Unit 05: Physchosis and mood Flashcards
(31 cards)
what is psychosis
- severe disturbances in brain function in which normal perceptions in environment are disrupted or dissociated (loss of contact with reality)
- auditory and visual hallucinations, suspicion, paranoia, attachment of excessive personal significance to daily events
*etiology (cause or origin) not known
what causes drug induced psychosis
long term cocaine or amphetamine use
- affects dopamine neurotransmission and can lead to paranoia
- supports role of dopamine (DA) imbalance in psychosis
- hallucinogens such as PCP (NMDA receptor antagonist) and LSD (5-HT2A partial antagonist) can also induce hallucinations, paranoia and panic
- supports roles of glutamate and serotonin inbalance in psychosis
*glutamate and serotonin are linked with DA neurotramission in cortex and limbic system
what is schizophrenia
- mental disorder charcaterized by breakdown of thought processes and lack of typical emotions
- symptoms are described in terms of positive (initial) and negative (later in the disease)
- positive = those that an individual does not normally experience but are present in those with schizophrenia (hallucinations and paranoia)
- negative = discrepancies of the thought process and emotional responses like apathy, social withdrawal and extreme inattentiveness
how are intitial symptoms of schizophrenia treated
- antipsychotic drugs
- individuals diagnosed later in disease are not easily treatable
- many individuals with schizophrenia progress from more positive to more negative symptoms some will expereince both simultaneously
ie: hear voices while being socially withdrawn
what is the dopamine hypothesis
model that attributes psychosis to cahnges in dopamine function in the brain
- evidence for dopamine hypothesis comes from observations such as fact that anti-psychotic drugs block dopamine D2 receptors
-
drugs that increase dopamine activity _____
aggrevate or produce psychosis
- increase in dopamine receptor density has been reported in shcizophrenic patients and patients that were successfully treated for the disoder had dereased dopamine metabolits in their bodies
what are the 3 main dopamine pathways
- nigrostriatal - associated with movement
- cortical
- limbic - associated with behaviour
*high dopamine in limbic system has been linked with positive symptoms of psychosis while low dopamine in cortex has been linekd with negative symptoms
what are antipsychotic drugs
also called neuroleptics
- believed to decrease psychotic symptoms by decreasing dopamine synpatic activity in the limbic pathway
- binding affintiy of drug with D2 receptors correlates with its clinical potency as an antipsychotic agent
describe activation bc blocking D2 receptors
D2 receptors are G protein linked
- activation has inhibitory effects on cAMP
- blocking of D2 receptors in cortex would enhance negative symptoms of psychosis
- newer drugs have been designed to block both 5-HT2A and D2 receptors in order to normalize dopamine activity in limbin system
what are the structural categories of commonly used first generation antipsychotics
- phenothiazines, thiozanthenes and hutyrophenones
- Haloperidol is one of the most widely used typical antipsychotics from the butyrophenone class of drugs
Olanzapine is an example of a second generation (atypical) drug which can be used for psychosis.
receptor affinity Haloperidol
D2 > α1 > D4 > 5HT2A > D1 > H1
receptor affinity of Olanzapine
5HT2A > H1 > D4 > D2 > α1 > D1 (note, H1 is histamine receptor). Olanzapine is also an antagonist at muscarinic receptors.
what is believed to be the cause of difference in clincial effectiveness of antipsychotic drugs
- due to difference in affinity for D2 and 5-HT2A receptors
- antagonism at other receptors results in some adverse effects of antipsychotics
why is there often a dely in clinical effects of antipsychotics
- few theories support the delat in clincial effects
- blockage of D2 receptor alone does not explain the antipsychotic action of the drugs
- second has to do with location of D2 receptors both pre- and post synpatically
- activation of D2 receptors results in inhibitiroy response (dec cAMP) so an initial presynpatic receptor blockade by drug like haloperidol would prevent this inhibitory effect and cause an inc in dopamine release
*would inc amount of dopamine available to compete with haloperidol at postsynpatic receptor
*Research studies have shown that tolerance to presynaptic blockade develops over time, making post-synaptic blockade more effective.
treatment of negative symptoms
- negative symptoms are not efectively treated with classical antipsychotics - sometimes negative symptoms are a side effect of treatment
- hypothesis = negative symptoms are associated with dopamine hypofunction in cortex, newer drugs may be more effective due to differences in pharmacodynamic profile and the interaction between dopamine and serotonin in CNS
haloperidol and effect on dopamine transmission
* haloperidol has a higher affinity for blocking the D2 receptor compared to 5HT2A receptor
- animal studies measured dopamine transmission in presence of haloperidol found to be normal in limbin system but low in cortex
olanzapine effect on dopamine neurotransmission
Olanzapine preferentially blocks the 5HT2A receptor over the D2 receptor
- dopamine neurotransmission is found to be noral in both limbic and cortex
what is PCP and what can it do
- NMDA receptor antagonist that can induce psychosis
- is based on the glutamate hypothesis of psychosis which states tha NMDA antagonists increase DA neurotransmission in the limbic system
*explains how drugs like PCP would induce psychosis
*there is an inc number of PCP bidnign sites in cortex of schizophrenics which suggets that glutamate hypofunction in cortex is associated with negative symptoms
what types of drugs to treat psychosis are currently being investigated?
- newer drugs that increase NMDA receptor activation are under investigation as potential schizophrenia treatments
- drugs that increase glycine levels or bidn to glycine modulatory sites of NMDA receptor are also under investigation
describe the structure of ionitropic glutamate receptors
* picture A
- all 3 ionotrpic glutamate receptors are tetrameric complexes composed of the same (termed homomeric) or different (termed heteromeric) subunits
- structure on right shows one ionotropic glutamate receptor subunit which spans membrane 3 times and has a partially spanning hairpin turn that when juxtaposed w/ homologous turns from the other 3 subunits forms the lining of the ion channels pore
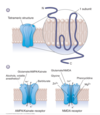
describe major binding sites on AMPA/kainate and NMDA classes of ionotropic glutamate receptors
picture B
- there is indirect evidence for the location of many of the drug binding sites that are schematically indicated in this diagram, the definitive localization of these sites remains to be determined.

describe the adverse effects of antipsychotics
- assocaited with a wide range of adverse effects
- in CNS - parkinson-like symptoms can occur as a result of D2 receptor blockade and sedation from H1 receptor blockade
- autonomic efects can occur like hypotension from α1-receptor blockade
adverse effect specific to olanzapine
Olanzapine also blocks muscarinic receptors; therefore atropine-like side-effects might result
- parkinson like extrapyramidal adverse effects
H1 blockade causing sedation
nonspecific blockage of muscarinic alpha receptors (lower bp)





