Anterior & Medial Thigh Flashcards
1
Q

A

2
Q

A

3
Q

A

4
Q

A

5
Q

A

6
Q

A

7
Q

A

8
Q

A

9
Q

A

10
Q

A

11
Q

A

12
Q

A
Osgood-Schlatter Disease (OSD) is a common pediatric knee problem that often affects active/athletic youngsters between the ages of 10 -15
Stress from the powerful quadriceps muscle inflames the not yet fully developed tibial tuberosity
Kids typically complain of pain just below the knee along the top of the shin
OSD is a self-limiting condition that typically last between 1-3 years
Most kids respond well to local therapy (rest, ice, decreased activity)
Occasionally…symptoms are so severe that a cast is applied to limit motion until the tuberosity totally ossifies
13
Q

A

14
Q

A

15
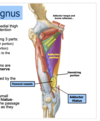
Q

A

16
Q

A
17
Q

A

18
Q

A

19
Q

A

20
Q

A

21
Q

A

22
Q

A

23
Q

A

24
Q

A

25


26

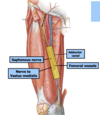
27


28


29

30


31
External iliac artery traverses beneath the inguinal ligament and becomes the \_\_\_\_
femoral artery
32
nFemoral artery passes through the adductor hiatus and becomes the\_\_\_
popliteal artery (behind the knee)
33
Popliteal artery gives rise to __ and \_\_
anterior and posterior tibial arteries
34
Anterior tibial becomes the _____ in the foot while the posterior tibial gives rise to \_\_\_\_
dorsal pedal artery (dorsalis pedis); plantar arteries (medial and lateral)
35
Deep fascia of the thigh is referred to as the \_\_\_\_
fascia lata
36
Deep fascia in the leg is referred to as the \_\_\_\_
crural fascia
37
The iliotibial band recieves fascia from
fascia lata and also receives aponeurotic contributions from the gluteus maximus muscle and a small muscle called the tensor fascia lata (TFL)
38
TFL is an ____ of the hip (and a flexor of the hip) because it positioned on the anterior/lateral aspect of the hip joint
abductor
39
TFL is innervated by the \_\_\_\_
superior gluteal nerve (L4, L5, & S1)
40
Distally, the Iliotibial (IT) band inserts into a tubercle on the **lateral condyle of the tibia** called ___ and the **patellar retinaculum**
(Gerdy’s tubercle)
41
anterior portion of the lower limb
hip flexors & knee extensors
42
medial portion of the lower limb
hip adductors
43
2 major Superficial Veins of the lower limb
1. Great Saphenous Vein
2. Small Saphenous Vein
44
Small Saphenous pierces the deep fascia behind the knee and enters the ____ (a deep vein)
popliteal vein
45
Great Saphenous ascends up the leg and thigh, passes through an opening in the fascia lata (saphenous hiatus) to enter the _____ (deep vein)
femoral vein
46
\_\_\_\_\_ vein is a common choice of
surgeons when performing vascular bypass graft surgery
Great Saphenous
47
Superficial nodes eventually drain into the \_\_\_\_\_
deep inguinal nodes
48
Deep inguinal nodes eventually drain into the ____ within the abdomen/pelvis
external iliac nodes
49
Many deep inguinal nodes are located beside the femoral vein and within the \_\_\_
“femoral canal”
50
The anterior thigh muscles can be divided into two groups:
1. Hip Flexors Muscles
2. Knee Extensors Muscles
51
These anterior thigh muscles are essentially _____ innervated
femoral nerve
52
Formed by the merger of two muscles- psoas major and the iliacus
Iliopsoas Muscle
53
Iliopsoas muscle is the chief ____ of the hip (thigh)
flexor
54
Iliopsoas passes **deep** to the **inguinal ligament** then inserts into the ___ of the femur
lesser trochanter
55
Fractures of the neck of femur (above the insertion of the iliopsoas muscle) produce a characteristic appearance of the affected limb
The fractured extremity presents **externally (laterally) rotated and shortened**
56
Psoas Abscess
Psoas arises from the lateral borders of T12 ~ L4, passes beneath the inguinal ligament, merges with the iliacus muscle…and inserts onto the lesser trochanter
The combined “iliopsoas” is an extraperitoneal (or retoperitoneal) structure which resides in close proximity to numerous organs:
**vAppendix**
**vColon**
**vSmall bowel**
**vKidneys/Ureters**
**vPancreas**
Hence, infections in these organs can spread to the iliopsoas muscle
In addition, the muscles rich vascular supply predispose it to hematogenous spread of infection from distant sites
Clinical features: Fever, low back pain, and hip/thigh pain (**Psoas Sign…pain on extension of thigh…stretches the muscle**)
Risk Factors: Diabetes, IV Drug abuse, AIDS, Immunosuppression
Patients will often prefer to be in a flexed/fetal position to relieve tension on the muscle
Treatment: Surgical drainage and IV antibiotics
57
Extensors of the Knee
Quadriceps Femoris
## Footnote
1. Rectus femoris
2. Vastus medialis
3. Vastus lateralis
4. Vastus intermedius
58
All 4 parts of the quadriceps femoris insert into the _____ and function in knee **extension/flexsion**
