Unstable: surgical management, depending on the patient’s hemodynamic status
How does threatened abortion present?
vaginal bleeding, closed cervix and an interuterine pregnancy with normal fetal cardiac activity
An early pregnacy of undetermine location occurs when a pregnancy that cannot be visualized on ultrasound at a B-hCG below the discriminatory zone (<1500) can be?
What do you do next?
ectopic or intrauterine.
In stable patients, the B-hCG level is repeated every 48 hours to determine whether the increase is consistent with normal pregnancy (> or = 35% rise every 48 hours).
What is used to predict the likelihood of streptococcal pharyngitis?
What is the PPV verus NPV?
When is diagnostic testing generally recommeded to confirm diagnosis?
Centor Criteria:
- Tonsillar exudates
2, tender anterior cervical lympadenopathy
- fever
- absence of cough
The presence of at least 3 has a roughly 50% PPV for strep pharyngitis (only minimally helpful) but there is an 80% NPV for streptococcal pharyngitis if the patient has less than 3 of these criteria.
Diagnostic testing is generally recommended in patients with at least 2 centor criteria.
If less than 2, no diagnostic testing is necessary and viral pharyngitis is therefore more likely and only symptomatic treatment should be given.
Bronchiolitits
Epidemiology
Clinical presentation
Diagnosis
Epidemiology - Age <3, RSV most common cause
Clinical presentation - Mild Upper respiratory symptoms, low grade fever and wheezing and crackles are typical.
diagnosis - clinical
Treatment for bronchiolitis
In healthy children, bronchiolitis is usually a self-limited disease;
however, young infants are at risk for respiratory distress.
Hypoxic patients or those with respiratory distress, apnea, or dehydration should be hospitalized in respiratory isolation to prevent nosocomial sspread of the extremely contagious virus.
Therapy consists of supportive measures (ex: IV fluids, nasal bulb suctioning, humidified oxygen)
What is used to prevent bronchiolitis?
What conditions do you use it for?
What also need to be done?
Palivizumab for infants with the following conditions:
-preterm birth < 29 weeks gestation
-chronic lung disease of prematurity
-hemodynamically significant congental heart disease
Antigen testing of nsal or pulmonary secrtions or nucleic acid amplification testing is reserved for infatns who receive palivizumad prophylaxis to detect breakthrough of RSV infection.
What is associated with RSV bronchiolitis?
Concurrent acute otitis media and future development of recurrent wheezing
Acute bronchitis
Etiology
Clinical presentation
Etiology - Precedig respiratory illness (90% viral)
Clinical presentation -
1. Cough
- >5 days to 3 weeks
- Can be productive (yellow, green or purulent sputum)
2. absent systemic findings (fever, chills)
3. Wheezing or rhonchi, chest wall tenderness
*Purulent yellow or green sputum is commonly present due to epithelial sloughing and is not a sign of bacterial inffection.
Acute bronchitis versus pneumonia
Both may have purulent yellow or green sputum (except in acute bronchitis it is due to epithelial sloughing and is not a sign of bacterial infection)
Patietns may have mild dyspnea and chest wall discomfort (from cough) as well as crackles that clear with cough, suggesting secretions that are easly mobilized (unlike pneumonia)
Fever is not typical in acute bronchitis and there is absence of evidence of consolidation (ex: crackles, focal increased breath sounds) on lung auscultation.
Diagnosis and treatment for acute bronchitis
What about chronic bronchitis?
ACUTE BRONCHITIS
Dx: clinical
- chest xray only in patients with suspected pneumonia
Treatment: symptomatic
- NSAID/Acetaminophen and/or bronchodilaotrs
- Antibotics NOT recommended
CHRONIC BRONCHITIS
PFT is indicated for the evaluation of chronic bronchitis, which is defined as cough > or = 3 months in 2 consecutive years.
Borderline personality disorder
What is it?
