The Foot Flashcards
1
Q

A

2
Q

A

3
Q

A

4
Q

A

5
Q
What is represented by the red dot and where does it pass through?

A
posterior tubercles provide groove for the flexor hallicus longus to run through

6
Q

A

7
Q

A

8
Q

A

9
Q

A

10
Q

A

11
Q

A

12
Q

A

13
Q

A

14
Q
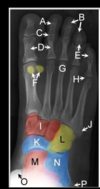
A

15
Q
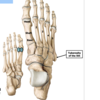
A
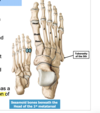
16
Q

A

17
Q

A

18
Q

A
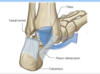
19
Q

A

20
Q
A

21
Q

A

22
Q

A

23
Q

A

24
Q

A

25


26


27


28


29

30


31
which bone of the foot is almost entirely covered with articular cartilage?
talus
32
\_\_\_\_ fracture
* Often result from forced **dorsiflexion** injuries (auto accidents)
* At one time, these fractures were referred to as “aviators fractures”
* Fractures through the neck of talus can disrupt the vascular supply to the bone- causing “avascular necrosis” and death of the talus
talus
33
Articulates with the talus superiorly at the **Subtalar joint**
Calcaneus
34
The tendon of _____ passes beneath the sustentaculum tali and inserts into the distal phalanx of the hallux
flexor halleus longeus
35
Medial view of foot one can appreciate the **large calcaneal tuberosity** and medially projecting boney shelf or _____ which supports the head of the talus
Sustentaculum Tali
36
\_\_\_\_\_ fracture
Often results from a fall from a ladder or jumping from a height- injuries that produce a high axial load on the rearfoot
MUST rule out associated fractures of the spine- particularly the lower thoracic and lumbar vertebrae
Calcaneal Fracture
37
Base of the **5th metatarsal** has a large tuberosity for insertion of the \_\_\_\_\_
fibularis brevis
38
\_\_\_ metatarsal fractures- extremely common fractures in the foot
5th
39
Deep fascia of the plantar surface (sole) of the foot is referred to as the \_\_\_
plantar fascia
40
\_\_\_\_ extremely thick central portion of this plantar fascia
Plantar aponeurosis
41
\_\_\_\_ nerve innervates 14 foot muscles; ____ innervagtes the other 4
Lateral plantar; medial plantar
42
the four muscles that the medial plantar nerev innervates
1. Flex Digitorum Brevis
2. Abductor Hallucis
3. Flex Hallucis Brevis
4. 1st (medial) Lumbrical
43
nALL Intrinsic plantar muscles are innervated by ____ nerve roots
S2 & S3
44
tarsal tunnel contents
1. Tibialis Posterior Tendon
2. Flexor Digitorum Longus Tendon
3. **Posterior Tibial Artery and Tibial Nerve**
4. Flexor Hallucis Longus Tendon
45
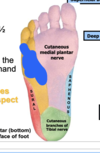
**Cutaneous sensory innervation to 3½ toes and the medial aspect of foot**
Medial Plantar Nerve
46
Cutaneous sensory innervation to 1½ toes and to the lateral aspect of the foot
Lateral Plantar Nerve
47
**Lateral plantar artery** ultimately becomes the ____ which anastomoses with the **deep plantar artery** (a branch from the dorsalis pedis artery) connecting the vascular supply between the dorsal and plantar aspects
deep plantar arch
48
diabetes tends to result in the three “opathys”:
1. Retinopathy
2. Nephropathy
3. Neuropathy
Neuropathy results in loss or diminished function of peripheral sensory nerves
Patients suffering from peripheral neuropathy often experience these debilitating foot ulcerations due to loss of sensation in their feet
49
\_\_\_ joint Permits inversion and eversion motions during the gait cycle
Subtalar Joint aka Talocalcaneal joint
50
\_\_\_\_\_ ligament helps stabilize the subtalar joint
Interosseous Talocalcaneal
51
Transverse tarsal joint consists of two joints ___ and ___ which are stabilized by \_\_\_\_
1. Calcaneocuboid
2. Talonavicluar
Bifurcate ligament
52
Because the foot is composed of numerous bones connected by ligaments…it has considerable flexibility that allows it to deform with each ground contact thereby acting as a \_\_\_\_\_\_\_
In addition, the pedal bones are arranged in arches that add to the weight bearing capabilities and resilience of the foot
shock absorber
53
nStrength and tone of muscles of the foot are via \_\_\_\_, \_\_\_\_\_, \_\_\_\_, and ____ muscle ligaments
1. tibialis anterior
2. tibialis posterior
3. flexor hallucis longus
4. fibularis longus tendon
54
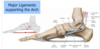
Major Ligaments
supporting the Arch
1. Calcaneonavicular “spring” Ligament- from sustentaculum tali to the navicular. Ligament has many elastic fiber providing “spring” or stretch support for the overlying talus (supports the head of the talus)
2. Long Plantar Ligament- from calcaneus to cuboid. Ligament passes across the cuboid groove and forms a tunnel for the fibularis longus tendon
3. Plantar aponeurosis- These ligaments help support the longitudinal and transverse arches of the foot
55
Plantar fasciitis
is one of the most common causes of heel pain
It involves inflammation of the thick plantar fascia/aponeurosis and associated muscles that arise from the calcaneal tuberosity
Plantar fasciitis commonly causes stabbing pain that usually occurs with
**Cause: Repetitive stretching and tearing (micro-tears) can cause the fascia to become irritated or inflamed, though in many cases of plantar fasciitis…the cause isn't clear**
**Treatment(s): Most patients who have plantar fasciitis recover with several months of conservative treatments, including resting, icing the painful area and stretching**
56




