Clinical applications of Pharmacokinetics Flashcards
(22 cards)
what is MEC
Minimum effective concentration
therapeutic requirements often _____ duration ____ the MEC
therapeutic requirements often exceed the duration above the MEC following a single dose
- prolonging the duraction above MEC by increasing the dose may produce a peak conc that is not desirable and toxic
- prolonged efficiacy thus usually achieved by administering multple small doses
try to make sure the drug concentration remains between ______
- MEC of advrese effect and MEC of desired effect
what is the most important pharmacokinetic parameter, what is it used for and how is it expressed
- drug clearance
- gives indication of efficiency of elimination of a drug from plasma
- used clinically to calculate the dosing rate and maintenace doses to maintain target drug conc
- expressed in units of volume/time
how is dosing rate calculated
Dosing rate (DR) = Clearance (CL) x Target Drug Concentration (TC)

- there is a peak effect that occurs after onset of effect is observed
- minimum effective conc for adverse and desired effects need to be considered when determining dose
- drugs should be administered within therapeutic window to create desired effect
what limits the rate of drug metabolism and excretion?
blood flow to target organ
most drugs follow a _____ kinetics meaning ____
- follow first order kinetics
- constant fraction of the drug is eliminated per unit time
Half-life can be used to describe elimination (defined by time to eliminate serum drug conc by 50%)
*half life is independent of serum drug concentraton
After 1 half-life, 50% of original dose is eliminated; after 2 half-lives, 75% of original dose is eliminated; after 3 half-lives, 87.5% of original dose is eliminated and after 4 half-lives, 93.75% of original dose is eliminated.

how is half-life calculated
Half-life = Ln2/k (k is elimination constant)
what are the 3 categories of drug concentrations from a clinical perspective?
- subtherapeutic, therapeutic and toxic ranges
- goal of most drug-drug regimens is to maintain the drug at concentrations within the therapeutic range

the first several doses of a drug are typically _____
- subtherapeutic
- occurs as the drug equilibrates to its steady state concentrations (approx 4 elimination half lives)
- Appropriate drug dosing and dosing frequency result in steady-state drug levels that are therapeutic, and the maximal and minimal concentrations of the drug remain within the therapeutic window

describe

- if the initial (loading) dose is larger than the maintenance dose the drug reaches therapeutic concentrations more rapidly
how is the magnitude of the loading dose determined?
- by the volume of distriubtion of the drug
describe

excessive maintenance doses or dosing frequency result in drug accumulation and toxicity
describe
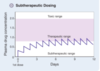
insufficient maintenance doses or dosing frequency results in subtherapeutic steady-state drug concentrations.
what does therapeutic dosing seek
- maintain the highest plasma drug concentration that is below the toxic concentration while maintaining a dose that is also above the minimally effective concentration
*drug conc divided itno subtherapeutic, therapeutic and toxic
what is steady state
- occurs when the amont of drug administered is equal to the amount of drug eliminated in the same time period
- it is affected by drug bioavailability, clearance, dose and dosing interval
The time taken to achieve steady-state does not depend on the rate at which the drug is administered
*when it comes to chronic dosing, the steady-state of plasma drug concentration (Css) is directly proportional to the rate of drug administration

how does drug administration relate to steady state when drug dosing is chronic
the steady-state of plasma drug concentration (Css) is directly proportional to the rate of drug administration.
If the rate of administration is doubled, the steady-state of plasma drug concentration is also doubled
what occurs upon administration of the drug
- plasma conc initially inc
- drug then distributes from blood to body tissues causing plasma conc to dec
- if drug dosage does not acount for Vd then therapetc range will not be reached
what is the purpose of the laoding dose, how is it calculated
- compensates for drug distribution to tissues
- dose is administered at higher dose then subsequent doses
Doseloading = Vd x Css
- once steady-state drug concentratiosn are achieved
what is a maintenace dose, how is it calculated
- dose needed to replace that lose through metabolism and excreation
- dependent on drug clearance
Dosemaintenance = Clearance x Css
*Css = steady state conc