How does it differ from primary mood disorders?
persistent pattern of unstable relationships and self-image, mood instability, impulsivity and recurrent suicidal behavior.
involved extremes of idealization and devaluation (splitting) on views.
In contrast to primary mood disorders, the mood shifts in BPD occur in response to situational stressors and typically lasts a few hours, rarely more than a few days.
First line treatment for Borderline Personality disorder
Psychotherapy, with the best evidence for dialectical behavior therapy (DBT).
DBT is a structured treatment developed for BPD that consists of weekly individual psychotherpy and group skills training for approximately one year.
Interpersonal psychotherapy versus Dialectical behavior therapy
Interpersonal psychotherapy - used for depression. Focuses on four problem areas: grief over loss, interpersonal disputes, role transitions and interpersonal skill deficits.
Dialectical behavior therapy - used for borderline personality disorder, weekly individual psychotherpy and group skills training for approximately one year.
What is the inital test of choice in patietns with iron-defiency anemia and postive fecal occult blood test?
Colonoscopy
In patients wih no obvious pathologic findings on colonoscopy, upper gastrointestional endoscopy should be performed.
schizoaffective disorder
What is it?
How do you distinguish it from the following:
- Major depressive or bipolar disorder with psychotic features
- Schizophrenia
> or = to 2 weeks of psychotic symptoms in the absence of a mood episode.
Major depressive or bipolar disorder with psychotic features - psychotic symptoms occur exclusively during mood episodes
Schizophrenia - Mood symptoms present for relatively brief periods
Extended immobilization can cause what?
This is most common in patients with what?
What can decrease this?
Hypercalemia due to release of calcium from the bones.
Most common in patiens with increased bone turnover (ex: adolescents, pagets disease).
Bisphosphates can decrease bone turnover and preserve bone mass.
*When patients are immobilized, bone resorption is further increased and bone formation is decreased, leading to release of calcium from bone stores.
Granulomatous disorders can cause hypercalemia due to what?
Granulomatous disorders (ex: sarcoidosis, tuberculosis) can cause hypercalemia due to extrarenal production of 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D.
Clinical symptoms of CO poisoning?
What is an important clue?
The diagnosis is confirmed by?
throbbing, headache, nausea, malaise, and dizziness
Several people simultaneously presenting with a headache is an important clue.
Diagnosis is confirmed by carboxyhemoglobin level measurement.
ADHD treatment in adolescents versus preschool child?
Stimulant medications are a first-line treatment for adolescents or school-aged children (age > or =6) and include mehylphendiate and amphetamines
Preschool child (age <6), then behavioral therapy would be first line option.
*Stimulant therapy for ADHD does not increase risk of developing a substance use disorder
Anterior uveititis is also known as?
what is it characteritized by?
how do you distinguish this from other causes of red eye?
Iritis
pain, redness, variable visual loss and constricted and irregular pupil.
Visualize the anterior segment of the eye with slit lamp examination - If leukocytes are seen in the anterior segment, which contains aqueous humor found between the corenea and the lens, then the diagnosis of iriritis is confirmed.
A havy “flare” which is indicative of protein accumulation secondary to a damaged blood aqueous barrier, may also be seen

What is uveitis?
How is it broken up?
Uveitis is inflammation inside the eye, specifically affecting one or more of the three parts of the eye that make up the uvea:
- the iris (the colored part of the eye),
- the ciliary body (behind the iris, responsible for manufacturing the fluid inside the eye) and
- the choroid (the vascular lining tissue underneath the retina).
Anterior uveitis: Inflammation in the front (anterior) part of the eye, in the area between the cornea and the iris. This inflammation derives primarily from inflammation of the iris.
Intermediate uveitis: A term used to denote an idiopathic inflammatory syndrome mainly involving the anterior vitreous, peripheral retina, and ciliary body, with minimal or no anterior segment or chorioretinal inflammatory signs
Posterior uveitis: Inflammation predominately located in the posterior vitreous, retina, and/or choroid. Posterior uveitis is a vision disorder characterized by inflammation of the layer of blood vessels underlying the retina, and usually of the retina as well.