quadriceps tendon/ extension
59
quadriceps femoris is innervated by
nInnervated by the femoral nerve (L2, L3 & L4)
60
vertebrae of femoral nerve
nInnervated by the femoral nerve (L2, L3 & L4) quick the garbage out the door
61
the ___ of the quadriceps femoris crosses both the hip and knee joints (hence it is considered a hip flexor and knee extensor) meaning increased risk of tear
rectus femoris
62
\_\_\_ nerve Passes beneath the inguinal ligament
femoral
63
Innervates the **quadriceps** and the **sartorius** and **pectineus muscles**
Gives rise to several **anterior femoral cutaneous branches** to the anterior thigh region
Terminates as the **saphenous nerve** (also a cutaneous nerve) which provides **sensation** along the medial lower leg and foot (longest sensory nerve in the body)
femoral nerve
64
Medial Thigh Muscles
Adductor longus
Adductor brevis
Adductor magnus
Gracilis
Obturator externus
There are 5 muscles in the medial compartment which collectively **adduct the thigh at the hip**
65
medial thigh muscles mainly innervated by
nAll innervated by the Obturator Nerve (L2,3,4) ..with a couple exceptions
66
Largest and most powerful medial thigh muscle
Adductor Magnus
67
adductor magnus Classically described as having 3 parts:
1. Minimus portion (most superior portion)
2. “Adductor” portion (middle portion)
3. “Hamstring” portion (attaches to the adductor tubercle of femur)
68
adductor magnus
## Footnote
Adductor and minimus portions are innervated by the \_\_\_\_
Hamstring portion is innervated by the \_\_\_\_
obturator nerve; sciatic nerve
69
Both ____ and _____ insert into the pes anserinus on the medial tibial condyle (along with the ____ which we will study tomorrow)
gracilis, sartorius, and semitendinosus
70
between the
## Footnote
1. “Adductor” portion (middle portion)
2. “Hamstring” portion (attaches to the adductor tubercle of femur)
adductor hiatus
71
Pectineus function and innervation
can both **flex and adduct** the hip-hence can be innervated by both **femoral and/or obturator**
72
Gracilis function
long, thin **adductor muscle** (can be used for muscle grafts)
73
Sartorius function
long-thin muscle which **abducts**, **externally rotates and flexes** the hip
74
nFour major routes which structures pass from the abdomen/pelvis into or out of the lower limbs:
1. Obturator canal
2. Beneath the inguinal ligament
3. Greater sciatic foramen
4. Lesser sciatic foramen
75
Femoral Triangle
Contents:
nFemoral Nerve
nFemoral Artery
nFemoral Vein
76
femoral sheath
Encloses the proximal portions of the femoral vessels and the femoral canal
Does NOT enclose femoral nerve
77
nProtects the femoral artery and vein beneath inguinal ligament during hip movements
femoral sheath
78
femoral sheath is divided into 3 compartments
1.Lateral compartment: Femoral artery
●
2.Intermediate compartment: Femoral vein
●
3.Medial compartment: “Femoral canal” which contains deep lymphatic nodes --\> Top of the canal is referred to as the “femoral ring”
79
Femoral Hernia
nFemoral hernia is a protrusion of abdominal viscera (loop of bowel) through the femoral ring and into the femoral canal
nInitially the hernia is contained within the femoral canal but with time- can enlarge and pass through the saphenous hiatus into the subcutaneous tissues
nThe mass is generally palpated within the femoral triangle (inferior to the inguinal ligament) (ACC Case Faith Herrington)
nOccasionally- the **lacunar** ligament can “strangulate” the loop of bowel and interfere with blood supply resulting in death or necrosis of the intestine segment
nMore common in females than males
80
Femoral artery and vein then exit the femoral triangle and enter the ____ deep to the sartorius muscle
Adductor Canal
81
n4 structures course through this adductor canal:
1. Femoral artery
2. Femoral vein
3. Saphenous nerve (a sensory branch of the femoral nerve)
4. Nerve to vastus medialis (a motor branch
82
Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve-supplies ____ and ____ thigh region. This nerve can become entrapped or pinched beneath the inguinal ligament…called ____ causing burning pain and/or paresthesia to the outer thigh
superior lateral; **“Meralgia”**
83
Femoral artery and vein course through the \_\_\_, \_\_\_, and ___ finally entering the popliteal fossa behind the knee
femoral triangle, adductor canal, and the adductor hiatus
84
Adductor muscles are ____ innervated
obturator nerve (L234)
85
nLarge and powerful quadriceps muscle are ___ innervated
femoral nerve innervated (L234)
86
\_\_\_\_ common pediatric clinical condition causing knee pain
Osgood-Schlatter…
87
NAVEL
nNAVEL- nerve, artery, vein, empty space and lacunar ligament are important structures from lateral-to-medial beneath the inguinal ligament:


