Skeleton (Joints of the Upper limb) Flashcards
1
Q
What are 3 Joints of the Pectoral Girdle?
A
- Sternoclavicular joint
* Clavicular movement - Acromioclavicular joint
* Scapular movement - Glenohumeral joint
* Humeral movement
*All three joints move at the same time
2
Q
What is the Sternoclavicular Joint?
A
- Sellar Joint or “saddle joint”
* Flexion-Extension
* Abduction-Adduction - Articular surface:
- Clavicle (sternal end)
- Manubrium sterni (sternal notch)
- 1st costal cartilage
- Articular disc: divides the joint’s interior into 2 compartments
- Dislocation is rare
* Clavicle breaks first - Costoclavicular ligament
- Anchors sternal end of 1st rib
- Limits elevation of pectoral girdle

3
Q
What is the Acromioclavicular Joint?
A
- Plane Joint (gliding/sliding)
- Movement:
- Associated with scapular and humeral movements
- Elevatation/Depression
- Protraction/Retraction
- Rotation
- Articular surfaces:
- Lateral end of clavicle
- Acromion of scapula
- Partially separated by an articular disc
- Contains:
- Coracoclavicular ligament- Maintains joint integrity
- Trapezoid ligament
- Conoid ligament
- Dislocation- Not uncommon
* Rupture of coracoclavicular ligament

4
Q
What is the Glenohumeral Joint?
A
- Spheriodal
* Synovial ball-and-socket joint - Articular surface:
- Humeral head
- Glenoid cavity (deepened by Glenoid labrum)
- Articular capsule
- Very loose
- Attaches to anatomical neck of humerus (laterally)
- Supported by rotator cuff
- Main stabilizing factor
- Weakest area
- Inferior part of the capsule
- Synovial membrane
* Tubular synovial shealth for the tendon of the Long Head of Biceps Brachii - Dislocation-
- Usually Anterior/inferior
- Damage to axillary nerve (seen in young individuals)
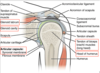
5
Q
What are the ligaments of the Glenohumeral Joint?
A
- Ligaments:
- Glenohumeral (Superior, Middle, Inferior) Ligament
- Reinforces the Anterior part of the capsule
- Coracoacromial Ligament
- Blends with supraspinatus tendon
- Transverse humeral Ligament
- Bridges the intertubercular groove
- Coracoacromial arch
- Coracoacromial ligament
- Coracoid process
- Acromion
- Bursae: Protect tendons from rubbing against the bone
- Subscapular bursa
- Behind the subscapularis tendon
- Subacromial bursa
- Between the Coracoacromial arch and Supraspinatus tendon

6
Q
What injuries occur in the Glenohumeral Joint?
A
- Subacromial bursitis
* Pain even at rest - Supraspinatus tendinitis
* Calcification of tendon - Painful arc syndrome
* Pain beyond 50 degree motion of abducting the arm - Anterior shoulder dislocation
- Head of humerus losing contact with the glenoid cavity
- Hyperextension
- Excessive lateral rotation
*

7
Q
What is the Elbow Joint?
A
- Articular Surface
- Humeral trochlea
- Hinge: Flexion/Extension
- Trochlear notch
- Humeral capitulum
- Spheroidal
- Radial head
- Articular Capsule
- Medial and lateral Epicondyles (outside the capsule)
- Radial and Ulnar collateral ligament
- Anular Ligament
- Superior radioulnar capsule

8
Q
What injuries occur on the Elbow Joint?
A
- Articular capsule
- Thin anterior and posterior
- Dislocation- falling on the hands and elbow flexed
- Common in children
- Dislocation- falling on the hands and elbow flexed
- Bursae:
- Subcutaneous olecranon
- Pressure/Friction
- Student’s elbow
- Pressure/Friction
- Subtendinous elecranon
- Repeated flexion/extension
- Inflammation
- Repeated flexion/extension

9
Q
What is the Proximal Radioulnar Joint?
A
- Pivot Joint
* Pronation/Supination - Articular surfaces:
- Circumference of radial head
- Radial notch of ulna
- Articular capsule
* Covers the Joint - Annular ligament- attach to the radial notch of ulna
- Osteofibrous ring
- Pronation /Supination of radiusr

10
Q
What is the Distal Radioulnar Joint?
A
- Pivot Joint
* Pronation/Supination - Articular Surface:
- Head of ulna
- Ulnar notch of radius
- Main uniting structure
- Articular/ Triangular disc
- Superior surface articulates with ulnar head
- Inferior surface articulates with Lunate/triquetral
- Appears in L shaped joint cavity

11
Q
What injuries occur in the Proximal Radioulnar Joint?
A
- Subluxation of radial head
- Nursemaid elbow- dislocation of radial head
- Lift to upper limb while forearm is pronated
- Tearing of the loosely attachment of the annular ligament of the radial head

12
Q
What is the Radiocarpal Joint?
A
- Ellipsoid Joint
- Flexion-Extension
- Abduction-Adduction
- Articular Surface
- Carpal articular surface of radius
- Articular (triangular) disc
- Proximal row of carpal bones (except pisiform)
- Ligaments
- Palmar (volar) radiocarpal and ulnocarpal
- Dorsal radiocarpal and ulnocarpal
- Collateral (radial and ulnar)

13
Q
What is the Intercarpal Joint?
A
- Plane
* Increase the range of movement of radiocarpal joint - Articular surface:
- Carpal bones
- First row
- Second row
- Midcarpal

14
Q
What is the Carpometacarpal of the Thumb?
A
- Sellar or saddle joint
* Flexion-Extension
* Abduction-Adduction - Articular surface
- Trapezium
- Base of 1st metacarpal

15
Q
What is the Intermetacarpal Joint?
A
- Plane Joint
* Common fibrous capsule - Articular surface
* Metacarpal bases with each other - Ligaments
- Carpometacarpal (Dorsal and palmar)
- Metacarpal (Dorsal and palmar)

16
Q
What is the Metacarpophalangeal Joint?
A
- Ellipsoid
- Flexion-Extension
- Abduction-Adduction
- Articular surface
- Head of metacarpals
- Base of proximal phalanges
- Articular capsule
- Collateral ligamens
- Deep transverse metacarpal ligaments (connection)

17
Q
What is the Interphalangeal Joint?
A
- Hinge Joint
* Flexion-Extension - Articular surfaces
- Head of phalanges
- Base of phalanges
- Articular capsule
* Collateral ligaments



