unit 5 drugs Flashcards
(28 cards)
what is donepezil
acetylcholinesterase inhibtor used to treat AD
- easily enters the CNS and inhibts breakdown of acetylcholine
- effective tratment for mild to moderae AD when sufficient cholinergic neruons are still present
side effects: mainly autonomic and similar to AChE inhibitors
drugs to treat parkinsons
depamine agonists: levodopa and repinrole
monoamine oxidase inhibitors: selegiline and deprenyl
antimuscarinic drugs: benztropine
what is Haloperidol
one of the most widely used typical antipsychotics from the butyrophenone class of drugs.
D2 > α1 > D4 > 5HT2A > D1 > H1
what is olanzapine
example of a second generation (atypical) drug which can be used for psychosis.
5-HT2A antagonist > D2 antagonist
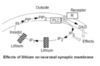
what is lithium
- small monovalent cation effective against the mainic phase of bipolar disorder
- can inc serotonin neutrotransmission and dec NE and dopamine neurotransmission
- causes decrease in precurors for IP3 and DAG synthesis - dec IP3 and DAG when receptors linked to these secondary messangers are activated like muscarinic, α1 and 5-HT2A receptors.
what is imipramine
- Tricyclic antidepressants- heterocyclic compounds (name based on their 3 ringed structure)
- inhibit reuptake of norepinephrine and serotonin - elevate the conc of them
- effective in more than 70% of patients but are not used as first lines of treatment due to side effects and drug-drug interactsions
ex: Imipramine
adverse effects of imipramine
- block caridac sodium channels (simialr to antiarrhythmic quinidine)
- antagonist muscarinic, histaminic (H1) and α1 receptors: potent antihistamines, anticholinergics and vasodilators (dont want that)
what is fluoxetine
brand name = prozac
- SSRI used to treat depression, panic disorder, anxiety, obsessive compulsive disorder and bulimia
- less side effects then tricyclics like imipramine but can cause insomnia and sexual dysfunction
* dec reuptake of serotonin
- also inc sucide rate in youth so dont give to youth
what is phenelzine
non-selective and irreversible MAOI
*most widely used MAOI for the treatment of depression
- decreases metabolism of morepinephrine, dopamine and serotonin
what is bupropion
- antidepressent
- mechanisms of poorly understoof but modest inhibitor of re-uptake and stimulates release of dopamine and norepinephrine
- does not block histaminic, adrenergic or muscarinic receptors but still increases dopamine levels (do not use in patietns with psychosis)
*like SSRIs it inhibits CYP2D6 so do not take with other drugs metabolised by that enzyme
what is diazepam
- increases GABAA receptor activation
- enhances the effect of GABA causing a sedative hypnotic (sleep inducing) and anxiolytic (anti-anxiety) effects
what is phenobarbital
barbituarate
- drugs that act to depress the CNS producing a wide spectrum of effects from mild-sedation to total anesthesia
- have sedative, hypnotic and anxiolytic activity and also nehance GABA neurotransmission
describe ethanol
- same effects as sedative hypnotics
- effects are dose-dependent and cause CNS depressino via decreased memrbane excitability and increased GABAA and decrease NMDA receptor activation
- other effects include:diuresis, decreased myocardial contractility, slurred speech, and impaired judgment.
prescription of clonidine
help with autonomic symptoms of withdrawal and low-dose benzodiazepines can be used to treat ethanol withdrawal
*MOA of clonidine described in autonomic and cardiovasuclar pharmacology sections
What is the main excitatory neurotransmitter?
What receptor does it act on?
Mechanism of action?
What decreases the release
what decreases receptor activation
- Glutamate acts on NMDA receptors
- inc Ca, Na conductance and dec K of the ion channel
- Morphine, heroin and THC DEC the release of glutamate
PCP and ethanol DEC activation of the receptor
What is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter?
What receptor does it act on?
Mechanism of action?
What decreases the release?
what ____ receptor activation
- GABA acts on GABAA and GABAB receptors
- GABAA = ion channel, GABA inc Cl conductance
GABAB = G protein, GABA inc K conductance
- THC, morphine and heroin decrease release of GABA
- Diazepam, phenobarbital and ethanol inc GABA activation
What receptors does acetylcholine act on? what is the mechanism of action at these receptors?
What is an indirect agonist of acetyl choline?
what is a ntagonist of acetylcholine?
Acts on:
M1,M3 and M5 G protein receptors: Inc IP3, DAG and dec K+ conductance (excitatory)
M2, M4 G proteins: dec cAMP (inhibitory)
N ion channel: inc Na+ and K+ conductance
Indirect agonsits: donepezil
Antagonist: benztropine
*alzheimers is los of cholinergic projection neurons
What receptors does NE act on and what is the mechanism of action?
What increases the release of NE?
What decreases the release of NE?
What decreases the reuptake?
what decreases the metabolism?
α1 G protein receptor: inc IP3, DAG and dec K+ conductance
α2 G protein: dec cAMP (inhibitory)
β1 G protein: Inc cAMP
Inc release = amphetamine and tyramine
dec release = morphine and heroin
dec reuptake: imipramine and cocaine
dec metabolism: phenelzine
what receptors does dopamine act on and the mechanism of action?
What increases the synthesis?
what inc release?
what decreases reuptake?
what decreases metabolism?
what is an agonist?
What is an antagonist?
Acts on pre and post synaptic D2 g protein receptors
Presynaptic: dec Ca2+ conductance
postsynaptic: inc K+ conductance
inc synthesis = L-DOPA
inc release = amphetamine
dec reuptake = cocaine
dec metabolism = phenelzine and selegiline
D2 agonist = ropinirole
D2 antagonist = haloperidol and olanzapinethe
*parkinsons is loss of nigro-striatal dopamine projection neuron
*excess dopamine neurotransmission in limbic system linked to psychosis/schizophrenia
describe the receptors serotonin acts on and the mechanism of action
what increases release?
what decreases reuptake?
what decreases metabolism?
Partial agonists?
Antagonists?
5HT1A G protein receptor: dec cAMP and inc K+ conductance
5HT2A G protein: Inc IP3 and DAG and dec K+ conductance
Inc release = amphetamine
dec reuptake = imipramine, fluoxetine and cocaine
dec metabolism = phenelzine
5HT2A partial agonist: LSD
5HT2A antagonist = haloperidol and olanzapine
**reduced monoamine neurotransmission is linked to depression
agonist and antagonists to opioid receptor
mu receptor
agonist = heroin, morphine and methadone
antagonist = naloxone
what binds to cannabinoid receptor
= CB1 binds THC
what are the 2 receptors olanzapine attacks? which is preferred?
5-HT2A > D2


