Tejidos Flashcards
Identify tissue, parts and location

Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
(lumen, basement membrane, nuclei)
(ovary surface, kidney tubules, ducts of small glands)
Identify tissue, parts and location.

Simple Culumnar epithelium
(nucleus, basement membrane, goblet cells)
(non-ciliated lines the digestive tract (stomach to rectum), gallblader; Ciliated lines small bronchi, uterine tubes, uterus)
Identify tissue, parts and location

Simple Squamos epithelium
(nucleus, basement membrane, lumen)
(air sacs of lungs, kidney gomerulli, lining of heart, blood vessels)
Identify tissue, parts and location

Simple Squamos epithelium
(nucleus, basement membrane, lumen)
(air sacs of lungs, kidney gomerulli, lining of heart, blood vessels)
Identify tissue, parts and location

Stratified Squamous keritanized epithelium
(keratin layer, layers of dead cells (stratum granulosum), layer of keratinocytes (stratum spinosum), basement membrane)
Epidermis of skin
Identify tissue, parts and location

Stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium
(layers of squamous cells, basement membrane)
(moist lining of vagina, esophagus, mouth)
Identify tissue, parts and location

Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
(nucleus, basement membrane, goblet cells and cilia)
(Trachea, most of the upper respiratory tract)
Identify tissue, parts and location

Transitional epithelium
(resembles both stratified squamous and cuboidal; basal cells cuboidal or columnar; surface cells dome shape or squamouslike), Basement membrane, connective tissue
(ureters, bladder, part of the urethra)
Identify tissue, parts and location

Osteon, Haversian canal, Osteocytes in lacuna, volkman’s (perforating) canal, lamellae, canaliculi

Identify tissue, parts and location

Loose connective Tissue (adipose)
cytoplasmic rim of adipocytes, nucleus, vauoles (occupied by lipid droplets)

Identify tissue, parts and location

Loose Connective tissue (areolar)
(fibroblast nuclei, elastic fibers, collagen fibers, ground substance)
(surrounds capillaries, lamina propia of mucous membranes, packages organs)

Identify tissue, parts and location

Dense regular Connective Tissue
(Fibroblast nuclei, collagen fibers woven, elastic fibers occupy free space)
(Tendons, most ligaments, aponeuroses)
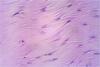
Identify tissue, parts and location

Dense Irregular Connective tissue
(nuclei of fibroblast, collagen bundles in masses, irregular arranged in various directions)
(dermis of the skin, fibrous capsules of organs and joints)

Identify tissue, parts and location

White Fibrous Connective Tissue (Dense regular)
(Fibroblasts flattened in rows, collagen fibers in parallel bundles)
(The Eyes - the sclera, bursa)

Identify tissue, parts and location
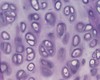
Hyaline Cartilage
(Chondrocytes in lacuna, homogeneous matrix)
(embrionic skeleton, covers ends of long bones in joint cavities; costal cartilage, nose, trachea, larynx)

Identify tissue, parts and location

Elastic Cartilage
(Chondrocytes in lacuna, matrix with elastic fibers)
(external ear (pinna), epiglottis)

Identify tissue, parts and location

Fibrocartilage (similar to Hyaline cartilage)
(Chondrocytes in train like row, collagen fibers in matrix (wavy and parallel in arrangement),
(intervertebral disc, pubic symphysis, meniscst)

Identify tissue, parts

Blood smear - Wright’s stain
(Erithrocytes, white blood cells, platelets)

Identify the parts and type of tissue

Stratified squamous epithelium keritinized

With seabseous glands
Identify structure

Lymph node
- Identify structure
- Name at least 3 histological details

- Lymph node
- histological details:
- Lymphoid follicles
- cortex,
- germinal center (contains lymphocytes),
- medulla, medullary cords, lymphatic vessels
Identify structure

Lymph node
Identify structure and functions

- Lymph node
- Filter lymph
- Produce lymphocytes
- Produce plasma cells
Identify structure

Spleen
Identify structure and its function.

- Spleen
- Its primary function is to filter the blood of antigens, microorganisms, and defective or worn-out red blood cells.
- Identify the structure
- What is the name of the structure at the tip of the pointer?

- Spleen
- White pulp = blood vessel with lymphocytes around.
- Identify the structure
- What is the name of the structure outside the pointer?