Walking is typically acquired around what age?
When should evaluation and treatment be considered?
Around 12 monhts, but is considered normal at age 9-16 months.
Considered if a child is not walking by 16 months OR delays are present in multiple development categories.
Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Inheritance pattern?
What is it characterized by?
What is a presenting sign?
Screen with what?
X-linked disorder
characterized by proximal muscle weakness and cardiomyopathy.
Although delayed walking can be a presenting sign, almost all patients also have cognitive delays.
Screening with a creatine kinase level, which is elevated in this condition
Conjunctivitis versus Anterior Uveitis
Conjunctivitis is a diagnosis of exclusion and is made in a patient with red eye and discharge only if vision is normal and there is no evidence of glaucoma, iritis or keratitis.
Infectious keratitis
Infectious keratitis (inflammation of the cornea)
is characterized by severe photophobia and difficulty keeping the affected eye open.
Penlight examination reveals corneal opacitiy or infiltrate
Acute stress disorder
How does this differ from PTSD?
> or = 3 days and < or = 1 month following exposure to the traumatic event.
PTSD is > 1 month
Intervals for follow up colonoscopy after polypectomy
Depends on the number, size and type of polyps.
Small rectal hyperplastic polyps - 10 years
1 or 2, small (<1 cm) tubular adenomas - 5 years
> or = 3 polyps, any polyps > 1cm, villous adenoma with high grade dysplasia features - 3 years
Very large polyps (>2 cm) or carcinoma in-situ - 2 to 6 months to verify complete excision.
Patients with familal adenomatous polyposis are at especially high risk and should have annual colonscopy.
Recurrent pneumonia in an elderly smoker may be the first manifestation of?
What is the most useful test to confirm the diagnosis of this patient?
bronchogenic carcinoma
Flexible bronchoscopy for the confirmation of the diagnosis.
This is an simple, invasive test that will enable the physican to visualize the actual endobronchial lesion, and take a tissue biopsy at the same time.
The common primary sites of origin of brain metastasis in order of frequency
Lung, breast, unknown primary, melanoma and colon cancer.
Main modifiable osteoporosis risk factors
Smoking,
excessive alcohol intake (> 3 drinks/day),
sedentary lifestyle
Best inital approach to smoking cessation in a pregnant women?
What else can be considered?
Physican directed counseling should be recommended for smoking cessation during pregnancy.
Other than counseling, it is not clear how best to treat pregnant smokers.
In the event that patient fail to stop smoking or do not respond to behavioral therpy, nicotine replacement therapy or buproprion can be considered after an informed discussion of the benefits and risks.
Calcium, Phosphate, PTH and 25 Hydroxy vitamin D levels in the following disorders:
Pseudohypoparathyroidism (PHP)
Hypoparathyroid
Vitamin D deficiency
PHP - PHP Resistance of PTH on its target tissue
Calcium: LOW, Phosphate: HIGH, PTH: HIGH, 25-OHD: Normal
Hypoparathyroid:
Calcium: LOW, Phosphate: HIGH, PTH: LOW, 25-OHD: Normal
Vitamin D Deficiency:
Calcium: LOW, Phosphate: LOW, PTH: HIGH, 25-OHD: LOW
Variety of Pseudohypoparathyroidism
TYPE 1A- has features of Albright Hereditary Osteodystrophy in addition to hypoparathyroidism.
Hypocaclemia with Hyperphosphatemia (as evidenced by bilateral cateracts and calification of his basal ganglia - Fahr’s syndrome)
Short stature, round face, short fourth and fifth metacarpels and a short neck.
TYPE 1B - do not have features of AHO
PPHP (pesudopseudohypoparathodism) do not have hypocalemia and hypercalemia because the resistance to PTH is mild, but they do have AHO.

