Staph Aureus Bacteraemias Flashcards
(20 cards)
what is Staphylococcus aureus and its effects?
- Most virulent of the many staphylococcal species
- Remains a major cause of morbidity and mortality
does staph. aureus cause disease through toxin or non-toxin mediated mechanisms?
• Causes disease through both toxin-mediated and non-toxin-mediated mechanisms
is staph. aureus cause disease in hospital or the community?
• Responsible for both healthcare associated and community-based infections
is staph. areus part of the normal gut flora?
• S.aureus is a part of the normal human flora
is staphylococci gram positive or negative?
Staphylococci are Gram-positive cocci that form grape-like clusters on Gram stain
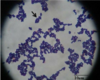
S. aureus Blood stream infections - traditionally how are they classified?
Traditionally, classified according to the environment of acquisition:
- healthcare associated or
- community acquired
Absence or presence of identified associated sites
of infection means it could either be what?
primary or secondary
what is the spectrum of infection?
- Skin & Soft Tissue Infections - S. aureus is the most commonly identified agent
- Localised pyogenic staphylococcal infections - furuncles and carbuncles
- Deep-seated abscesses, necrotising fasciitis, pyomyositis
- Osteomyelitis, Septic arthritis, Discitis
- Infective endocarditis
- Pneumonia, Empyema
- In the hospital setting - wound infection and vascular line - or catheter-related infection
Approximately one-third of patients with S.aureus bacteraemia develop local __________ or distant septic __________
complications
metastases
What are frequent sites of distant metastases?
- Bones and joints (especially when prosthetic materials are present)
- Epidural space and intervertebral discs
- Native and prosthetic cardiac valves, Cardiac devices
- Visceral abscesses in spleen, kidneys and lungs
Case of Staphylococus aureus carbuncle involving the cervical region spreading to involve the pectoral region in a patient with type 2 diabetes
(Invasive Staphylococcus aureus infections in diabetes mellitus
Hakeem et al The BJDVD)

Boil on neck evolved into a soft tissue infection
Required debridement and course of antibiotic therapy
Shows gas in soft tissue

Transoesophageal echocardiography (TOE) image of a patient with S. aureus bactraemia
(Invasive Staphylococcus aureus infections in diabetes mellitus
Hakeem et al The BJDVD)
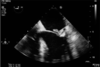
Needed about 6 weeks of antibiotic therapy
Thigh MRI showing a large multi-loculated suprapatellar collection that extended up anteriorly
(Invasive Staphylococcus aureus infections in diabetes mellitus
Hakeem et al The BJDVD)

Collection in the pre-patellar region
Needed 3 month course of antibiotic and theatre for debridement
what investigations would be carried out?
- Microscopy and culture of specimens
- multiple blood cultures before commencing antibiotic therapy
- Repeat blood cultures are recommended 48–72 hours after commencing antimicrobial therapy
- Biopsy samples may be of value for bone infections
- Imaging- X-ray, CT, MRI, Radionuclide imaging
- Transthoracic echocardiography, TOE
what management is required?
Basis of treatment for invasive staphylococcal infections-
- Antibiotic therapy
- Source identification and clearance
- and appropriate surgical intervention
Delay in the administration of appropriate antibiotic therapy and persistent bacteraemia after 72–96 hours of appropriate therapy, has been associated with an increased risk of complications and higher mortality
what antibiotics can be used in the management? and what is their use?
- Flucloxacillin - minimum duration of treatment for uncomplicated S. aureus bacteraemia is 14 days
- Vancomycin- far from an ideal drug due to poor tissue penetration, slow bactericidal activity, inconvenient administration and side effects
- Teicoplanin - has an advantage in terms of its single daily dosing and could also be used three times weekly after appropriate loading
- Linezolid - bacteriostatic, synthetic oxazolidinone, good penetration into bone and excellent oral bioavailability
- Daptomycin - cyclic lipopeptide with rapid bactericidal activity against S. aureus. Well tolerated. Has the advantage of once daily dosing. Has a long half life so one dose covers you for 2 weeks, excellent antibody for people with difficult venous access
Need to find if the S. aureus is medicine resistant and if so wont be sensitive to penicillin based ones like the top one
Case 1:
- 47 year old lady with a background history of Injecting drug use presents to hospital with 5 day history of fever, cough and shortness of breath. She also complained of a painful swollen right groin
- She was alert and orientated on examination. O2 saturations were 90% on air, She was pyrexial at 38.5C. BP was 110/60, Pulse rate was 110 bpm, Respiratory rate was 32
- She did not have any known allergies
- No history of travel
- Bloods showed- WCC 31.9, Urea 8
- Dopplar US showed a DVT ? Infected Right leg
What organism is likely to be responsible for the CXR findings?
- Steptococcus pneumoniae
- Mycoplasma
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Legionella species
- Haemophilus influenzae
What antibiotics would you commence her on?
- iv Amoxycillin
- iv Flucloxacillin
- iv meropenum
- iv Co amoxicalv
- iv levofloxacin

- Staphylococcus aureus
- No allergies iv Flucloxacillin
Case 2:
- Blood cultures were positive for S. aureus
- Despite 2 weeks on therapy, She complains of ongoing cough, fever and right sided chest discomfort and right groin pain and discharge
- Bloods showed WCC of 18 and CRP of 210
You would perform the following investigations:
- ECHO
- CXR
- Repeat blood cultures
- Ultrasound groin
- All of above
•All of above
What does the CXR show?/ What is the diagnosis?
- Post pneumonic effusion
- Empyema
- pneumothorax
- ongoing pneumonia
- non of the above

White area on right side is fluid
Answer is one of top 2
Ongoing symptoms so answer is empyema
pH would be low of the empyema


