The Heart and Mediastinum Flashcards
What is the mediastinum?
Where does it extend from/to?
Broad central region that separates the two laterally placed pleural cavities
Extends from the thoracic inlet (aperture) at rib 1 to the diaphragm (T12) and from the sternal manubrium to the vertebral bodies
Is the patient on this x-ray in inspiration or expiration?

Inspiration:
- Flattening out of costodiaphragmatic recess
- Large lung fields
Label the features of the x-ray

Top arrow: arch of aorta
Bottom arrow: Pulmonary trunk
Line: hilum
What is the mediastinum divided by?
Sternal plane (T4/T5) divides the mediastinum into inferior and superior parts.
Inferior part divided into:
- Anterior
- Middle
- Posterior
- Divided by the pericardial sac

What can collect in the costodiaphragmatic recess?
Effusion fluid
What does the anterior mediastinum contain?
What are its borders?
- Anterior border: sternum
- Posterior border: pericardial sac
- Superior border: sternal plane
- Inferior border: diaphragm
Contains:
- Thymus (part of)
- Internal thoracic arteries
- Fat
- Connective tissue
What can the internal thoracic arteries be used for?
Which arteries branch off them?
Which arteries do these meet?
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG)
Anterior intercostal arteries branch off them
- Form anastamotic relationship with posterior intercostal arteries in each intercostal space.
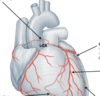
Label the structures on the diagram


Where is the thymus normally located?
What is the thymic sail sign?
What happens to the thymus with age?
In the anterior and/or superior mediastinum
The thymus is relatively large in children therefore can be seen on x-ray
Thymus shrinks with age

What does the superior mediastinum contain?
Label them on the diagram

Arch of aorta
Great vessels
Trachea
Oesophagus
Thoracic duct
Phrenic and Vagus nerves

Where does the trachea normally bifurcate?
Around T4
Where do the great veins sit in relation to the arteries?
Label the vessels on the diagram

Anteriorly

What is the ligamentum arteriosis?
What happens if it stays open?
Was previously the ductus arteriosis vessel, fuses soon after birth. Open in utero to help blood bypass the lungs which are not fully developed.
If it stayed open, it would create a mix of high O2 and low O2 blood from the arch of aorta and pulmonary trunk
Where do the phrenic and vagus nerves travel in lungs?
Which important branch comes off the vagus? Where does it branch?
Phrenic nerve passes anterior to the hilum of the lung and the great vessels
Vagus nerve passes posterior to the hilum of the lung, recurrent laryngeal artery.
- Right recurrent laryngeal branches off around the right subclavian artery in the superior mediastinum
- Left recurrent laryngeal branches off around the arch of the aorta behind the ligamentum arteriosum.
What do the recurrent laryngeal nerves do?
Sensory below vocal chords
Motor to all extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the larynx except cricothyroid (external laryngeal nerve)
On which side would a hilar lymph node cause a hoarse voice? Why?
On which side could a pancoast tumour cause a hoarse voice? Why?
Hilar lymph node enlargement on the left side
- Could compress the left laryngeal nerve
Pancoast apical tumour could on the right side could compress the right recurrent laryngeal nerve against the right subclavian artery
Describe the route of the vagus nerve in the mediastinum
Vagus nerves form a plexus around the trachea and oesophagus and give off anterior and posterior vagal plexuses on the surface of the oesophagus:
- Left vagus: anterior plexus
- Right vagus: posterior plexus
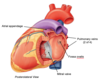
Where does the left atrium of the heart sit against?
What can this anatomical relationship be used for?
Sits against the oesophagus
Can be used for trans-oesophageal ultrasound of the heart
What does the posterior mediastinum contain?
What are its borders?
- Superior border: sternal plane
- Posterior border: vertebral column
- Anterior border: pericardial sac
- Inferior border: diaphragm
Contains:
- Oesophagus and vagal plexus
- Descending aorta
- Thoracic duct
- Sympathetic chain
- Azygous system
What type of muscle is the oesophagus made up of?
What type of motor supply do they have?
Upper 1/3 = skeletal muscle
- Somatic control
Lower 2/3 = smooth muscle
- Autonomic control
What does the middle mediastinum contain?
What are its borders?
- Superior border: sternal plane
- Lateral borders: parietal pleura of the lungs
- Inferior borders: pericardial sac against diaphragm
- Anterior and posterior: paricardial sac
Contains:
- Heart and paricardium
- Lower superior vena cava
- Lower ascending aorta
- Lower pulmonary trunk
- Phrenic nerves (run along edges of fibrous pericardium)
- Cardiac plexus
What attaches the heart to the diaphragm?
Fibrous pericardium via the central diaphragmatic tendon
Describe the surfaces of the heart
Posterior surface: base
Inferior surface: diaphragmatic surface

Which chambers of the heart can be viewed anteriorly?
Why is this?
- Right ventricle
- Right atrium
- Small amount of left ventricle
Due to the left rotation of the heart during embryological development