Gluteal Region and Posterior Thigh Flashcards
1
Q

A

2
Q

A

3
Q

A

4
Q

A

5
Q

A

6
Q

A

7
Q

A

8
Q

A

9
Q

A

10
Q

A

11
Q

A

12
Q

A

13
Q

A

14
Q

A

15
Q

A

16
Q

A

17
Q

A

18
Q

A

19
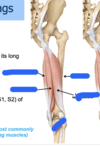
Q

A

20
Q

A

21
Q
A

22
Q

A

23
Q

A

24
Q

A

25


26


27


28
hip bone Large bone formed by the union of three bones:
1. Ilium
2. Ischium
3. Pubis
29
illieum, pubis, and ischemia are separated by ____ in younger kids
tri radiate cartilage
30
when the tri radiate cartilage fuses it forms the
acetabulum
31
\_\_\_\_ is the articular surface where the head of femur articulates in the acetabulum
Lunate surface
32
Congenital Hip Dysplasia/Dislocation (CHD)
* **Girls** have a greater incidence than boys
* Physicians can utilize the position of the **tri-radiate cartilage and the femur** to determine the presence of CHD
* Ossification center for the developing femoral head should be found with the **lower inner quadrant**
* Acetabular index should be **about 30º or less** in a normal hip
* **Shenton’s line (S)**…denoted by a **continuous** and symmetrical line between the obturator foramen and the medial aspect of the femur
33
the hip joint is a ____ synovial joint consisting of the head of the femur and the acetabulum of the hip bone
and consists of a ____ strong and dense fibrous capsule that surrounds the joint
Ball-and-Socket; articular capsule
34
Articular capsule is strengthened by three intrinsic ligaments which are ____ , ___ , and \_\_\_\_\_. Which one is the most important and why?
1. Iliofemoral Ligament (or the Y ligament of Bigelow)- strongest and located on anterior aspect of joint- **prevents hyperextension** of the joint
2. Pubofemoral Ligament- anterior/inferior aspect of the joint capsule (prevents hyperabduction)
3. Ischiofemoral Ligament (ligament of Bertin)-a strong triangular ligament located **posteriorly**
35
Fibers of all three ligaments are oriented in a ____ fashion around the hip so as to become tight in extension
“spiral”
36
The rim of the acetabulum is surrounded by a strong fibrocartilagenous tissue called the ____ (helps protect and deepen the joint cavity)
acetabular labrum
37
The labrum stretches across the inferior aspect of the lunate surface forming the \_\_\_\_
Transverse Acetabular Ligament
38
\_\_\_ attaches to the transverse acetabular ligament and to the femoral head at the fovea
Ligament of the Head
39
\_\_\_\_ (a branch of the obturator artery) courses within the ligament of the head of the femur and helps vascularize femoral head
Small “artery of the head”-
40
Numerous arteries help vascularize the head of the femur:
* **Medial Circumflex Artery**- from deep (profundal) femoral artery (major contributor…Step 1)
* Lateral Circumflex Artery- from deep (profundal) femoral artery
* Retinacular Arteries (aka…femoral neck vessels) – are the small actual branches from the medial and lateral circumflex arteries that perfuse the femoral head
* Artery of the head- from the obturator artery that courses within the ligament of the head (considered a minor contribution)
41
two types of femoral fractures and they are referred to has hip fractures
Femoral neck fractures
and
Intertrochanteric fractures
42
\_\_\_\_ often associated with osteoporosis…have a high incidence of **avascular necrosis (AVN)** of the femoral head due to rupture of **retinacular arteries** (femoral neck vessels)
Femoral neck fractures
43
\_\_\_\_\_\_ also common "hip fracture" in elderly patients, usually from a fall. More likely to use surgical repair than mechanical device/foriegn body replacement
Intertrochanteric fractures
44
The two joints of the pelvic girdle include
sacroilliac joints (ventral and dorsal) and the pubic symphysis
45
*in addition to the sacralillio and pubic symphisis ligaments*
two strong posterior ligaments the sacrospinous ligament and sacrotuberous ligament
46
Structures of the Greater Sciatic Foramen (GSF):
1. Piriformis muscle
2. Sciatic nerve
3. Superior & inferior gluteal nerves & vessels
4. Posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
5. Pudendal nerve & Internal pudendal artery exit the GSF
47
Contents of the Lesser Sciatic Foramen
1. After exiting the GSF…the Pudendal nerve & Internal pudendal artery then enter the LSF and travel to the perineum
2. Obturator internus tendon
48
gluteal maximus is innervated by the
nInnervated by the inferior gluteal nerve (L5,S1, S2)
49
function of gluteus maximus
Functions mainly to **extend and laterally rotate** the thigh (hip)
50
function of gluteus minimus and meatus
nThese two muscles are abductors of the hip (including the tensor fascia lata)
51
innervation of gluteus minimus and meatus
nAll 3 abductors are innervated by the superior gluteal nerve (L4, L5 & S1)
52
Trendelenburg Gait
secondary to weakness of the medius/minimus or damage to the superior gluteal nerve
“compensatory” gait… where an individual shifts their body weight over the weakened side to swing the contralateral limb through the gait cycle
53
Trendelenburg test
when a patient is asked to stand on one leg to check the strength of these hip abductors…positive test is when the pelvis sags on the contralateral side which indicates weak hip abductors on the stance leg side
54
Lateral Rotators of the Hip Joint
1. Obturator Internus
2. Superior Gemellus
3. Inferior Gemellus
4. Quadratus Femoris
5. Piriformis
55
Lateral Rotators
of the Hip innervation
* All branches off the sciatic nerve
* Piriformis receives its own nerve- “nerve to piriformis”
* Obturator internus & superior gemellus are both innervated by the “nerve to obturator internus”
* Quadratus femoris & gemellus inferior are both innervated by the “nerve to quadratus femoris”
56
Posterior Thigh
Muscles
The Hamstrings
1. Semitendinosus
2. Semimembranosus
3. Biceps Femoris
57
posterior hamstring muscles innervated by
Innervated by (L5 & S1, S2) of the sciatic nerve
58
\_\_\_\_ muscle is most commonly injured of the hamstring muscles
biceps femoris
59
hamstring muscles essentially arise from the ____ and insert distal to the knee joint
ischial tuberosity
60
The hamstrings are vascularized by the ___ that arise from the deep (profundus) femoral artery
perforating arteries
61
hamstring action
Hence…they are flexors of the knee joint and extensors of the hip joint (thigh)
62
Sciatic nerve Actually contains two nerves within a common sheath:
nTibial nerve
nCommon fibular (peroneal) nerve
63
Posterior Hip Dislocations (PHD)