Standard contigency table
How do you have TP, TN, FN, TN, Sensitivity, Specificity, PPV, NPV and Accuracy
Accuracy = (TP + TN) / TP+FP+TN+FN

Variety of Pseudohypoparathyroidism
TYPE 1A- has features of Albright Hereditary Osteodystrophy in addition to hypoparathyroidism.
Hypocaclemia with Hyperphosphatemia (as evidenced by bilateral cateracts and calification of his basal ganglia - Fahr’s syndrome)
Short stature, round face, short fourth and fifth metacarpels and a short neck.
TYPE 1B - do not have features of AHO
PPHP (pesudopseudohypoparathodism) do not have hypocalemia and hypercalemia because the resistance to PTH is mild, but they do have AHO.

Standard contigency table
How do you have TP, TN, FN, TN, Sensitivity, Specificity, PPV, NPV and Accuracy
Accuracy = (TP + TN) / TP+FP+TN+FN

Calcium, Phosphate, PTH and 25 Hydroxy vitamin D levels in the following disorders:
Pseudohypoparathyroidism (PHP)
Hypoparathyroid
Vitamin D deficiency
PHP - PHP Resistance of PTH on its target tissue
Calcium: LOW, Phosphate: HIGH, PTH: HIGH, 25-OHD: Normal
Hypoparathyroid:
Calcium: LOW, Phosphate: HIGH, PTH: LOW, 25-OHD: Normal
Vitamin D Deficiency:
Calcium: LOW, Phosphate: LOW, PTH: HIGH, 25-OHD: LOW
What is used to diagnose Cushing’s disease?
What would suggest the diagnosis?
A low dose suppression test
Cushing’s can be a secondary cause of hypertension. patient would have obesity, muscle weakness, hyperpigmentation, brusing, or other Cushingoid features.
Hazard Ratio
Defined as?
What is a measure of?
What is it used in?
What is the null value and what does it mean?
Likelihood of an event occuring the treatment group relative to the control group.
Measure of effect used in survival analysis (or time to event analysis)
Null value for HR is 1.0, which means there is no difference in risk between the two groups.
HR <1.0 = protective effect (event less likely to occur in the treatment group than the control group)
HR >1.0 indicates a detrimental effect (event more likely to occur in the treatment group than the control group)
Asthma
Diagnosed by?
What would this testing reveal in active versus those without active symptoms at the time of testing?
Pulmonary function testing (PFT)
Patients with active symptoms at the time of testing should reveal the characteristic obstructive pattern consistening of a reduced FEV1 and a reduced FEV1/FVC ratio
(total lung capacity and difffusing capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxid (DLCO) are typically normal or sometimes elevated).
In these patients, a bronchodilator (ex: albuterol) can be administered and should result in signifcant improvement in FEV1 (ex: 15% from baseline)
Those without active symptoms: are likely to have normal PFT findings.
The administration of methacholine in these patients is likely to cause > or =20% reduction in FEV1, which is diagnostic of airway hyperresponsiveness.
Most patients with asthma have a positive methacholine challenge (high sensitivity), and a negative test is reliable in ruling out asthma (high negative predictive value)
When is total lung capacity reduced?
How does the FEV1 and FVC look?
In restrictive lung disease (ex: intersittial lung disease, obsesity hypoventilation syndrome)
FEV1 and FVC are both decreased, but fairly proportionally, therefore the FEV1/FVC ratio is normal or increased.
What does pulmonary arterial hypertension do to the DLCO and lung volumes?
pulmonary arterial hypertension (due to intimal hyperplasia of the pulmonary arteries) causes reduced DLCO due to a combination of impaired blood delivery to the pulmonary capillaries and impaired diffusion of gas across the alveolar-pulmonary capillary membrane.
Lung volumes are typically normal.
DLCO in asthma versus COPD
Like asthma, COPD demonstrates an obstructive pattern on PFT characterized by a reduced FEV1/FVC ratio.
