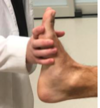
Upper and Lower Extremity Checkoff Specialty Tests Flashcards
Apprehension Test
What does a positive test indicate?
How do you peform this test?
- Patient is seated or supine.
- Shoulder abducted to 90° and elbow flexed to 90°.
- Stabilize shoulder with one hand (blocking linkage) and force arm into external rotation with the other hand.
Positive Test (apprehensive) indicates Glenohumeral Instability

Empty Can Test
What does a positive test indicate?
How do you peform this test?
- Flex patient’s shoulders to 90° while horizontally abducting to 45°.
- Internally rotate both arms so thumbs are pointing down.
- Press down on forearms while patient resists.
Positive test (pain/weakness) indicates Rotator Cuff Pathology (specifically Supraspinatus)

Drop Arm Test
What does a positive test indicate?
How do you peform this test?
- Patient abducts arm to 90°
- Slowly drops arm.
Positive test (arm drop upon tap) indicates full thickness tear of supraspinatus

Painful Arc Test
What does a positive test indicate?
How do you peform this test?
- Patient abducts arm starting at their side toward his head.
Positive Test: Pain is elicited within 60 and 120 degrees of shoulder abduction.
Indicates subacromial impingement and/or rotator cuff injury

Neer Impingement
What does a positive test indicate?
How do you peform this test?
- Stabilize patient’s shoulder.
- With forearm pronated, passively flex shoulder to fully flexed position.
Postive test (pain) indicates **subacromial bursa or rotator cuff impingement**
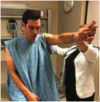
Cross Arm Test
- Physician passively adducts patient’s arm across their chest
- Rest patient’s hand on their opposite shoulder. (+) Test: Pain in AC joint with end range adduction
Positve test (pain) indicates AC joint pathology

Hawkins Test
What does a positive test indicate?
How do you peform this test?
- Flex shoulder to 90° and flex elbow to 90°
- Passively rotate the humerus into internal rotation.This opposes rotator cuff against coracoacromial ligament and acromion.
Positve test (pain) indicates **rotator cuff or subacromial bursa impingement**
Valgus Stress Test (Elbow)
How do you peform this test?
What does a positive test indicate?
- Arm slightly abducted and externally rotated.
- Forearm supinated and flexed to approx. 30º.
Elbow toward body and forearm goes away
Positive test (pain/laxity/tenderness) indicates Sprained Medial (Ulnar) Collateral Ligament
Varus Stress Test (Elbow)
How do you peform this test?
What does a positive test indicate?
- Arm slightly abducted and internally rotated.
- Elbow flexed to approximately 15º.
Elbow away from body and forearm goes toward
Positive test (pain/laxity/tenderness) indicates Sprained Lateral (Radial) Collateral Ligament
Tinel Test
How do you peform this test?
What does a positive test indicate?
- Tap between olecranon and medial epicondyle in ulnar groove
Positive test (tingling sensation in forearm) indicates Ulnar Nerve Entrapment/Cubital Tunnel Syndrome
Medial Epicondylitis
How do you peform this test?
What does a positive test indicate?
- Place eblow in full extension
- Have patient resist wrist flexion
Positive test (pain/tenderness around medial epicondyle) indicates Golfer’s Elbow/Medial Epicondylitis.

Lateral Epicondylitis
How do you peform this test?
What does a positive test indicate?
- Place eblow in full extension
- Have patient resist wrist extension
Positive test (pain/tenderness around lateral epicondyle) indicates Tennis Elbow/Lateral Epicondylitis.
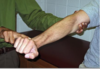
Tinel Sign
How do you peform this test?
What does a positive test indicate?
- Tap over the transverse carpal ligament/flexor retinaculum
Positive test (pain/tingling sensation in lateral side of hand) indicates Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
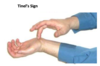
Phalen’s Sign
How do you peform this test?
What does a positive test indicate?
- Place dorsal aspects of patient’s hands together and force into wrist flexion.
- Hold for 60 seconds.
Positive test (paresthesia in lateral side of hand) indicates Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
DeQuervain’s Tenosynovitis
How do you peform this test?
What does a positive test indicate?
Finkelstein Test
- Examiner asks patient to make a fist encompassing their thumb
- Ulnar deviate the wrist.
Positive test (increased pain in lateral wrist) indicates DeQuervain’s Tenosynovitis.
Labral Loading
What compartment is this testing?
How do you peform this test?
What does a positive test indicate?
Central Compartment
- Flex the patient’s knee and hip to 90°
- Load into the femur towards the innominate
Positive Test (pain) indicates Labral or Cartilaginous Pathology
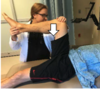
Labral Distraction
What compartment is this testing?
How do you peform this test?
What does a positive test indicate?
Central Compartment
- Flex the patient’s knee and hip to 90°
- Distract femur away from the innominate
Positive Test (distraction of pain) indicates Labral or Cartilaginous Pathology
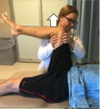
Scour
What compartment is this testing?
How do you peform this test?
What does a positive test indicate?
Central Compartment
- Flex and externally rotate patient’s hip.
- Load into socket and articulate through annular range of motion.
Positive Test (pain) indicates Labral or Articular Cartilage Pathology

