Travel Related Infection Flashcards
Modern Tropical Medicine - lots of different diseases from a variety of _________
destinations
what are some unfamiliar features of imported diseases that people may experience?
- Presenting features
- Isolation requirements
- Diagnostic methods - Blood film for malaria
- Treatment/Management
- Unexpected complications - Bleeding, coma, shock, seizures
What increases vulnerability of travelers to infection?
- Temptation to take risks away from home - food, water, animals, sex
- Different epidemiology of some diseases - HIV, TB, polio, diphtheria
- Incomplete understanding of health hazards
- Stress of travel
- Refugees: deprivation, malnutrition, disease, injury
Some infections are common worldwide such as what?
- influenza
- community-acquired pneumonia
- meningococcal disease
- sexually transmitted diseases
Infections Controllable by Public Health measures include what? - Sanitation
Travelers’ diarrhoea
Typhoid
Hepatitis A or E
Giardiasis
Amoebiasis
Helminth infections
Viral gastroenteritis
Food poisoning
Shigella dysentery
Cholera
Cryptosporidiosis
Infections Controllable by Public Health measures include what? - Immunization
Poliomyelitis
Diphtheria
Infections Controllable by Public Health measures include what? - Education
HIV
STD’s
what are examples of Water-related infections? (drinnking and swimming)
- Schistosomiasis
- Leptospirosis
- Liver flukes
- Strongyloidiasis
- Hookworms
- Guinea worms
what are exmples of Arthropod-borne infections?
- Malaria (mosquitos)
- Dengue fever (mosquitos)
- Rickettsial infections (ticks: typhus)
- Leishmaniasis (sand flies: Kala-azar)
- Trypanosomiasis (tsetse fly: sleeping sickness)
- Filariasis (mosquitoes: elephantiasis)
- Onchocerciasis (black flies: River Blindness)
what are some Emerging Infectious Diseases?
- Zika: Latin America, Caribbean
- Ebola virus disease: West Africa
- MERS-CoV: Middle East
- Swine ‘flu (H1N1): worldwide
- Avian ‘flu (H5N1 and H7N9): China
- SARS: Far East, worldwide
- West Nile Virus: USA
- …etc.
what are some Important Tropical Diseases?
- Malaria
- Typhoid
- Dengue Fever
- Schistosomiasis
- Rickettsiosis
- Viral haemorrhagic fevers
- Zika fever
what is malaria?
Parasitic infection of the red blood cells of the human
what is the Epidemiology of malaria?
- Most important imported disease
- United Kingdom (HPA, 2015)
- 1400 cases/year
- 6 deaths/year
•Worldwide (WHO, 2012)
- 207 million cases/year
- 627,000 deaths/year
Disease of the tropics

what is the Malaria vector?
female Anopheles mosquito
what is the life cycle of malaria?
Injects sporozoites as it is taking a blood meal - they are premature forms of the parasite, migrate to liver and invade the liver cells and they replicate and then enter into the circulation, red blood cells
Female mosquito takes blood meal and the gametocytes fuse to form zygote and then the mosquito gets more sporozoites
Many drugs work in the different stages of this
7 days for this to happen

what are the 5 species of malaria and their severities?
Plasmodium falciparum - Potentially severe
“benign”:
- Plasmodium vivax
- Plasmodium ovale
- Plasmodium malariae
- Plasmodium knowlesi (like P malariae; Far East, 2004)
what are the symptoms of malaria?
Often vague and unspecific symptoms
Symptoms common to many infections
Often people think its influenza
- fever
- rigors
- aching bones
- abdo pain
- headache
- dysuria
- frequency
- sore throat
- cough
what are the signs of malaria?
- none
- splenomegaly
- hepatomegaly
- mild jaundice
what are some complications of malaria?
- Cerebral malaria (encephalopathy) - non- immune visitors, children in endemic areas hypoglycaemia, convulsions, hypoxia
- Blackwater fever - severe intravascular haemolysis, high parasitaemia, profound anaemia, haemoglobinuria, acute renal failure
- Pulmonary oedema
- Jaundice
- Severe anaemia
- Algid malaria - Gram-negative septicaemia
how is a diagnosis of malaria made?
- Thick & thin blood films - Giemsa, Field’s stain
- Quantitative buffy coat (QBC) - centrifugation, UV microscopy
- Rapid antigen tests - OptiMal, ParaSight-F
Diagnosis based on clinical suspension if a person has come back from a at risk area
(purple dots are malaria parasites)