DLCO is also reduced (allowing for diagnostic differentation from asthma) due to emphysematous destruction of the alveolar-pulmonary capillary membrane.
Management of hyperglycemia in hospitalized patients in non-critical setting
Basal insulin (glargine, detemir, or NPH) must be continued in type 1 diabetics to prevent DKA and severe hyperglycemia.
During hospitalization, the dose of insulin should generally decreased by 20-30% because patients are eating less.
However, in some patients, the basal insuin may need to be increased due to insulin resistance caused by infection, stress, inactivity and medications such as corticosteriods.
Short - acting insulin analogue (aspart, lispro, or glulisine) every 4 hours or regular insulin every 6 hours, based on glucose readings.
Short acting is not required if patients are not eating.
Three parameters for Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS)
When is intubation recommended?
Best eye (E) response (max. 4 points)
Best Verbal (V) response (max 5 points)
Best motor (M) response (max 6 points)
Intubation is recommended for GCS score or = to 8.
When should you suspect ectopic pregnacy?
Most common location for ectopic pregnancy?
How do you diagnose rupture ecoptic pregnancy?
Positive urine HCG, lower abdominal pain and/or vaginal bleeding
fallopian tubes
Ruptured ectopic pregnancy is a clinical diagnosis that is confirmed during surgery.
Hemodynamically unstable patients (ex: hypotension, tachycardia) with signs of hemoperitoneum (abdominal rigidity, rebound, guarding) and adrenxal tenderness, ruptured ectopic pregancy is diagnosed.
Management of ectopic pregnancy? stable versus unstable.
Unstable - Immediate surgical intervention via emergency laparoscopy.
Stable - B-hcg levels <1,500 IU/L can be repeated in 48 hours.
In normal pregnancy, the B-hcg levels increses by at least 35% every 48 hours and a intrauterine pregnancy usualy becomes visible on transvaginal ultrasound at b-hcg > or = to 1,500.
When should you suspect periotonitis from hollow viscus perforation?
What do patients tend to do?
Best inital test?
experiencing sudden-onset abdominal pain with significant tenderness and guarding.
Patietns with peritonitis tend to lie still to minimize peritoneum irritation.
An upgright chest x-ray showing pneumoperitonium can identify perforation.
*it is important to keep the patient in an upright position so that the air within the peritoneal cavity can be visualized underneath the diaphgram.

What is charactersitic for Transverse myelitis
rapid progresive weakness of the lower extremities following an upper respiratory infection, accompanied by sensory loss and urinary retention
When is Maternal serum AFP levels measured?
Alpha fetal protein during pregnancy is made from?
What level of AFP is associated with fetal abnormalities?
Patients with elevated levels should under go?
measured at 15-20 weeks gestation as a screening test for a variety of fetal abnormalities.
AFP is made by the fetus and excreted from the fetal kidney into the aminoic fluid.
Although the function of AFP is unknown, there is an associated between abnormal levels and fetal abnormalities.
An elevated AFP level < or = 2.5 MoMs) is frequently associated with neural tube defects (ex: open spinal bidfida, anencepaphly) and ventral wall defects (ex: omphalocele, gastroschisis).
Elevated levels should undergo detailed anatomic ultrasound.
When should you suspect periotonitis from hollow viscus perforation?
What do patients tend to do?
Best inital test?
experiencing sudden-onset abdominal pain with significant tenderness and guarding.
Patietns with peritonitis tend to lie still to minimize peritoneum irritation.
An upgright chest x-ray showing pneumoperitonium can identify perforation.
*it is important to keep the patient in an upright position so that the air within the peritoneal cavity can be visualized underneath the diaphgram.

Diagnosis of schizophrenia
Good prognostic factors
presence of psychotic symptoms (not due to substances or a medical condition) for more than 6 months
Good prognostic factors:
later age of onset,
acute onset,
positive psychotic symptoms (ex: delusions, halluciinations) - typically responds well to antipsychotic medications
Hypoxemia in chronic COPD is primilary caused by?