**Note the characteristic shortened, adducted, flexed, and internally rotated position of the affected extremity**
PHD often result from motor vehicle accidents when the femur is **flexed and adducted (sitting)**
These injuries can fracture the posterior aspect of the acetabulum and cause **sciatic nerve injury** (~10%)
These high impact injuries are considered a medical emergency- often resulting in **avascular necrosis (AVN)** due to torn/damaged femoral neck vessels
64


65
\_\_\_\_\_\_ innervates the gluteus medius, minimus, and tensor fascia lata muscles after exiting the greater sciatic foramen
The superior gluteal nerve (L4, L5 & S1)
66
nDamage to the superior gluteal nerve can result in a \_\_\_\_
Trendelenburg gait
67
nGluteus maximus is innervated by the ____ and this muscles functions when “getting up from a chair”
inferior gluteal nerve (L5, S1 & S2)
68
\_\_\_\_\_ can traumatize the sciatic nerve and have a high incidence of avascular necrosis (AVN)
nPosterior hip dislocations
69
\_\_\_\_\_ of the hip helps prevent hyperextension of the joint
nIliofemoral ligament
70
\_\_\_\_…major vascular contributor to the femoral head
nMedial circumflex artery
71
\_\_\_\_ cross the hip and knee joints… hence they extend the hip and flex the knee joint (cross two major joints)
Hamstrings muscles


