Tejidos + articulaciones Flashcards
Identify tissue, parts and location

Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
(lumen, basement membrane, nuclei)
(ovary surface, kidney tubules, ducts of small glands)
Identify tissue, parts and location.

Simple Culumnar epithelium
(nucleus, basement membrane, goblet cells)
(non-ciliated lines the digestive tract (stomach to rectum), gallblader; Ciliated lines small bronchi, uterine tubes, uterus)
Identify tissue, parts and location

Simple Squamos epithelium
(nucleus, basement membrane, lumen)
(air sacs of lungs, kidney gomerulli, lining of heart, blood vessels)
Identify tissue, parts and location

Simple Squamos epithelium
(nucleus, basement membrane, lumen)
(air sacs of lungs, kidney gomerulli, lining of heart, blood vessels)
Identify tissue, parts and location

Stratified Squamous keritanized epithelium
(keratin layer, layers of dead cells (stratum granulosum), layer of keratinocytes (stratum spinosum), basement membrane)
Epidermis of skin
Identify tissue, parts and location

Stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium
(layers of squamous cells, basement membrane)
(moist lining of vagina, esophagus, mouth)
Identify tissue, parts and location

Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
(nucleus, basement membrane, goblet cells and cilia)
(Trachea, most of the upper respiratory tract)
Identify tissue, parts and location

Transitional epithelium
(resembles both stratified squamous and cuboidal; basal cells cuboidal or columnar; surface cells dome shape or squamouslike), Basement membrane, connective tissue
(ureters, bladder, part of the urethra)
Identify tissue, parts and location

Compact bone tissue. Osteon, Haversian canal, Osteocytes in lacuna, volkman’s (perforating) canal, lamellae, canaliculi

Identify tissue, parts and location

Loose connective Tissue (adipose)
cytoplasmic rim of adipocytes, nucleus, vauoles (occupied by lipid droplets)

Identify tissue, parts and location

Loose Connective tissue (areolar)
(fibroblast nuclei, elastic fibers, collagen fibers, ground substance)
(surrounds capillaries, lamina propia of mucous membranes, packages organs)

Identify tissue, parts and location

Dense regular Connective Tissue
(Fibroblast nuclei, collagen fibers woven, elastic fibers occupy free space)
(Tendons, most ligaments, aponeuroses)

Identify tissue, parts and location

Dense Irregular Connective tissue
(nuclei of fibroblast, collagen bundles in masses, irregular arranged in various directions)
(dermis of the skin, fibrous capsules of organs and joints)

Identify tissue, parts and location

White Fibrous Connective Tissue (Dense regular)
(Fibroblasts flattened in rows, collagen fibers in parallel bundles)
(The Eyes - the sclera, bursa)

Identify tissue, parts and location

Hyaline Cartilage
(Chondrocytes in lacuna, homogeneous matrix)
(embrionic skeleton, covers ends of long bones in joint cavities; costal cartilage, nose, trachea, larynx)

Identify tissue, parts and location

Elastic Cartilage
(Chondrocytes in lacuna, matrix with elastic fibers)
(external ear (pinna), epiglottis)

Identify tissue, parts and location

Fibrocartilage (similar to Hyaline cartilage)
(Chondrocytes in train like row, collagen fibers in matrix (wavy and parallel in arrangement),
(intervertebral disc, pubic symphysis, meniscst)

Identify tissue, parts

Blood smear - Wright’s stain
(Erithrocytes, white blood cells, platelets)

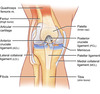
Functional Classification of Joints
1) Synarthroses (syn = together; arthro = joint): immovable joints
2) Amphiarthroses (amphi = on both sides): slightly movable
3) Diarthroses (dia = through, apart): freely movable

Diarthroses
dia = through, apart; arthro = joint freely movable. ex. in the limbs.
Synovial joints (usually)

Synarthroses
syn = together; arthro = joint immovable joints ex. in the Axial skeleton
Fibrous joints (usually)

Amphiarthroses
amphi = on both sides slightly movable ex. in the Axial skeleton

Structural classification of Joints
1) Fibrous = (Suture, Syndesmosis, Gomphosis)
2) Cartilaginous = (Synchondrosis, Symphysis)
3) Synovial = (Plane, Hinge, Pivot, Condylar, Saddle, Ball and socket)
Fibrous Joints
Bone ends / parts united by collagen fibers 1) Suture = short fibers / immobile (Synarthrosis) 2) Syndesmosis, = longer fibers / slightly movable (amphiarthrosis) & immobile 3) Gomphosis = periodontal ligament / immobile (synarthrosis)