What can be given to improve the hypoxemia?
V/Q mismatch
The emphysematous component of COPD causes airflow lmitation due to loss of elastic tissue and small bronchiolar collapse and chronic bronchitis contributes to airflow limitation as well.
The result is numerous localized areas of lung that have a low V/Q ratio, which is the major cause of hypoxemia in patietns with COPD.
These poorly ventilated lung regions (low V/Q regions) undergo hypoxic vasoconstriction to improve overall gas exchange efficiency, but nonetheless still have low V/Q ratio.
Despite restricted airflow, supplemental oxygen is able to successfully reach the alveoli in these regions, resuling in an increase in Q (due to the alleviation of hypoxic vasoconstriction) and improved gas exhange to the blood (improved hypoxemia)
What is indicated in all patients with perforated peptic ulcer?
Emergency surgery (open or laproscopic) is indicated in all patients.
In preparation for surgery, patients with perforated viscus should receive fluid resuscitation and broad-spectrum IV antiboitics with good coverage of Gram Neg organisms.
IV PPI therapy is also suggested for patients with perforated peptic ulcer.
Ogilvie’s syndrome
a.k.a acute colonic pseudo-obstruction
characterized by dilation of the cecum and right colon in absence of a mechanical obstruction to the flow of intestional contents.
Acute ischemic stroke
After inita assessment and stabilization, what is the first step?
First step is evaluation for intracranial hemorrhage with emergency CT scan of the head without contrast.
In patients without intracranial hemorrhage, the next step is restoration of blood flow to the ischemic area.
Current guidelines recommend consideration of tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) in patients up to 4.5 hours (optimally first 3 hours) after the onset of neurologic symptoms.
After treatment with tPA, patient is monitored in ICU or dedicated stroke unit.
Strict blood pressure management. Must keep <185/105 but >140/90 to maintain adequate perfusion.
Strict BP control is recommended with IV (not oral) drugs such as labetol, nitroprusside, or nicardipine to avoid the risk of hemorrhagic transformation.
What is the best test to evaluate a pancreatic cyst to differentiate malignancy from nonmalignant causes?
Endoscopic ultrasound with aspiration
EUS uses ultrasound guidance of the the endoscope for needle biopsy of lesions too small to be identified by CT/MRI or that are encased by vascular structures (making percutaneous biopsy difficult).
EUS is most effective for biospying lymph nodes and lesions in the pancreas, liver, adrenal glad, bile duct, peritoneal fluid and pleural fluid.
Requirements for hospice
Prognosis of less < or = to 6 months and the patient’s willingness to forego life-sustaining treatment.
*If patient is unable to vocalize a choice due to delirium, etc. (and therefore cannot give consent), family members can offer a substituted judgement in which they decide for the patient based on what she/he would have wanted under current circumstances.
*Physicians should educate patients and famililes that full code status, co-morbid conditions, and inability to give full informed consent are not contraindications to hospice care.
Type I HIT versus Type 2 HIT
immune/nonimmune
days of exposure after heparin therapy
platelet counts
consequences
Type 1 HIT occurs due to nonimmune direct effect of heparin on platelet activation and usually presents within the first 2 days of heparin exposure. The platelet cound then normalizes with continued heparin therapy and there are no clincal consequences.
Type 2 HIT is a more serious immune-mediated disorder due to antibodies to platelet factor 4 (PF4) complexed with heparin. This leads to platelet aggregation, thrombocytopenia, and thrombosis (both arterial and venous). Platelet counts usually drop to < or = to 50% from baseeline with a nadir of 30,000-60,000. Type 2 HIT usually presents 5-10 days after the initation of heparin therapy and may lead to life-threatening consequences (ex: limb ischemia, stroke)
What is released in response to tissue injury and what does it do?
Tissue factor and initiates the blood coagulation cascade.