Apprehension Faber
What compartment is this testing?
How do you peform this test?
What does a positive test indicate?
Central Compartment
- Patient’s hip is flexed, abducted and externally rotated.
- Physician induces further external rotation by applying a posterior force at the knee.
Positive Test (anterior subluxation of hip or pain) indicates Labral Pathology

Rectus Femoris Test
What compartment is this testing?
How do you peform this test?
What does a positive test indicate?
Peripheral Compartment
- Patient supine.
- One hip is flexed up to the chest.
- The other leg is bent over the edge of the table.
Positive Test (knee flexion <90o) indicates Rectus Femoris Contraction
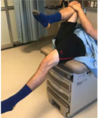
PACE/FAIR Test
What compartment is this testing?
How do you peform this test?
What does a positive test indicate?
Lateral Compartment
- Patient is supine with knees and hips flexed.
- Patient abducts and externally rotates against physician.
Positive Test (pain) indicates Piriformis Pathology

Trochanteric Bursitis
What compartment is this testing?
How do you peform this test?
What does a positive test indicate?
Lateral Compartment
- Patient seated.
- Pressure is applied to greater trochanter.
Positive Test (patient jump) indicates Trochanteric Bursitis

Straight Leg Raise Test
What compartment is this testing?
How do you peform this test?
What does a positive test indicate?
Lateral Compartment
- Patient supine.
- Passively flex patient’s ipsilateral hip with knee extended.
Positive Test (pain over lateral leg at >15o) indicates IT Band contracture
- Positive signs usually occur between 30-60˚ if cause is lumbosacral radiculopathy and/or sciatic neuropathy.
- Positive signs at >70˚ is more likely mechanical low back pain due to muscle strain or joint disease.

Piriformis Test
What compartment is this testing?
How do you peform this test?
What does a positive test indicate?
Lateral Compartment
- Patient supine with hip and knee flexed, one ankle crossed over contralateral knee.
- Patient abducts against resistance.
Positive Test (pain over posterior aspect of greater trochanter) indicates Piriformis Spasm or Pathology

Patrick’s Faber (Lateral Compartment)
How do you peform this test?
What does a positive test indicate?
Lateral Compartment
- Patient’s hip is flexed, abducted and externally rotated.
- Physician braces contralateral ASIS.
- Patient externally rotates/abducts against resistance.
Positive Test (pain) indicates Gluteus Medius Pathology
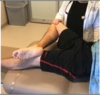
Patrick’s Faber (Anterior Compartment)
How do you peform this test?
What does a positive test indicate?
Anterior Compartment
- Patient’s hip is flexed, abducted and externally rotated.
- Physician braces contralateral ASIS.
- Patient internally rotates/adducts against resistance.
Positive Test (pain) indicates Iliopsoas Insufficiency or Pathology

Thomas Test
What compartment is this testing?
How do you peform this test?
What does a positive test indicate?
Anterior Compartment
- Patient supine and pulls knees to chest.
- One leg is lowered to the table to test the flexibility of the hip flexors.
Positive Test (extended leg raises off table) indicates Hip Flexor Contraction.

Valgus Test (Knee)
How do you peform this test?
What does a positive test indicate?
- Patient supine with the knee flexed to 30°.
- Physician supports the lower leg with one and other hand placed on the lateral aspect of the patient’s knee.
- Apply a medial force to the proximal tibia while abducting the lower leg.
- This test is done at 30° flexion and neutral.
- Knee toward body and leg goes away*
Positive Test (increased laxity/pain) indicates Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) Disruption.

Varus Test (Knee)
How do you peform this test?
What does a positive test indicate?
- Patient supine with the knee flexed to 30°.
- Physician supports the lower leg with one and other hand placed on the medial aspect of the patient’s knee.
- Apply a lateral force to the proximal tibia while adducting the lower leg.
- This test is done at 30° flexion and neutral.
- Knee away from body and leg goes toward*
Positive Test (increased laxity/pain) indicates Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL) Disruption.

