Thorax and Lung Flashcards
(70 cards)
Pleuritic/pleurisy
Pain with breathing
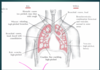
Lung fields vs lobes
Lung fields= 6 regions (upper/middle/lower right/left)
At what spinal level does the trachea bifurcate?
T4, at the sternal angle
Visceral pleura
covers outer surface of lungs
Parietal pleura
lines inner rib cage and upper surface of the diaphragm
Thorax and lung physical exam
inspect palpate percuss auscultate
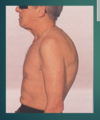
A-P diameter- barrel chest
AP diameter increased

A-P diameter normally
Thorax normally 2x wider than it is deep May increase with aging and COPD (i.e. emphysema, chronic bronchitis, etc)

Kyphosis
Hunch back

Pectus excavatum
Sternum caved in, ribs on either side are higher

Pectus Carinatum
Sternum protrudes

stridor
a wheeze that is high pitched and largely inspiratory; usually louder in the neck
What does stridor indicate
laryngeal/upper airway obstruction (can be associated with epiglotitis, foreign body aspiration
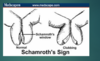
Schamroth’s sign
Clubbing Possible sign of COPD
reduces respiratory rate from 20 to 12-15 breaths/min, increases tidle volume, decreases PaCO2, increases PaO2
How do you check chest expansion?
Place thumbs at the level of the 10th ribs, fingers parallel to lateral rib cage.
Unilateral decrease/delay in expansion= fibrosis, pleural effusion, possibly lobar pneumonia
What is the purpose of percussion?
To determine if underlying tissues are air filled, fluid or solid
When would you use the direct technique vs indirect for percussion?
direct- over spine and kidneys (CVA) to check for tenderness
indirect- check for degree of resonance of lung
What should chest percussion sound like?
resonance= air
dullness= solid/fluid filled areas
Percussion tones- hyper-resonant
intensity= very loud
pitch= low
examples: Emphysema, local pneumothorax
Percussion tones- resonant
intensity= loud
pitch= low
example= healthy lungs
Percussion tones- Tympanic
intensity= loud
Pitch= high
example= gastric bubble (or puffed out cheek)
Percussion tones- Dull
intensity- soft- moderate
pitch- moderate-loud
example: liver, consolidation (pneumonia), pleural effusion
Percussion tones- flat
intensity- soft
pitch- high
ex: muscle, consolidation (PNA), pleural effusion
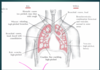
What are the required number of levels for auscultation/percussion of the anterior and posterior chest
anterior- 3
posterior- 4 + 1 lateral site on each side