It is also released in large amounts in disseminated intravascular coagulation, which is typically associated with systemic infection (sepsis), malignancy, or obsteric complications.
Warfarin and transient hypercoagulable state - why does this occur?
How do you counteract this?
Protein C is a vitamin K-depedent anticoagulant produced in the liver.
warfarin decreases protein C levels, leading to a transient hypercoagulable state. Patient needs to be adequately anticoagulatd for 3 days with heparin before the start of warfarin.
What should you do when you suspect a patient with HIT?
All forms of heparin (including LMWH such as enoxparin) must be stopped immediately in paitents with suspected HIT while awaiting diagnostic confirmation.
Patients with HIT remain at high risk of thrombosis even after discontinuation of heparin.
Therefore, an alternate, rapid acting, non-heparin anticoagulant such as direct thrombin inhibitor (ex: argatroban, bivalirudin) must be started immediately.
Warfarin therapy alone increases the risk of venous gangrene in patients with DVT due to rapid lowering of protein C levels. It can be resumed once the patient has been stably anticoagulated using an alternate anticoagulant and the platelet counts have increased >150,000.
Once a patient is diagnosed with HIT, they must avoid?
avoid all forms of heparin (including LMWH) for life. This includes heparin flushes for arterial lines and heparin coated catheters.
Treatment of scleroderma renal crisis.
ACE inhibitors
They reverse the angiotensin-induced vasoconstriction
Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonkeotic state (HHS) is characterized by?
What are the common causes?
Inital mangagement of HHS?
Very high glucose (frequently >1,000 mg/dL), mental status changes and no associated keotacidosis.
Common causes: infections, major illnesses, dehydration, and drugs such as corticosteriods, psychotics, diuretics, sympathomimentic agents and beta blockers.
Inital management of HHS includes high flow IV fluids, continous IV insulin infusion and careful potassium replacement.
Stablized patients can transition to subcutaneous insulin with a basal-bolus regimen.
Subcutaneous insulin can generally be started once the glucose has been corrected to <200.
*Management of DKA and HHS is the same
Tourette syndrome
What age does it appear?
Who is it more common in?
What is required for diagnosis?
Commmon comorbidities?
Appears at 6-15
more common in boys
Dx: multiple motor tics and at least one vocal tic (range from coughing, grunting, throat clearing, sniffing to blurting out inapprpriate comments and obscenitis - coprolalia)
ADHD and OCD are common
Chronic tic disorder versus tourettes
Tourettes has both motor and vocal whereas chronic tic disorder invoves one more motor or vocal (but not both) for > or = 1 year.
Treatment of Tourette Syndrome
Includes psychotherapy and/or medications.
Habit reversal therapy (HRT), a form of cognitive-behavioral therapy, is the most effective nonpharmacological treatment.
When tics are severe and interfer with social and academic functioning or if the response to HRT is suboptimal or HRT is not available, pharmacolgical treatments may be required.
1st-generation antipsychotics (fluphenzine, pimozide, halperiodol) have demostrated efficiacy and are approved by the FDA. However, 2nd generation antipsychotics (risperodone, arpripizole) are typically preferred due to 1st genration side effects (extrapyramidal symptoms, QtC prolongaiton with pimoizde).
Other pharmacological treatment include alpha-2-aderengeric receptor agonists (ex: clonidine, guanfacine) and terabenazine (a dopamine depleter)
Subclinical hypothyroidism is defined as?
When is treatment warranted?
Mild elevation in TSH levels (5-10) accompanied by normal free T4 levels.
Treatment is warranted in the presence of:
- Antithyroid antibodies.
- abnormal lipid profile
- symptoms of hypothyroidism
- ovulatory and menstrual dysfunction
How do you differentiate traumatic Lumbar puncture from SAH?
Traumatic lumbar puncture results from accidental damage of a blood vessel during the procedure.