Quantitative Buffy Coat (QBC) Test
Quantitative buffy coat (QBC) is a laboratory test to detect infection with malaria or other blood parasites

what is a blood film?
a thin layer of blood smeared on a glass microscope slide and then stained in such a way as to allow the various blood cells to be examined microscopically
Severity assessment:
Complicated malaria = one or more of…
- Impaired consciousness or seizures
- Hypoglycaemia
- Parasite count >=2%
- Haemoglobin <= 8mg/dL
- Spontaneous bleeding / DIC
- Haemoglobinuria
- Renal impairment or pH <7.3
- Pulmonary oedema or ARDS
- Shock (algid malaria) - ?Gram negative bacteraemia
what are the Treatment options for
uncomplicated P. falciparum malaria?
- Riamet ® (artemether-lumefantrine) 3 days
- Eurartesim ® (dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine) 3 days
- Malarone ® (atovaquone-proguanil) 3 days
- Quinine 7 days - S/E nausea, tinnitus, deafness (cinchonism), rash, hypoglycaemia - plus oral doxycycline (or clindamycin)
what are the Treatment options for
complicated or severe P. falciparum malaria?
- IV artesunate (unlicensed in UK)
- IV quinine (S/E cardiac depression, cerebral irritation, N&V) plus oral doxycycline (or clindamycin)
When patient is stable & able to swallow, switch to oral treatments
what is the Treatment of
P. vivax, P. ovale, P. malariae, P. knowlesi?
(treatment for the other types of malaria)
- chloroquine 3 days
- Riamet ® (artemether-lumefantrine) 3 days
•add primaquine* (14 days) in vivax and ovale, to eradicate liver hypnozoites
*check for G6PD deficiency
what are some malaria control programmes?
- Mosquito breeding sites - Drainage of standing water
- Larvacides - (Paris green), temphos, biological
- Mosquito killing sprays - DDT, malathion, (dieldrin)
- Human behaviour - Bed nets, Mesh windows
Typhoid (Enteric) Fever is caused by what?
- Salmonella typhi
- Salmonella paratyphi
- Global cases: 27 million infections/yr
- Global deaths: over 200,000/yr
UK cases: 500/yr
Type of salmonella fever
Mainly developing world
poor sanitation, unclean drinking water
what are the clinical feature sof typhoid fever?
- Incubation period: 7 days - 4 week
- 1st week: fever, headache, abdo. discomfort, constipation, dry cough, relative bradycardia, neutrophilia, confusion
- 2nd week: fever peaks at 7-10 days, Rose spots, diarrhoea begins, tachycardia, neutropenia
- 3rd week (Complications): intestinal bleeding, perforation, peritonism, metastatic infections
- week 4 (Recovery): 10 - 15% relapse
how is the diagnosis of typhoid fever made?
- Clinical - not easy, evolution of features
- Laboratory (Salmonella typhi, S. paratyphi):
Culture blood, urine & stool
Culture bone marrow
what is the treatment of typhooid fever?
- Oral Azithromycin - now drug of choice for Asian-acquired, uncomplicated enteric fever
- IV Ceftriaxone - if complicated, or concerned regarding absorption
- Increasing ciprofloxacin resistance
what is Dengue?
- Commonest human arbovirus infection
- Dengue infection: 100 million cases/year
- Dengue Deaths: 25,000/year
Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne tropical disease caused by the dengue virus. Symptoms typically begin three to fourteen days after infection. These may include a high fever, headache, vomiting, muscle and joint pains, and a characteristic skin rash. Recovery generally takes two to seven days
what is the Transmission of Dengue?
Tiger mosquito
Day time biting mosquito
Likes little pools of water
Lives near humans
what are the features of Classical Dengue Fever
- Sudden fever
- Severe headache, retro-orbital pain
- Severe myalgia and arthralgia
- Macular/maculopapular rash
- Haemorrhagic signs: petechiae, purpura, positive tourniquet test
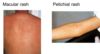
How is a Dengue Diagnosis made?
• Clinical:
- Thrombocytopenia
- Leucopenia
- Elevated transaminases
- Positive tourniquet test (a clinical diagnostic method to determine a patient’s haemorrhagic tendency. It assesses fragility of capillary walls and is used to identify thrombocytopenia)
• Laboratory: PCR, serology
what is the management of dengue?
- No specific therapeutic agents
- Complications
- Dengue haemorrhagic fever (DHF)
- Dengue shock syndrome (DSS)
- Rx: IV fluids, fresh frozen plasma, platelets
•Prevention - avoid bites and new vaccine (Dengvaxia), 2016; limited use
Schistosomiasis is from what?
fresh water and freshwater snails
what are the types of distribution of schistosomiasis?
- S. haematobium
- S. mansoni
- S. japonicum