- Spleen
- Red pulp = blood sinuses w/ lymphocytes. Most of the spleen is red pulp
Identify at least 2 structures

- Artery
- Vein
- Is this an artery or a vein?
- Name the structures labeled as A, B and C

- An artery
- The tunica intima (A) = is simple squamous epithelium.
- Tunica media (B) of smooth muscle and various amounts of elastic connective tissue.
- The tunica externa (C)
- Is this an artery or a vein?
- Name the structures labeled as A, B and C
- Artery and vein size comparison

- Vein
- A, B, C
- Thin tunica media (B) of smooth muscle.
- The tunica intima (A) is simple squamous epithelium.
- The tunica externa (C) is often difficult to detect. Venules are smaller versions of a vein.
- If an artery and vein of the same size are compared, the lumen of the vein would be larger and its tunica media thinner.
Identify structure # 5

5 - lymphoid follicle of the cortex of Lymph node
Identify structure # 4

4 - medullary cords of Lymph node
Identify structure # 1

1 - cortex of Lymph node
Identify structure # 5

5 - lymphoid follicle of the cortex of Lymph node
Identify whole structure

Trachea
What type of tissue is this in the trachea?

hyaline cartilage
What type of tissue is this in the trachea and its function?

- Ciliated Pseudostratified columnar epithelium with goblet cells
- Function: Windpipe
- Goblet cells secrete mucus
- Cilia sweeps mucus and dirt out of the lungs
Name the types of tissue # 5 and # 9 in the trachea

- # 5 = ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium trachea
- # 9 = hyaline cartillage
Type of tissue

Lung tissue
Identify A, B and C in this slide

- alveoli (A)
- arteriole. (B)
- bronchiole (C)
Identify 4 structures in this slide

- R = respiratory bronchioles
- AD = alveolar ducts
- TR = terminal bronchioles
- BV = blood vessel

Identify 4 structures in this slide

- R = respiratory bronchioles
- AD = alveolar ducts
- T = terminal bronchioles
- BV = blood vessel
- AR - rings surrounding the alveolar ducts
- AS - alveolar sac (end of the duct)

- Where is this tissue from?
- Identify 1, 3, 4, 5

- Lymph node
- (1) Capsule
- (3) germinal center
- (4) Lymphatic nodule = follicle
- (5) trabecular sinus
- What type of tissue is this?
- In what part of the digestive system we can find this type of tissue and why?
- What other part in the body ?

- Stratified squamous epithelium non-keratinized
- Esophagus, Rectum, to resist abrasion.
- Vagina
- Identify these organ.
- Identify structure #2.
- Identify structure #5.
- Identify structure #6

- Esophagus
- # 2 = Stratified squamous epithelium non-keratinized
- # 5 = Submucosa
- # 6 = Muscularis externa
Identify this organ

Esophagus
Identify this organ

Intestine
- Identify this organ.
- Identify the name of at least 3 distinctive layers

- Small ntestine

Identify this organ.

small intestine
- Identify this organ.
- Identify the name of at least 3 distinctive characteristics

- Small intestine
- Villi
- Simple columnar epithelial
- Goblet cells
- Microvilli

- Identify this organ.
- Identify the name of at least 2 distinctive characteristics.

- Pancreas
- islets of langerhans (IL),
- acinar cells,
- trabeculae (CT) ;
- blood vessels (BV)

- Identify this organ.
- Identify the struture on the pointer

- Pancreas
- islets of langerhans (IL),

- Identify this organ.
- Identify the name structures #1, #2, #3

- Pancreas
- islet of Langerhans (1) form distinctive clusters that stain lighter than the surrounding cells.
- The bulk of the cells in this photo are acini cells (2), which produce the “pancreatic juice.”
- Pancreatic duct (3).

- Identify this tissue.
- In what organ is found?

- semineferous tubules
- Testis

- Identify this tissue.
- Give at least 2 characteristics that help you to identify the structure

- semineferous tubules
- large tubular structure - center of image, with spermatocytes (black, tiny, ovoid bodies). Sertoli cells and interstitial cells.

- Identify this tissue.
- In what organ is found?

- Urethra
- Penis

- Identify this tissue.
- Describe at least 2 characteristics that helped you to identify the structure

- Urethra of penis
- Penile urethra
Corpus spongiosum

- Identify this tissue.
- Describe at least 2 characteristics that helped you to identify the structure

- Ovaries
- Characteristics:
- Primary follicles
- Graafian follicle with antrum without the oocyte,
- primordial follicle

- Identify this tissue.
- Describe at least 2 characteristics that helped you to identify the structure

- Ovaries
- Characteristics:
- 1) primordial follicle
- 2) Primary follicles are somewhat larger than the primordial follicles,
- 3) Secondary follicles are larger still, and have multiple layers of epithelium;
- 4) Graafian follicle have a single large fluid-filled cavity (antrum)
- 5) oocyte

Identify structures #1 and #3 in the ovary

- 1) primordial follicle
- 3) Secondary follicles are larger, and have multiple layers of epithelium;

- Identify the tissue.
- Describe at least 2 characteristics that helped you to identify the structure

- Liver
- hexagonal lobules, central vein, hepatocytes; portal triad

- Identify the tissue.
- Describe at least 2 characteristics that helped you to identify the structure

- Liver
- hexagonal lobules, central vein, hepatocytes; portal triad

- Identify the tissue.
- Describe at least 1 characteristics that helped you to identify the structure

- Bladder
- Transitional epithelium



