The Heart and Vasculature Flashcards
Draw and label the diagram to show the subdivisions of the mediastinum


Label the heart diagram


Label this


What is the sternal angle? What is its clinical importance?
The joint between the manubrium and sternum= manubrio-sternal joint or sternal angle.
This intersects T4 and T5. This angle subdivides the mediastinum into superior and inferior. It is also where the trachea bifurcates so is clinically important in choking
Describe the pericardium and its function
Pericardium is a fibro-serous sac enclosing the heart and the roots of the great vessels.
The lubricated later is the serous layer.
Function: restrict excessive heart movements, serve as a lubricated container in which diff parts of the heart can contract.
Describe anatomy of the right atrium and where it receives blood from
Bonus- what is the coronary sinus?
Forms right border of heart
Receives blood through the SVC, IVC and coronary sinus
Coronary sinus returns blood from the walls of the heart itself.
The coronary sinus is the big vein on the back of the heart where all the veins empty into

Label this right atrium and explain the function of each label


Describe and label the anatomy of the right ventricle

Blood entering from RA moves in a horizontal and anterior direction
Outflow tract: pulmonary trunk.
Pulmonary trunk closed by pulmonary valve, which has 3 semilunar cusps

Explain anatomy of the left atrium
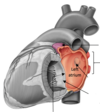
Forms most of base of heart, sits quite posteriorly
Blood enters thru 4 pulmonary veins
Anterior half of the LA is continuous with left auricle
Valve of the foramen ovale= depression on interatrial septum
Blood moves into LV via AV-orifice, guarded by the mitral valve

Describe anatomy of the left ventricle
Wall x3 thicker than RV
Blood passes via AV orifice to apex (guarded by mitral valve)
Blood flows into the aortic vestibule (guarded by aortic valve)
Blood recoils after ventricular contraction, it fills the aortic sinuses and is forced into coronary arteries

What is the importance of the papillary muscles?
When the ventricle contracts, papillary muscles contract, preventing the cusps turning inside out into the atrium as intra-ventricular pa rises

What do great vessels refer to?

describe the pulmonary trunk

T5-T6, opposite left border of sternum it divides into left and right pulmonary arteries
Left: inferior to aortic arch
Right: posterior to ascending aorta and SVC

Describe the vena cava
Superior VC: inferior half is within pericardial sac. Passes through fibrous pericardium at C2 and enters right atrium
Inferior VC: passes through diaphragm at T8 and enters fibrous pericardium. Short portion of it is w/in the pericardial sac before entering the RA
Describe the aorta, where it originates, where the arch lies etc

Originates at aortic orifice (lower edge of C3), continues to C2
The arch lies behind sternum and in front of trachea, and moves up and back to become continuous w descending aorta at the sternal angle
Ligamentum arteriosum connects bifurcation of pulmonary trunk w aorta

What are the branches of the aortic arch?
.

The aorta descends downwards; describe the thoracic aorta, where it begins and descends etc

Begins at T4-T5 from arch of the aorta and descends in the posterior mediastinum.
It passes through the aortic hiatus of the diaphragm at T12. The aortic hiatus means the aorta doesn’t get compressed by the diaphragm when it contracts.

Label the vascular network of the thoracic cavity


Label the vessels of the trunk


What do each of these vessels supply?

Coeliac trunk: stomach, liver and upper abdominal organs.
Sup mesenteric: small + large intestines. Inf mesenteric supplies large intestine.
Renal: to kidney. Gonadal: to ovaries/testes.
Lumbar: posterior abdominal wall
Common iliac bifurcates to ext iliac (supplies lower limb) and internal iliac (all pelvic contents).
Describe the upper limb arteries.
The right and left subclavian pass under the clavicle and become the axillary artery.
Once this artery emerges from the armpit it becomes the brachial artery.
This then bifurcates into radial and ulna, which connect in a palmer arch.
What is the femoral triangle? Label the numbers on the image

Femoral triangle: formed by upper thigh muscles between the anterior abdominal wall and the lower limb
The femoral nerve, artery, and vein and lymphatics pass between the abdomen + lower limb under the inguinal ligament and in the femoral triangle

What does this image show?

Shows the femoral artery, which is the continuation of the external iliac.

Use the images to label the arteries of the leg


Describe the veins of the lower limb.

Deep veins= under the deep fascia, accompanying the major arteries.
Superficial veins=in the subcutaneous tissue, drain into the deep veins:
Great Saphenous ascends the medial side of the leg, anterior to the ankle, posterior to the knee
Small Saphenous ascends the posterior leg, empties into the popliteal vein

2 types of pericardium: fibrous and serous. Describe fibrous pericardium
Fibrous pericardium= strong layer. Firmly attached below to the central tendon of the diaphragm
Attached to sternum by sternopericardial ligaments

Describe Serous pericardium
Serous Pericardium= 2 layers:
Parietal, which lines the fibrous pericardium
Visceral, which closely covers heart (epicardium)
Space between=pericardial cavity. This contains pericardial fluid which acts as a lubricant

Label this


What is pericardial effusion and pericarditis?
Pericardial effusion: passage of fluid from capillaries to (or accumulation of pus in) the pericardial cavity. The heart gets compressed and ineffective as a result
Inflammation of the pericardium (pericarditis) causes sharp chest pain (relieved by sitting forwards)

Describe pericardial sinuses
Formed bc of folding of the heart during embryological development. Transverse pericardial sinus is posterior to ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk
Functions: separates the hearts arterial outflow from venous inflow. Can be used to identify and ligate arteries of the heart during CABG


