Immunisation and Prophylaxis Flashcards
(42 cards)
what types of immunity is there?
Can be innate or adaptive
Adaptive – body produces antibodies in response to an infection, this is active

what is an antibodies primary and secondary response to an infection like?
Antibodies produced in response to primary infection
When exposed second time, total antibody response happens much quicker and at a higher level to prevent being infected again

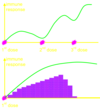
what is the immune response like in a killed vacicne comapred to a live vaccine? and how many of each do you require?
(killed is top
Pink blotch is exposure to vaccine
Can be killed or live
Killed will produce antibodies but will come down that’s why you need multiple doses
Live vaccine only needs one as when the live vaccine replicates the body produces more antibodies and you have a sustained response to the pathogen
has smallpox been eradicated?
Eradication of smallpox by vaccination
Use of vaccine has resulted in dramatic reduction in incidence of smallpox and now being eradicated

where can someone get details about vaccinations?
green book
BNF
what different types of vaccines is there?
- live attenuated
- inactivated (killed)
- detoxified exotoxin
- subunit of micro-organism
- purified microbial products
- recombinant
what are examples of Live attenuated vaccines?
- Measles, mumps, rubella (MMR)
- BCG
- Varicella-zoster virus
- Yellow fever
- Smallpox
- Typhoid (oral)
- Polio (oral)
- Rotavirus (oral)
what are examples of Inactivated (killed) vaccines?
(these need 2 or 3 doses)
- Polio (in combined vaccine D/T/P/Hib)
- Hepatitis A
- Cholera (oral)
- Rabies
- Japanese encephalitis
- Tick-borne encephalitis
- Influenza
Detoxified exotoxin vaccines - how are they made?
e.g. Diphtheria, Tetanus
Formalin renders it inactive and then the patient is treated with the toxoid

what are examples of Subunit vaccines?
Good against bacteria
Vaccine is made up of a subunit of that pathogen
A subunit vaccine is a vaccine that contains only the minimal microbial elements necessary to stimulate long-lasting protective/therapeutic immune responses
- Pertussis (acellular)
- Haemophilus influenzae type b
- Meningococcus (group C) - conjugated: capsular polysaccharide antigen & Corynebacterium diphtheria protein
- Pneumococcus
- Typhoid
- Anthrax
- Hepatitis B
how are Recombinant vaccines made e.g. Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B antigen is produced and this is very immunogenic
Production of antibodies against the antigen and then offers immunity

what is the “6 in 1” vaccine: Infanrix hexa?
(Can bundle many together)
D = purified diphtheria toxoid
T = purified tetanus toxoid
aP = purified Bordetella pertussis
IPV= inactivated polio virus
Hib= purified component of Haemophilus influenzae b
HBV= hepatitis B rDNA
what is the UK Childhood Immunisation Schedule?
- 2 months: 6-in-1 vaccine + pneumococcal conjugate + rotavirus + Men B (Get started early to prevent infection)
- 3 months: 6-in-1 vaccine + rotavirus (repeat 6 in 1)
- 4 months: 6-in-1 vaccine + pneumococcal conjugate + Men B
- 1 year: Hib/Men C+ MMR + pneumococcal conjugate + men B
- 2 -8 years: influenza nasal
- 3 - 5 years: 4-in-1 booster (DTaP/IPV) + MMR
- Girls, 12-13 yrs: Human papilloma virus
- 14 years: 3-in-1 booster (dT/IPV) + Men ACWY
Concept of “herd immunity” - what is the target coverage?
Concept of “herd immunity” - Target 90-95% coverage
Vaccine needs to cover 90-95% of the population to slow transmission
Vaccination programs interrupted in times of war and vaccine rates fall/decrease

What are some examples of Immunisation for special patient and occupational groups?
- BCG
- influenza
- pneumococcal
- hepatitis B
- varicella-zoster (chickenpox)
- herpes-zoster (shingles)
who needs the Bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG) vaccine?
(For against TB)
• Some infants (0-12 months)
- areas of UK with annual incidence of TB >40/100,000
- Parents/grandparents born in a country with annual incidence of TB >40/100,000
- Children screened at school for TB risk factors, tested and vaccinated if appropriate
- New immigrants (previously unvaccinated) from high prevalence countries for TB
- Contacts (<35yrs) of resp TB patients
- Healthcare workers
what is the struggle with the influenza vaccine?
• Influenza A and B constantly change antigenic structure
- haemagglutinins (H)
- neuraminidases (N) on surface of virus
• New vaccine each year (WHO)
WHat is involved in the influenza vaccine giving and structure?
• 2017-18 Vaccine contains
- A/ (H1N1)
- A/ (H3N2)
- B/
(A and B are the antigens on the surface)
- Single dose
- Caution in egg allergy
what are the indications for a influenza vaccine?
- Age >65 years
- Nursing home residents
- Some health care workers
- Immunodeficiency,
- Immunosuppression
- Asplenia/hyposplenism
- Chronic liver disease
- Chronic renal disease
- Chronic cardiac disease
- Chronic lung disease
- Diabetes mellitus
- Coeliac disease
- Pregnant women
- Heath care workers
what are the two pneumococcal vaccines?
• pneumococcal conjugate polysaccharide vaccine (13 serotypes): Prevenar13®
- Part of childhood immunisation schedule
- 3 doses
• pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (23 serotypes) Pneumovax II ®
- for those at increased risk of pneumococcal infection
- single dose
what are the indications for the •pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (23 serotypes) Pneumovax II ®?
Immunodeficiency
Immunosuppression
Asplenia/hyposplenism
Sickle cell disease
Chronic liver disease
Chronic renal disease
Chronic cardiac disease
Chronic lung disease
Diabetes mellitus
Coeliac disease
who gets the hepatitis B vaccination?
(4 doses over the course of a year)
- All new born children from 2018 (6-in-1)
- Children at high risk of exposure to HBV
- Health care workers, PWID, MSM, prisoners, ch. liver disease, ch. kidney disease,
- Given at 0, 1 month, 2 months and 1 year
what type of vaccine and how many doses of the varicella-zoster (chickenpox)
vaccine do people get?
- Live attenuated virus
- 2 doses, 4-8 weeks apart
who gets the varicella-zoster (chickenpox)
vaccine?
- patients who have a suppressed immune systems, for example having cancer treatment or organ transplant
- children if in contact with those at risk of severe vzv
- Health case workers (if sero-neg and in contact with patients)


