Upper limb (Fasciae Muscles of Pectoral Girdle and Arm) Flashcards
What does the Superficial fascia contain?
- Fat
- Superficial blood vessels
- Superfical lymph vessels and nodes
- Known as the Cubital or supratrochlear nodes
- Located above the medial epicondyle of the humerus
- Superficial fascia of the neck has the Platysma

What are Superficial veins?
- Cephalic
- Basilic
- Median cubital
- Median antebrachial
*All located in the Cubital Fossa for venipuncture

What nerves are in the Brachial plexus of the Superficial Fascia?
- Lateral pectoral nerve
- Lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve
- Superficial branch of radial nerve
- Medial brachial cutaneous nerve
- Medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve
- Dorsal branch of ulnar nerve

What are the Cervical plexus nerve in the Superior Fascia?
- Supraclavicular nerves

What is the Deep Fascia of the Pectoral?
- Invests pectoralis major
- Continuous with the Axillary and Deltoid fascia

What is the Axillary fascia?
- Forms the floor of the Axilla and Clavipectoral fascia
- Clavipectoral fascia has two parts:
- Costocoracoid membrane
- Contains:
- Pectoralis minor
- Subclavius
- Cephalic vein
- Lateral pectoral nerve
- Throacoacromial artery
- Contains:
- Suspensory ligament of the axilla
- Continuous with: Latissimus dorsi fascia

What is the Deep fascia of the Brachial fascia?
- Medial intermuscular septa
- Contains:
- Ulnar nerve
- Superior ulnar collateral artery
- Lateral intermuscular septa
- Contains:
- Radial nerve
- Radial collateral branch (deep brachial artery)
- Intermuscular septa
- Attach to supracondylar ridge of the humerus
- Divides arm into anterior and posterior fascial compartments
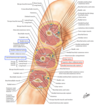
What is the Deep fascia of the Antebrachial fascia?
- Contains the Cubital fossa that forms the Bicipital aponeurosis
- Connected to biceps brachii tendon
- Protects neurovascular structures (brachial artery and medial nerve)
- Antebrachial fossa attaches to the posterior border of ulna
- Connecting with:
- Medial and Lateral Intermuscular septum
- Both attach to the bone of the forearm with the ulna, radius, and interosseous membrane
- They divide the forearm into anterior and posterior fascial compartments

What is teh Deep fascia at the Wrist?
Forms:
- Extensor retinaculum
- Fibrous septa extend to the distal third dorsal surface of the radius and ulna to form 6 separate tunnels
- Tunnels
- Allows some tendons of the posterior compartment of the forearm to pass into the hand
- Lined by synovial sheath
- Extends above and below the retinaculum on the tendons
- Palmar carpal ligament
- Contains:
- Palmar branch of median and ulnar nerve

What is the Deep fascia at the Hand?
Forms:
- Flexor retinaculum
- Superficially contains the Ulnar vessels and nerve
- Upper border:
- At the level of the distal transverse skin crease on the anterior surface of the wrist
- Continous with the antebrachial fascia
- Lower border:
- Attached to the apex of the palmar aponeurosis
- Carpal tunnel contains:
- Flexor digitorum superficialis
- Flexor digitorum profundus
- Flexor carpi radialis
- Flexor pollicis longus
- Median nerve
- Palmar aponeurosis
- Fibrous digital sheaths

What is the Deep fascia of Palmar aponeurosis?
- Provides attachment, protection, and making a grip more efficient
- Attachments:
- Palmaris longus tendon
- Four digital bands
- Each diverge around the flexor tendons and fibrous digital sheath
- Extends: Medially and Laterally
- Medial fibrous septum
- Attaches to 5th metacarpal bone
- Lateral fibrous septum
- Attaches to 3rd metacarpal bone
- Septums divide palm into:
- Hypothenar compartment
- Thenar compartment
- Midpalmar compartment

What is Dupuytren’ contracture?
- Fibrous degeneration
- Excessive formation of collagen affecting the digital bands
* Most common affecting 4th and 5th digital bands - Results in TRIGGER FINGER