Anterior Drawer Test
How do you peform this test?
What does a positive test indicate?
- Patient supine with knee flexed to 90°.
- Examiner sits on the patient’s foot
- Examiner grasps the proximal tibia with both hands, pulling the tibia anteriorly.
Positive Test (excessive translation) indicates ACL Insufficiency.
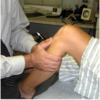
Lachman’s Test
How do you peform this test?
What does a positive test indicate?
- Patient supine.
- Examiner places cephalad hand on the distal thigh, superior to patella.
- Caudad hand grasps the proximal tibia.
- Flexing the knee to 10-30°, the examiner uses his caudad
hand to pull the tibia anteriorly while the cephalad hand
stabilizes the thigh.
Positive Test (increased laxity) indicates ACL Insufficiency.
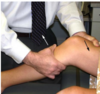
Posterior Drawer Test
How do you peform this test?
What does a positive test indicate?
- Patient supine with knee flexed to 90°.
- Examiner sits on the patient’s foot.
- Examiner grasps the proximal tibia with both hands, pulling the tibia posteriorly.
Positive Test (excessive translation) indicates PCL Insufficiency.
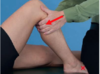
McMurray’s Test
How do you peform this test?
What does a positive test indicate?
- Patient supine with knee flexed to 90°.
- Examiner uses caudad hand to control the ankle and cephalad hand placed on distal femur.
-
Lateral Meniscus: Examiner rotates the tibia into
internal rotation and applies a varus stress, then
continues the leg into extension -
Medial Meniscus: Examiner rotates the tibia into
external rotation and applies a valgus stress, then
continues the leg into extension
Positive Test (pain) indicates Medial or Lateral Meniscus Tear.

Apley’s Grind Test: Compression
How do you peform this test?
What does a positive test indicate?
- Patient prone with knee flexed to 90°.
- Examiner uses downward force on the foot to provide a compressive force on the meniscus, while rotating the foot internally and externally.
Positive Test (pain) indicates possible meniscal injury, collateral ligament injury, or both.

Apley’s Grind Test: Distraction
How do you peform this test?
What does a positive test indicate?
- Patient prone with knee flexed to 90°.
- Examiner stabilizes the thigh, then applies upward traction to the leg while rotating it.
Positive Test (pain) indicates collateral ligament injury.
Positive Test (relief of pain) indicates possible meniscal injury.
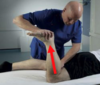
Patella-Femoral Grinding Test
How do you peform this test?
What does a positive test indicate?
- Compress patella caudally into trochlear groove
- Instruct patient to tighten quadriceps against resistance
Positive Test (pain) indicates roughness of articulating surfaces
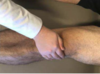
Anterior Drawer Test (Ankle)
How do you peform this test?
What does a positive test indicate?
- Grasp posterior calcaneus with one hand and distal tibia/fibula with the other hand.
- Monitor anteriorly at the anterior talus.
- Provide anterior force on calcaneus while stabilizing the distal tibia/fibula.
- Normal springing of calcaneus back to neutral should occur.
Positive test (pain) indicates ATF ligament pathology/tear (lateral ankle sprain)
ATF = Always tears first

Talar Tilt Test
How do you peform this test?
What does a positive test indicate?
- Grasp distal tibia/fibula with one hand and inferior calcaneus with the other, blocking motion of the calcaneus on the talus.
- Invert the talus to evaluate ROM.
Positive test (laxity/pain) indicates Calcaneofibular ligament pathology/tear, also tests some ATF (lateral ankle sprain)
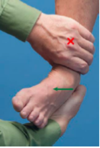
Eversion Test
How do you peform this test?
What does a positive test indicate?
- Grasp distal tibia/fibula with one hand and plantar surface of the mid-foot with the other hand.
- Evert the talus to evaluate ROM.
Positive test (laxity/pain) indicates Deltoid ligament pathology (medial ankle sprain)

Thompson Test
How do you peform this test?
What does a positive test indicate?
- Patient prone with foot off the table.
- Squeeze the patient’s calf.
- Observe for plantarflexion.
Positive test (absence of plantar flexion) indicates Achilles Tendon Rupture.
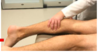
Squeeze Test
How do you peform this test?
What does a positive test indicate?
- Wrap hands around leg proximal to the ankle, contacting distal tibia/fibula with both thenar eminences.
- Squeeze for 2-3 seconds, then rapidly release.
Positive test (pain) indicates Syndesmosis pathology (high ankle sprain)
Homan’s Sign
How do you peform this test?
What does a positive test indicate?
- Patient laying or seating with knee extended.
- Dorsiflex the patient’s foot.
- Can apply lateral compression to calf.
Positive test (pain with dorsiflexion) indicates DVT or thrombophlebitis.
Not always a good idea to peform this test incase of embolus.