what is the Schistosomiasis life cycle?
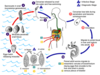
what are the clinical feature sof schistosomiasis?
- Swimmers Itch (1st few hrs) - clears 24-48hrs
- Invasive stage (after 24hrs) - cough, abdo discomfort, splenomegaly, eosinophilia
- Katayama Fever (after 15-20 days) - prostrate, fever, urticaria, lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly, diarrhoea, eosinophilia
- Acute disease (6-8 weeks) - eggs deposited in bowel (dysentery) or bladder (haematuria)
- Chronic disease
how is the diagnosis of schistosomiasis made?
Clinical diagnosis
Antibody tests
Ova in stools and urine
Rectal snip
what is the treatment of shcistosomiasis?
PRAZIQUANTEL 20mg/kg, two doses 6hrs apart
Prednisolone if severe
what does Rickettsiosis cause?
- Tick typhus (commonest imported to UK) - from Southern Africa, Mediterranean, Arabian Gulf
- Clinical features - abrupt onset swinging fever, headache, confusion, endovasculitis, rash (macular, petechial), bleeding
what is the diagnosis and management of Rickettsiosis?
- Diagnosis: clinical features, serology
- Management: tetracycline
Viral Haemorrhagic Fevers - Serious infections but rare in UK, what are some examples?
Ebola
Congo-Crimea haemorrhagic fever
Lassa fever
Marburg disease
how are viral haemorrhagic fevers delt wirh?
- Maximum incubation period 3 weeks
- Rule out common severe infections
- Isolation: High Security Infection Unit
- Treatment: supportive!
what is the zika virus
- flavivirus
- Transmitted by daytime-biting Aedes mosquitos
- Also by sexual contact, blood transfusion
- Related to dengue, yellow fever, Jap B encephalitis and West Nile viruses
- Pacific outbreak 2013-14
- Latin America pandemic 2015-16
what are the clinical feature sof zika virus?
- Clinical: no or mild symptoms - headache, rash, fever, malaise, conjunctivitis, joint pains (like dengue)
- In pregnancy, can cause microcephaly and other neurological problems
- Can cause Guillain-Barre syndrome
what is the management of zika virus?
- No antiviral therapy
- Mosquito control measures
- Vaccines in development
what are Covid 19 symptoms?
- Fever, dru cough and tiredness
- Aches and pains, nasal congestion, headache, conjunctivitis, sore throat, diarrhoea, loss of taste or smell, rash, discoloration of fingers/toes
- Symptoms usually mild and begin gradually
what are Risk factors of covid 19?
- Most (80%) recover without needing hospital treatment
- Around 1 out of every 5 people become seriously ill and develops difficulty breathing
- Older people, and those with medical problems like high blood pressure, heart and lung problems, diabetes, or cancer, are at higher risk of serious illness
- Anyone can become seriously ill with COVID
what is the management of covid 19?
- IPC/PPE
- Supportive
- No proven RX (trials)
- Preventing the spread of the virus
what should be asked in a history of a fever in the returning traveller?
- Is it tropical?
- Travel history - Is it travel related?
- Precautions taken
- Risks - e.g. swimming in fresh water
- Symptoms
- Incubation periods
Approach to fever in the returning traveller - what are some examination signs?
- rash - typhoid, typhus, dengue
- jaundice - hepatitis, malaria, Yellow fever
- lymph nodes - leishmania, trypanosomiasis
- liver - malaria, typhoid, amoebic abscess
- spleen - visceral leishmaniasis, typhoid, malaria
Approach to fever in the returning traveller - what are some investigations?
Normal tests as well as specific ones for specific conditions that you think they have
General:
- FBC
- malaria films
- liver function tests
- stool microscopy & culture
- urine analysis & culture
- blood culture(s)
- CXR
Specific tests (as indicated):
dengue
respiratory viral/atypical
hepatitis A, B, C
tick typhus (Rickettsia)
schistosomiasis
amoebic
leptospirosis/hantavirus
viral haemorrhagic fevers
Approach to fever in the returning traveller - what treatment is required?
- Isolation: ?personal protective equipment
- Supportive measures (resuscitation)
- Empirical treatment if patient unwell
- Antimicrobial therapy based on likely diagnosis
- aim to treat life-threatening conditions e.g. typhoid, septicaemia
•Specific treatment - once diagnosis is established


