Thorax Flashcards
What is the thorax composed of?
Thoracic walls
Pleural cavities
Mediastinum
What is the purpose of the thorax?
Passageway between the abdomen, neck and upper limbs for vessels nerves and organs.
Protection of thoracic organs
Breathing
Which ribs end in cartilage in the midline?
Which ribs are floating?
Ribs 1-10 end in cartilage
Ribs 11-12 floating, embedded in muscle.
What is the posterior and anterior boundaries of the thoracic inlet?
What marks the lower boundary of the thoracic cavity?
Thoracic vertebrae marks posterior boundary of thoracic inlet, sternal manubrium marks anterior boundary.
Costal margin marks lower border of thoracic cavity.
What effect can rib fractures have on rib movement during respiration?
Paradoxical movement of fragmented bone segments which move out on expiration and in on inspiration (opposite to movement of normal thoracic wall)
What does the thoracic superior aperture contain?
How might the contents be injured?
Subclavian veins and arteries, compression can lead to vascular symptoms in upper limb.
Parts of brachial plexus (C5-7): compression can lead to wasting of 1st dorsal webspace
Can be damaged by cervical rib (C7)
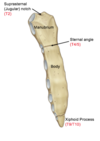
Label the parts of the sternum
What vertebral levels are they normally found at?
What is the sternal angle a landmark for?

Sternal angle is a landmark for the attachment of rib 2.
Marks the approximal level of T4/T5 junction and the sternal plane. Divides sternum and mediastinum into superior and inferior parts.
What sits in the costal groove?
Neurovascular bundle
Superior to inferior: Vein, artery, nerve (VAN)

How do the ribs articulate with the vertebrae?
Most ribs articulate with their own vertebra and that one above.
Head of the rib articulates with the articular facets on the body of their own vertebra and the one above.
Tubercle of the rib articulates with the articular facetes on the transverse process of their own vertebra

What is the clinical significance of the angle of the rib?
Intercostal nerve blocks
What type of joints form the articulation between the ribs and the thoracic vertebra?
What movements do these allow?
Synovial
Allows movement of the ribs during inspiration and expiration.
How are the ribs classified?
-
Vertebrosternal (1-7)
- From vertebra directly to the sternum
- Vertebrocostal (8-10)
- From vertebrae to costal cartilage of another rib.
-
Floating (11-12)
- Embedded in muscle
What are the 3 layers of intercostal muscle?
What are their roles?
Label them on the diagram

External intercostal: Inspiration
Internal intercostal: Expiration
Innermost intercostal

What are the neurovascular bundles that sit in the intercostal spaces?
What muscles do they sit between?
Between internal and innermost intercostal muscles
- Main neurovascular bundle (VAN)
- Collateral neurovascular bundle

Where should chest drains be inserted into?
Why?
Inferior part of intercostal spaces to avoid damage to the main neurovascular bundle in the costal groove in the superior part of intercostal space.
Label the intercostal muscles and structures of the thoracic wall on the diagram


Where do intercostal nerves originate from?
What innervation do they supply?
What arrangement do they follow?
Ventral rami of the spinal nerves
- Supply motor and sensory (dorsal ramus, lateral and anterior cutaneous nerves) to the intercostal space and surrounding tissue:
- Skin
- Cartilage
- Bone
- Muscle
- Parietal pleura
Follow dermatomal arrangement

What could the consequences be of damaging the main neurovascular bundle in the intercostal space?
Segmental numbness
Motor loss of the intercostal muscles - paradoxical movement on inspiration and expiration (same as fractured rib)
Where does the sympathetic chain run from and to?
T1 - L2 on the posterior thoracic wall
What can a tumour in the apex of the lung lead to?
What is this type of tumour called?
Pancoast tumour in the apex of the lung can cause horner’s syndrome:
- Lack of sympathetic supply to the ipsilateral face:
- Miosis
- Anhydrosis
- Ptosis
Describe the blood supply to the thoracic wall
Descending aorta → posterior intercostal arteries (neurovascular bundle)
Internal thoracic arteries (becomes musculophrenic arteries below thoracic cage) → anterior intercostal arteries.
Anterior and posterior intercostal arteries anastamose in the intercostal space.

How does the anastamotic relationship between the anterior and posterior interthoracic arteries provide a collateral blood supply?
In an aortic coarctation (constriction of aortic arch), the blood can divert into the internal thoracic/musculophrenic arteries → anterior thoracic arteries → posterior thoracic arteries → descending aorta → rest of the body.
What can the internal thoracic arties be used for?
Can be harvested and used for coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) as they resist atherosclerosis better than most arteries in the body. Anastamotic relationship means they can be harvested without compromising blood supply.
Describe the venous drainage of the thoracic wall
Label the veins on the diagram

The azygous system: unpaired azygous veins:
- Azygous veins drains right-sided structues → SVC
- Hemiazygous and accessory azygous veins drain left-sided structures → midline azygous → SVC
- Some of the upper intercostal spaces drain into the brachiocephalic veins.





