MSK Upper Limb 1 Flashcards
What makes up the borders of the axilla
Ant:
Pectoralis Major
Pectoralis Minor
Post:
Terest Major
Latismuss Dorsi
Subscapularis
Lateral:
Chest wall & seratus anterior
Medial:
Intratubercle groove of humerus

Contents of the axilla
Axillary artery
Axillary Vein
Brachial Plexus
Axillary Lymph nodes
Coracobrachialis
Short head of biceps brachii

The Axillary Artery is a continuation of which Artery?
The Subclavian Artery
At what anatomical point does the Axillary Artery begin?
Lateral Border of the 1st Rib
The Axillary Artery continues beyond the Axilla as which Vessel?
The Brachial Artery
At what anatomical point does the Brachial Artery begin?
Inferior Border of Teres Major
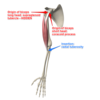
- What Rami forms the Brachial Plexus?
- What Spinal Levels do these Rami come from?
- Ventral Rami
- C5, C6, C7, C8, and T1
What nerve roots form the Upper Trunk?
C5 & C6
What is Erb’s Point?
The point where C5 and C6 converge to form the Upper Trunk
What nerve roots form the Lower Trunk?
C8 T1
What nerve roots form the MiddleTrunk?
C7
What nerve(s) are formed by the posterior cord
Radial
Axillary
What nerve(s) are formed by the medial cord
Ulnar nerve
Medial side of median nerve
What nerve(s) are formed by the lateral cord
Musculocutaneous
Lateral side of median nerve


State the superficial veins of the arm
Cephalic
Basilic
Medial Cubital nerve

State dermatomes of upper limb
C5-T1

State the axillary lymp nodes
Anterior
Posterior
Apex
Central
Lateral
What bones make up the pelvic girdle
Scapula
Clavicle
What joints make up the pelvic girdle
Acromioclavicular joint
Sternoclavicular joint
Label the clavicle


How to distinguish the sides of the clavicle
- The lateral aspect of a clavicle is flatter than the medial aspect
- The superior surface is smoother than the inferior surface
- The conoid tubercle – attachment for the conoid ligament – is on the inferior aspect of the lateral portion of the clavicle
Which part of the clavicle is weakest and commonly breaks (fractures) during a fall?
Between middle and most lateral thirds of the clavicle (mainly middle 1/3)
Thin and lacks muscle support
Label the Scapula