Urinary 1 Flashcards
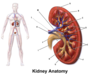
What are some of the functions of the kidneys?
Regulation of body fluid
Regulation of electrolytes
Blood filtration
Blood pressure regulation
Within what cavity is the urinary system located?
Abdomino-pelvic cavity
What system is the urinary system closely related to anatomically?
Reproductive system
What are the components of the urinary system?
Kidneys
Ureter
Urinary bladder
Urethra
What is the function of the kidneys?
Maintains homeostasis by blood filtration
What is the function of the ureter?
Urine transported from kidneys to bladder
What is the function of the urinary bladder?
Temporary storage of urine
What is the function of the urethra?
Transport of urine out of the body
Where do the kidneys lie?
In the paravertebral gutters on the posterior abdominal wall on either side of vertebrae T12-L3
Besides what vertebrae do the kidneys lie?
T12-L3
What plane does the hilus of the kidney lie on?
Transpyloric plane
What is the hilus of the kidney?
Part on the medial concave border of the kidney through which blood vessels and the ureter enter/leave the substance of the kidney
At what vertebral level does the transpyloric plane lie?
L1

Which kidney is lower and why?
Right kidney due to the liver
What is the covering of the kidneys called?
Fascial coverings of the kidneys
What 4 layers enclose each kidney (fascial of the kidneys)?
Fibrous renal capsule
Fatty renal capsule
Renal fascia (fibro-fatty tissue)
Pararenal fatty tissue (mainly on the posterior aspect of the kidney)
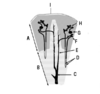
What is A?

Kidney
What is B?

Renal capsule
What is C?

Perirenal fat
What is D?

Renal fascia
What is E?

Pararenal fat
What is the significance of having fatty tissue around the kidney?
Protection
What are the posterior relations (muscles) to the kidneys?
Diaphragm
Psoas major
Quadratus lumborum
What is A?

Diaphragm