A high RBC count without xanthochromia
Stages of Change Model
Precontemplation - not ready to change
Contemplation - thinking of changing
Preparation - ready to change
Action - making change
Maintenance - changes integrated
Pharmacological treatment for patients with treatment-resistant depression versus partial responders?
Patients with no improvement (nonresponders) or unacceptable tolerability generally benefit from switching to another antidepressant.
Partial responders who are otherwise tolerating their current antidepressant, augmentation is considered first-line option.
Augumentation strategies include adding a second-generation antipsychotic, an antidipressant with a different mechanism of action, or occasionally lithium or triiodothyronine.
Bupropion
What is it?
What is an ideal choice for treating SSRI-induced sexual side effects?
Bupropion
Norepnephrine dopamine reuptake inihibitor
Does not cause weight gain or sexual side effects and has been used to treat SSRI-induced sexual side effects.
Side effects of Mirtazpine
Does not cause sexual dysfunction, but it is associated with increased appetite, weight gain, and sedation
Phenelzine
MAO?
What would you not combine it with an SSRI?
What does it require if you want to use this drug as an alternate monotherapy in a treatment-resistant patient with SSRI?
MAO inhibitor
Risk of sertotonin syndrome
Reqires a 2-week washout period (5 weeks for fluoxetine due to its longer half life due to the risks of hypertensive crisis or serotonin syndrome
Breast implants
- Association with any major rheumatologic, autoimmune, or neurologic disorder?
- Most morbidity from silicon breast implants are assoicated with?
- effects on developing fetus
- risk with breastfeeding
- Mammograms Screening with beast implants
- does not cause any major rheumatologic, autoimmune, or neurologic disorder.
- Morbidity assocated with local complications, such as capsular contracture, implant deflation and rupture.
-Do not cause any disease/defects in developing fetus
-No evidence of harmful effects in babies who are breastfed by mothers with silicon breast implants
- Should continue to have screening mammograms at regular intervals
Neonatal screening for hypothyroidism
How is it done?
When?
What is suggestive of primary hypothyroidism? Next step in management?
performed by obtaining a small sample (few drops) of blood from the heel pad and using a piece of filter paper to absorb the blood sample.
Done within 2-5 days following delivery
- *Performed after first 24 hours because there is a normal physiologic TSH surge following delivery.*
- Afer the first 24 hours, the TSH levels gradually drop to normal levels or may remain slightly elevated for the next few days.*
Low T4 and elevated TSH levels of the blood sample from heel pad are suggesitve of primary hypothyroidism
Confirm the dignosis by measuring free T4 and TSH levels from regular blood draw before starting levotyroxine therapy.
Typical features of subacute thyroiditis?
What is this also known as?
What is it charaterized by?
How does this differ from silent thyroditis and hashimoto thyroiditis?
Hyperthyroidism, elevated ESR, enlarged thyroid
Quervain’s thyroiditis or granulomatous thyroiditis
Subacute thyroidits - painful ; mixed inflammatory thyroid infiltrate consisting of lymphocytes, neutrophils, hisitocytes and multinucelated giant cells.
Silent thyroiditis & Hashmimoto thyroiditis - painless; predominately lymphocyte infiltration
Thyrotoxicosis in subacute thyroiditis is due to?
How will the radioidine uptake be in the thyroid?
What other conditions will you see this as well?
release of stored thyroid hormones from inflammatory damage to thyroid follicles.
Patients will have suppressing TSH, with resulting decrease iodine uptake and new thyroid hormone synthesis.
They will have typically low radioiodine uptake in the thyroid.
Low radioactive idone uptake is also seen in silent (painless) thyroiditis, postpartum thyroiditis, surreptitious thyroid hormone abuse, and iodine-induced thyroiditis.
Hot nodule within a cold thyroid on raidoidone uptake scan indicates?
How does this differ from subacute thyroiditis?
presence of hyperfunctioning adenoma.
These patients have symptomatic hyperthyroidism but are less likely to have fever or thyroid tenderness and would have nodular enlargement, rather than diffuse enlargement.