Upper GI Flashcards
(62 cards)
What drugs is implicated in this condition?

Phenytoin
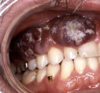
What condition does this patient have?

Diabetes
[Periodontitis]
Identify this condition and mutation associated with it.

Peutz-Jegher syndrome, SKT11 gene mutation
Identify this lesion

Oral Melanoma
What drug is implicated in this condition?

sulphonamides
[Stevens-Johnson syndrome]
Identify this lesion and list its 4 causes?

Target lesions seen in Erythema multiforme
Etiologies:
- HSV
- Drugs
- Carcinoma and Lymphoma
- Collagen Vascular disease
Describe the lesion seen in Erythema multiforme?
Self limited symmetrical lesion, seen especially on the hands. [+/- mucous membrane involved]

What condition does this patient have?

Addison disease

What abnormality might indicate pharyngeal cancer?
Asymmetric tonsils or lingula
Age group associated with this lesion

frquenct in first two decades
Diagnose and describe this lesion

Aphthous Ulcers
- Superficial mucosal ulcer that have a hyperemic base covered by a thin exudate and rimmed by a narrow zone of erythem
- Resolves spontaneously 7-10 days [can recurr]
Epidemiology of this condition

- Unknown etiology, tends to be familial
- affects 40% of population
- frequent in first 2 decades of life
[Aphthous Ulcers]
What conditions are associated with this lesion?

Celiac
IBD
Behcet disease
What are the viral and bacterial causes of this condition?

Bacterial:
- Streptococcus pharyngitis [Group A b-hemolytic streptococcus]
Viral:
- Adenovirus
- Rhinovirus
- Influenza
- Coronavirus
- RSV
What is this lesion? Describe it.

Tonsilitis [Viral]
Swelling and redness
What is this lesion? Describe it

Bacterial tonsilitis
Exudate
How to diagnose this lesion?

Monospot test
[quick screening Gray-white exudative test detects heterophil membrane antibodies caused by the EBV]
List all you know about this condition

- Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)
- Children and young adults
- Classic triad: fever, pharyngitis, lymphadenopathy
What is a complication of this condition?

respiratory failure due to pseudomembrane formation or aspiration
What is the causative organism?

C diphtheria
How to prevent this condition?

Immunization
What is the cause of this condition and how is it spread?

- Cause: Group A β-hemolytic streptococci
- Spread: by inhalation
Describe the presentation of a patient with this condition

- Pharyngitis
- Fever
- Rash
What condition does this patient have?

Scleroderma