What is Compartment syndrome?
- Affects Fascial compartments
- Painful condition from increased pressure within a closed body space, especially forearm or leg
- Two types acute or chronic
What is Acute Compartment syndrome?
Acute:
- Develops when swelling or bleeding occurs within a compartment (b/e fascia doesn’t stetch or expand)
Causes:
- Fracture of a bone
- Badly bruised muscle
- Crush injuries
- Tight casts (contricting bandages)
- Anabolic steriod use
Clinical:
- Increase pressure within compartment
- Compresses veins causing impaired venous drainage
- Accumulation of waste products and swelling
- Tissue pressure compromises arterial blood flow resulting in muscle and nerve ischemia
Manifestations:
- Lack of oxygenated blood
- Pain
- Classic sign and increase when muscles are streched/squeezed
- Paresthesias
- Tingling or burning sensation (Nerve irritation)
Late Manifestations: (Indicates permanent tissue injury)
- Absence of distal pulse
- Paralysis
Treatment:
- Surgical emergency (called Fasciotomy)
- Incision of the skin and fascia of the affected compartment to allow more space for the muscle to swell
- No effective nonsurgical treatment
What is Chronic Compartment Syndrome?
- Also known as Exertional compartment syndrome
- Reoccuring syndrome from exercise or work
- Subsides when activity is stopped but resume when activity is resumed
- Symptoms:
- Numbness
- Visible muscle bulging
- Difficulty moving affected limb
- Treatment:
- Not a surgical emergency
- Avoid activity causing the condition
- Physical therapy
- Anti-inflammatory drugs
- Surgical treatment (Fasciotomy, if regular treatment fails)
What is the Pectoralis major?
- Attaches:
- Clavicular head
- Clavicle (medial half)
- Sternal head
- Sternum
- Superior 6 costal cartilages
- Aponeurosis of external abdominal oblique
- Insection:
* Intertubercular groove (lateral lip)

What is the Pectoralis minor?
Anterior thoracoappendicular muscle
- Origin:
* 3rd to 5th ribs - Insection:
* Coracoid process of scapula

What is the Subclavius?
Anterior thoracoappendicular muscles
- Origin:
* 1st rib and costal cartilage - Insertion:
* Inferior surface of clavicle

What is the Serratus anterior?
Anterior throacoappendicular muscle
- Origin:
* First 8 ribs - Insertion:
* Medial border of scapula

What is the Trapezius?
Posterior thoracoappendicular muscles
- Origin:
- Occipital bone
- Ligamentum nuchae
- C7 to T12 spinous process
- Insertion:
- Clavicle (lateral 1/3)
- Scapula (spine/acromion)
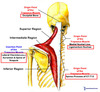
What is the Latissimus dorsi?
- Origin:
- Lower 6 thoracic vertebrae
- Thoracolumbar fascia (Iliac crest)
- Inferior 4 ribs
- Insertion:
* Intertubercular groove

What is the Levator scapulae and Rhomboids?
- Levator scapulae origin:
* C1 to C4 transverse process - Rhomboid Minor origin:
* C7 to T1 Vertebrae Spinous processes - Rhomboid Major origin:
* T2 to T5 Spinous processes - Insertion for Levator scapulae and Rhomboids
* Medial border of scapula

What is the Deltoid muscle?
Scapulohumeral Muscles
- Origin:
- Clavicle (lateral 1/3)
- Scapula (spine/acromion)
- Insertion:
* Deltoid tuberosity

What is the Teres major?
Scapulohumeral Muscles
- Origin:
* Scapula (inferior angle) - Insertion:
* Intertubercular groover (medial lip)

What is the Rotator cuff?
4 Muscles (3 posterior and 1 anterior)
- Insertion: Teres minor, Supraspinatus, and Infraspinatus
- Greater tubercle
- Teres Minor
- Greater tubercle
- Origin: Scapula (lateral border)
2. Supraspinatus - Origin: Supraspinatus fossa
3. Infraspinatus - Origin: Infraspinatus fossa
4. Subscapularis - Origin: Subscapular fossa
- Insertion: Lesser Tubercle

What is the Biceps brachii?
- Origin:
- Short head: Coracoid process
- Long head: Supraglenoid tubercle
- Insertion:
* Radial tuberosity - Clinical:
- Rupture of long head tendon of biceps brachii results in POPEYE deformity
- Localized bulge at distal part of arm

What is the Brachialis muscle?
- Origin:
* Humerus - Insertion:
* Coronoid process/tuberosity of Ulna

What is the Coracobrachialis muscle?
- Origin:
* Coracoid process - Insertion:
* Humerus

What is the Triceps brachii?
- Origin:
- Long head: Infraglenoid tubercle
- Lateral head: Superior to radial groove
- Medial head: Inferior to radial groove
- Insertion:
* Olecranon



