Thorax, tracheobronchial tree and lungs Flashcards
What spinal levels does the phrenic nerve derive from?
C3, 4, 5
How does the respiratory system develop embryologically?
What does the mesoderm form?
- The respiratory diverticulum begins to grow out of the gut tube at around 4 weeks gestation.
- Lung (bronchial) buds grow out of the inferior aspect of the respiratory diverticulum.
- Buds grow into splanchno-pleuric mesoderm at around week 5.
- Mesoderm forms blood vessels, cartilage, smooth muscle and visceral pleura
- Tracheo-oesophageal septum forms and the developing trachea separates from the gut tube (around week 4-5)

What embryological malformations can be formed from the developing embryonic lungs?
-
Proximal atresia with distal fistula:
- Blind-ended oesophagus
- Distal oesophagus forms fistula with trachea.
-
Fistula
- Both proximal and distal oesophagus form fistula with trachea
Both caused by failure of septation of the trachea and gut tube.

How do the bronchial buds branch?
What is the significance of week 26 in the development of the lungs?
Right lung bud branches into 3 secondary buds
Left lung bud branches into 2 secondary buds.
Segmental bronchi develop around 56 days
By week 16 all major lung parts have developed except those needed for gas exchange.
Respiratory epithelia (lining of terminal bronchioles and alveolar sacs) develops at around week 26 (hence why babies born premature to 26 weeks have very low chance of survival)

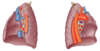
Label the lobes and fissures on the lungs


What do the medial surfaces of both lungs contain?
Label the structures on the diagram
Hilum

Where is the point of the pleural reflection?
At the hilum of the lungs
What type of blood do the pulmonary arteries carry?
What type of blood do the pulmonary veins carry?
Pulmonary arteries carry deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs
Pulmonary veins carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium
Label the structures on the diagram
Where does the phrenic nerve pass in relation to the hilum?
Which nerve passes posterior to the hilum?

Phrenic nerve passes anterior to the hilum
Vagus nerve passes posterior to the hilum

Label the vessels on the diagram

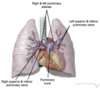
What do the lungs act as a filter for?
How can these enter the lungs?
Lungs can filter venous thromboses; these can be carried to the lungs via the pulmonary arteries.
Where do the right and left recurrent laryngeal nerves branch off the vagus nerve?
-
Right recurrent laryngeal nerve:
- Occurs at right lung apex under right subclavian artery
- Hoarseness of voice can indicate compression/damage to recurrent laryngeal nerve- if on right side could be from apical lung tumour.
-
Left recurrent laryngeal nerve:
- Occurs at lung hilum/aortic arch
- Can be compressed by aortic aneurysm
What do the lung pleura line?
How are the two pleura held together?
Visceral: line the lung tissues
Parietal: lines inside of thoracic cavity
Pleural layers are held together by surface tension
Define:
Pneumothorax
Haemothorax
Chylothorax
Effusion
Tension pneumothorax
- Pneumothorax: air in the pleural space
- Haemothorax: blood in the pleural space
- Chylothorax: lymph fluid in pleural space
- Effusion: fluid leaking out of lung into pleural cavity
-
Tension pneumothorax: each time the patient breathes in, more air enters the pleural space but none escapes.
- Medical emergency: pleural cavity can continue to expand and compress heart.
What can be seen on x-ray in a patient with a tension pneumothorax?
How would this be treated?
Tension pneumothorax:
- Mediastinal shift
- Tracheal deviation
- Diaphragmatic depression
- Increased intercostal space size
- Hyper-resonance
- Unilateral hyper-inflation
Needle decompression in 2nd intercostal space in mid-clavicular line.

What are the surface markings of the lung?
- Apex: around 2cm superior to the medial 3rd of clavicle
- Tracheal bifurcation: just below sternal plane or at T4/5 (approx 2nd costal cartilage)
- Border of middle/inferior lobe: 6th costal cartilage in MCL.
- Lower border of lung in normal breathing: 6th cc, 6th rib mid-clavicular line and 8th rib in mid axillary line.
- Oblique fissue: T3 spinous process to 6th costal cartilage anteriorly.
- Horizontal fissure: 4th costal cartilage horizontally back to oblique fissure
- Lower border of pleural reflection: 6th cc, 8th rib MCL, 10th rib MAL.

Where are the auscultation points of the lung?
Superior lobe: auscultate anteriorly
Middle lobe: Mid axillary line
Inferior lobe: Posteriorly, below oblique fissure (roughly marked by abducted scapula, T3 to 6th cc anteriorly)
What does the medial border of an abducted scapula roughly mark the location of?
Oblique fissure

During normal breathing, what paravertebral level approximately marks the lower border of the lung?
What paravertebral level marks the lower border of the lung at end tidal inspiration?
Normal breathing: T10 paravertebral level
End tidal inspiration: T12 paravertebral level
Where is the costodiaphragmatic recess found?
What is it? What is its clinical relevance?
Between T10 and T12 paravertebral levels, lies between the thoracic wall and diaphragm.
Region between lung and the pleural reflection.
Lung expands into the costodiaphragmatic recess during deep inspiration. It can also be a location for fluid collection in pleural effusion.

What are the anatomical relations of the costodiaphragmatic recess?
What vertebral levels are they at?
Kidneys
Liver
Spleen

Where is the triangle of safety for chest drain insertion?
What could be damaged by insertion of a chest drain posterior to the triangle of safety?
- Posterior border: Mid axillary line
- Inferior border: 5th rib
- Anterior border: posterior border of pectoralis major (anterior axillary fold)
- Roof: base of axilla
- Drain should be inserted within this triangle in the 4th intercostal space.
Insertion of a chest drain posterior to the triangle of safety could damage the long thoracic nerve causing loss of innervation to the serratus anterior (patient cannot raise arm above 90°)

Where can the trachea be palpated?
At what vertebral levels does it bifurcate and enter the hilum of the lungs?
What is located at the bifurcation? What should it look like on endoscopy?
Above the sternal notch
Bifurcates at T4/5
Enters the hilum of the lungs at T5/6
The carina is located at the bifurcation, should appear thin and pointed. Widens due to lymph node swelling beneath.
What is the significance of the right bronchus being wider than the left?
Aspirated food/liquid is more likely to enter the right bronchus (path of least resistance)







