Antimicrobial Chemotherapy Flashcards
Paradox - Antibiotics increase infections - how?

paradox - Antibiotics increase infection…and mortality in uninfected patients?
excessive antimicrobial usage causes measurable harm to patients and ar emor elikely to get infections like C. diff
With current trends in antimicrobial use, new _________ and increasing numbers of _________ (new clones) will be generated at home and abroad and spread internationally
Current control efforts are “firefighting”
Prevention requires a new attitude to Antibiotic Stewardship, requiring major _______ in antibiotic ___ and “antibiotic holidays”
resistances
infections
decline
use
- Patients with infections caused by ___________ _______ are generally at ________ risk of worse clinical outcomes and death, and consume ____ healthcare resources than patients infected with the ____ bacteria that are not _______. (WHO 2014)
- The use and misuse of antimicrobials __________ the emergence of drug-resistant strains
- Patients with infections caused by drug-resistant bacteria are generally at increased risk of worse clinical outcomes and death, and consume more healthcare resources than patients infected with the same bacteria that are not resistant. (WHO 2014)
- The use and misuse of antimicrobials accelerates the emergence of drug-resistant strains
There is a high correlation between antibiotic ___ and __________
use
resistance
how would you do IV to Oral Switch Therapy (IVOST)?
Consider switching patients from IV to oral antibiotics after 48hrs, provided that: the patient is improving clinically and is able to tolerate an oral formulation
i.e. if all the criteria below are met:
Able to swallow and tolerate fluids
Temp. 36-38°C for at least 48 hours
Heart rate < 100bpm for previous 12 hours
WCC between 4 and 12x109L
Healthcare workers can help tackle AMR by…
- Practicing effective infection prevention & control
- Prescribing and dispensing antibiotics only when truly needed
- Prescribing & dispensing the right antibiotic(s) for the right duration to treat the illness
“Our mission is not to prescribe as few antibiotics as possible but to identify that small group of patients who really need antimicrobial treatment and to explain reassure and educate the large group of patients who do not.”
Everybody can help tackle resistance! How?
- Use antibiotics only when prescribed
- Complete the full course
- Never share antibiotics or use leftover prescriptions
are all antiviral virustatic or virucidal?
All are virustatic, none are virucidal
• Viruses are _______ intracellular parasites
obligate
a parasitic organism that cannot complete its life-cycle without exploiting a suitable host
- As viruses utilise host cell enzymes in order to _______, there are limited viral proteins that are potential _______ for antiviral drugs
- Toxicity to host cell ___ uncommon: side effects
- Only used in a _______ of viral infections
replicate
targets
not
minority
what stage of the virus life cycle is the target?
- Several stages of the virus life cycle are targets
- Most target intracellular stages
- Greater effect on viral replication than on the host cell function
- Most antivirals are nucleoside analogues - inhibit nucleic acid synthesis
what may the treatment of antivirals be used for?
Prophylaxis (to prevent infection)
Pre-emptive therapy (when evidence of infection detected, but before symptoms apparent)
Overt disease
Suppressive therapy (to keep viral replication below the rate that causes tissue damage in asymptomatic infected patient)
Do antivirals eradicate the virus from latently infected cells?
Antivirals do NOT eradicate virus from latently infected cells, e.g. herpes viruses
Therefore, after successful treatment of an episode of overt infection, suppressive (maintenance) treatment may be needed
what can antivirals be used for in practice?
Herpesviruses: HSV 1 & 2, VZV, CMV
HIV
Hepatitis: hepatitis B, hepatitis C
Respiratory: influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
Use of Antivirals for HSV & VZV
Herpes simplex: Mucocutaneous: oral, genital, eye, skin, Encephalitis, Immunocompromised: any site
Chickenpox: in those at increased risk of complications, neonate, immunocompromised, pregnant, immunocompetent adult…only if begun within 24 hours of onset of rash
Shingles: Only decreases post-herpetic neuralgia in the immunocompetent host if begun within 72 hours of onset of symptoms
How are each of the following taken:
aciclovir
valaciclovir
famciclovir
foscarnet
aciclovir - oral, IV, eye ointment, cream
valaciclovir - oral
famciclovir - oral
foscarnet - IV
aciclovir-like drugs are only active in herpes infected cell - low toxicity for uninfected cells
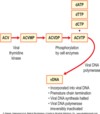
what is the mode of action of aciclovir?
- Aciclovir is converted by viral thymidine kinase to ACVMP,
- ACVMP then converted by host cell kinases to ACV-TP
- ACV-TP, in turn, competitively inhibits and inactivates HSV-specific DNA polymerase
- preventing further viral DNA synthesis
- without affecting the normal cellular processes
Antivirals and CMV - All available drugs have significant toxicity
when should they be used?
• Only treat life- or sight-threatening CMV infections
e.g. HIV patients: CMV retinitis, colitis, Transplant recipients: pneumonitis
- May also be used to treat neonates with symptomatic congenital CMV infection
- ganciclovir - IV, ocular implant
- valganciclovir - Oral
- cidofovir - IV
- foscarnet - IV
what is the use of antivirals in influeza?
Influenza A or B: oseltamivir, zanamivir
- Role in both treatment and prophylaxis
- Not always indicated, but if used, should usually start within 48 hours of onset of symptoms/contact
onto main antimicrobial chemotherapy powerpoint
what are the different locations that a drug can act in an orgamism?

Penicillins

Cephalosporins

Aminoglycosides














