MSK Anatomy Lower Limb 1 Flashcards

a. anterior superior iliac spine
b. iliac crest
c. iliac fossa
d. pubic tubercle
e. pubic crest
f. obturator foramen
g. acetabular cavity
h. ischial spine
i. ischial tuberosity

a. neck
b. lesser trochanter
c. lateral condyle
d. greater trochanter
e. medial condyle
f. head
g. intertrochanteric lin
The two superficial veins are the
great saphenous vein and lesser saphenous vein

Which superficial vein ascends anterior to the medial malleolus of the tibia?
Great saphenous vein
Which vein ascends posterior to the lateral malleolus
Small saphenous vein
Which superficial vein empties into the femoral vein?
Great saphenous vein
Which superficial vein empties into the popliteal vein?
Small saphenous vein
Name the lower limb lymph nodes
Superficial Inguinal
Deep Inguinal
Popliteal
State the dermatomes of the lower limb

Why is the hip joint more stable than the shoulder joint
Deeper socket, with stronger and bigger muscles and ligaments.
What is the acetabular labrum?
Fibrocartilage that lines the acetabulum cavity
Which part of the acetabular cavity does the labrum cover- and what is its function
All around besides inferior, to support compressive load
Name ligaments of hip and function
1. iliofemoral- prevents hyperextension of the hip joint
2. pubofemoral- hyper abduction of the hip joint
3. ischiofemor - reinforces medial rotation

The movements at the hip joint are:
- Flexion
- Extension
- Abduction
- Adduction
- Internal Rotation
- External Rotation
- Circumduction (a combination of the above)
Name hip flexor muscles
- iliacus
- Psoas major
- pectineus

iliacus
Hip flexor muscles
Origin
Insertion
Innervation
Origin:
Iliac fossa
Insertion
Lesser trochanter of femur
Innervation
Femoral nerve (L1-L3)
Psoas Major
Hip flexor muscles
Origin
Insertion
Innervation
Origin
Vertebra
Insertion:
Lesser trochanter of femur as iliopsoas tendon
Innervation
Anterior rami of spinal nerves L1-L3
iliacus
Hip flexor muscles
Origin
Insertion
Innervation
Origin
Superior pubic ramus (pectineal line of pubis)
Insertion
Pectineal line of femur,
Innervation
Femoral nerve (L2, L3) (Obturator nerve (L2, L3))
What is the main extensor of the hip
Hamstring:
long head of biceps femoris,
semitendinosus
semimembranosus,

Which compartment are the hip adductors located
Medial

Name these muscles

- Adductor longus
- Adductor Brevis
- Adductor Magnus
Hip Abductor Muscles
- Gluteus Medius
- Gluteus Minimus
- Piriformi

Label these external rotator muscles

1) Piriformis
2) Obturator Internus
3) Obturator Externus
4) Superior and Inferior Gemelli
5) Quadratus Femoris

Which muscle(s) are the medial rotators/internal of the hip joint?
- gluteus medius
- Gluteus minimus
- Tensor Fascia Lata
Which muscle makes up the bulk of the anterior compartment
Quadriceps Femoris:

- Rectus femoris
- Vastus medialis
- Vastus intermedius
- Vastus lateralis
Which nerve innervates these anterior group muscles?
Femoral Nerve
What is the action of rectus femoris on the hip joint?
Hip flexion
To which part of the tibia does the patellar ligament attach?
Tibia tuberosity
What are the 3 actions of sartorius on the hip joint?
- flexion of hip
- Abduction of hip
- Laterally rotates the thigh at hip joint
How do the muscles in the medial compartment of the thigh act on the hip joint?
adduction
Which nerve innervates the medial thigh muscles?
obturator
Through which bony foramen does the nerve that innervates the medial thigh muscles enter the thigh?
Obturator Foramen
Label

- adductor brevis
- adductor magnus
- adductor canal
- adductor longus
What structures pass through the adductor canal
Femoral artery
Femoral Vein
Femoral Nerve
Which fossa do they enter after passing through this canal?
Popliteal fossa
Borders of the femoral traingle
Medial boundary: adductor longus muscle
Lateral boundary: sartorius muscle.
Base of the femoral triangle/ Superior border? inguinal (upper)

Which muscles form the vast proportion of the floor of the femoral triangle
- Pectineus
- Adductor longus
What are the 3 major structures present in the femoral triangle?
- femoral nerve
- femoral artery
- femoral vein
What is th femoral sheath
Funnel shaped connective tissue tube which surrounds the proximal parts of femoral vessels (but not the nerve) and creates the femoral canal medial to them, which contains lymphatic vessels.

