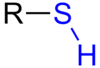Unit 3 - Chemistry for Biology Flashcards
What is the structure of DNA?
What are the 4 nucleic acids in DNA?
The four nucleic acids in DNA are Adenine, Guanine, Thymine, and Cytosine.
These names represent the different nitrogenous inside the DNA strand. The backbone of the strand is made from the sugar and phosphate part of the nucleic acids.

What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fats?
Saturated fats contain only alkyl carbons, while unsaturated fats also have double bonds.

What is the name of this bond present in the fatty
acid - glycerol link?

Ester bond.
[R-C=O-O-R]
What are the monomer and polymer for the protein?
Monomer: Amino Acid
Polymer: Polypeptide
What are the 6 properties of water?
Adhesion, cohesion, high specific heat, high heat of vaporization, lower density of ice, solubility.
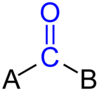
What is the Carbonyl group?
[R-C=O-R’]
Contrary to a ketone group, the R’ does not have to be a carbon based group.

Draw the structures of glucose, fructose, galactose.

What is cohesion, what is one benefit of water’s cohesion to life?
Water’s cohesion is caused by the ability for water molecules to attract one another. This allows for certain insects to walk on water.
What is high specific heat, what is one benefit of water’s high specific heat to life?
Hydrogen bonds take a lot of energy to break, and release a lot of energy when formed. This causes the high specific heat of water, which allows water to stabilize the temperature of organisms.
Identify this compound: [R-OH]
Hydroxil group
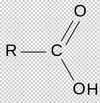
Identify this compound:

Carboxyl group
What is high heat of vaporization, what is one benefit of water’s high heat of vaporization to life?
Because of hydrogen bonding, it takes a lot of energy to convert liquid water into gas. This means that water’s evaporation has a cooling effect. One example is when we sweat.
What are the types of proteins?
Enzymes (lactase),
Transport(hemoglobin),
Structure (keratin),
Movement (actin),
Regulation (insulin),
Storage (albumin),
Cell Identity (Antibodies)
What is the bond between simple sugars?
Glycosidic bond
Which is the only macromolecule to not make polymers?
Lipids
How are proteins made from amino acids?
Amino acids are bonded together with peptide bonds by the ribosomes. When a polypeptide (multiple peptide bonds) chain is folded correctly, it becomes functional.

What is the structure of RNA and what are the 4 bases involved?
The four bases of RNA are Adenine, Guamine, Cytosine, and Uracil.
RNA’s backbone is made form the phosphate and sugar of the nucleic acids.
RNA is most often a single strand.
The four bases are adenine, uracil, guamine, and cytosine.
A&U bond together.
C&G bond together.
They bond through hydrogen bonding.
What are the types of nucleic acids? (3)
Gene: DNA
Gene expression: RNA
Energy transfer: ATP
What is the difference between a ribose and a deoxyribose?
Deoxyribose: DNA
Ribose: RNA
The difference between the two is the group placed on bottom left Carbon of the sugar.

By what type of reaction are polypeptides made?
Dehydration synthesis.
This occurs when water is formed as the amino acids link.
The bonds created are called peptide bonds.

What is the carboxyl group?
Also named carboxylic acid:
[R-C=O-OH]