State the content sof each compartment of the femoral sheath
Lateral
Femoral Artery
Intermediate
Femoral vein
Medial
Femoral canal

What are the contents of the femoral canal?
- Fat and loose connective tissue
- lymph nodes
Femoral artery is a branch of what
External iliac artery
Where does the femoral artery enter the thigh
midway between :
anterior superior iliac spine
and pubic symphysis
Which vein is the femoral vein a continuation of
popliteal vein
Which two important veins drain into it in the femoral triangle?
- profunda femoris vein
- Greater saphenous vei
What is the abductor canal
Narrow conical tunnel located in the thigh and serves as a passageway from structures moving between the anterior thigh and posterior leg

Label the lumbar plexus


Main lower limb nerves
Femoral
Obturator
Identify one main sensory nerve of the lumbar plexus supplying the lower limb
lateral cutaneous
What is the nerve root value of the motor nerves?
L2,3,4
What is the nerve root value of the sensory nerve?
L2,3
Label this


Label the ligaments of the pelvic girdle


Which sciatic foramen is the route for structures entering or leaving the pelvis
Greater (into gluteal region)
Which sciatic foramen is a route for structures entering or leaving the perineum
Lesser
Name these muscles


What are the actions of gluteus maximus muscle?
extends and laterally rotates hip
What is the action of gluteus medius, gluteus minimus and tensor fasciae latae?
They are abducts and medial rotators of hip joint
Name the two muscles which connect to the iliotibial tract
tensor fascia lata and gluteus maximus.
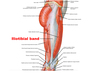
Function of iliotibial tract
stabilisation to the lateral aspect of the knee joint.
The sacral plexus lies on which muscle?
Piriformis

The sacral plexus is formed by the union of the ventral rami of spinal nerves
L 4, L5 and S 1 to S 4
Main branch to lower limb
sciatic nerve
Main branch to perineu
pudendal nerve
What are the root values of the sciatic nerve?
L 4 to S 3

What is the action of the hamstring muscles on the hip and knee joint?
Hip joint extension
Knee joint flexion
Which nerve innervates the posterior compartment of the thigh?
Tibial part of sciatic nerve (L5, S1,2
Which branch of the femoral artery contributes to the posterior muscle compartment blood supply?
Profunda femoris artery
Label these muscles

- semimembranosus
- semitendinosus
- long head of biceps femoris
- Short head of biceps femoris

Bones
- patella 2. fibula 3. tibia 4. femur
Articular Surfaces
a. medial femoral condyle b. lateral femoral condyle c. lateral tibial condyle d. medial tibial condyle e. tibial tuberosity
Which is the most important muscle which helps to stabilize the knee joint?
Quadricep femoris

- fibular collateral ligament/Lateral Collateral
- tibial collateral ligament/ Medial Collateral
- anterior cruciate ligament
- posterior cruciate ligamen
Where does the tendon of the popliteus muscle pass
deep to the LCL, separating it from the lateral meniscus.

Where does the MCL attache to the meniscus
At its midpoint
Why is the attachment of the MCL to the medial meniscus clinically important?
Injury in the tibial collateral ligament leads to a reduced mobility in the medial meniscus
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) prevents the femur from sliding …… on the tibia.
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) prevents the femur from sliding posteriorly on the tibia.
The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) prevents the femur from sliding……… on the tibia.
The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) prevents the femur from sliding anteriorly on the tibia.

- medial meniscus
- Lateral meniscus
- Anterior cruciate ligament
- Posterior cruciate ligament
What are the main functions of the menisci
Lubricate, absorb shock and provide nutrients to the knee joint
Which meniscus firmly adheres to the deep surface of the tibial or medial collateral ligament?
The medial meniscus
Which movement of the knee causes the patella to move?
Flexion and extension
Label these bursas

- subcutaneous prepatellar bursa
- Deep infrapatellar bursa
- Subcutaneous infrapatellar bursa
Which bursa communicates with the articular cavity of the knee joint
Suprapatellar bursa
What is housemaid’s knee (pre-patellar bursitis)
Swelling of the prepatellar bursa due to too much kneeling
Muscles of knee flexion
Hamstring, gracilis, sartorius
Knee Extension
Quadriceps (vastus intermedius, lateralis, medialis), rectus femoralis


