Swaps, Credit default swaps and Interest Rate Derivatives Flashcards
(39 cards)
Plain Vanilla Swap
Fixed for floating in the same currency
- Li (m)
- B0 (hj)
- M-day Libor on day i
- Present value factor on a zero-coupon instrument paying $1 on day j
Value of 1.0 in principal at hn - 1

FS(0, n, m)
Fixed swap interest payment rate
Present value of a series of fixed interest payments at the swap rate FS(0, n, m)

FS(0, n, m) price
*
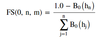
Swap value on day t
- Fixed payments = FS(0, n, m) * Σ Bt (hj) + 1 * Bt (hn)
- Floating payments = [(Value of the first floating payment on day 0) + 1] * Bt (h1)
- Value of the first floating payment on day 0 = L0 (m) * (m/360)
- Value = floating payments - fixed payments
Swap value (pay fixed/receive equity return)
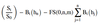
Swap value (pay floating/receive equity return)
(St / S0) - Value of the first floating payment on day 0 * Bt (h1)
CMT
Constant Maturity Treasury
OIS
Overnight Index Swap
Amortizing and accreting swaps are swaps in which the notional principal changes according to a formula related to the underlying
The more common of the two is the amortizing swap, sometimes called an index amortizing swap. In this type of interest rate swap, the notional principal is indexed to the level of interest rates
- Diff swap
- Arrears swap
- Capped swap
- Floored swap
- Combines elements of interest rate, currency, and equity swaps
- The floating payment is set at the end of the period and the interest is paid at that same time
- The floating payments have a limit as to how high they can be
- The floating payments have a limit as to how low they can be
Swaption
An option to enter into a swap
- Payer swaption
- Receiver swaption
- Allows the holder to enter into a swap as the fixed-rate payer and floating-rate receiver
- Allows the holder to enter into a swap as the fixed-rate receiver and floating-rate payer
Payoff of a payer swaption

Payoff of a receiver swaption

Variation margin
Additional margin deposited on a futures to get back to the initial margin
Invoice price
Contract size x Futures settlement price x Conversion factor + accrued interest
Cheapest-to-deliver
The bond with the highest implied repo rate
Converted price
Futures price x Conversion factor
Delivery options of the short on a CBOT Treasury bond futures contract
- Quality or swap option
- Timing option
- Wild card option
Credit derivatives types
- Total return swap
- Credit spread option
- Credit-linked note
- Credit default swap (CDS)
CDS terminology
- Single-name CDS - on one specific borrower
- Reference entity - the borrower
- Reference obligation - the particular debt instrument
- Cheapest-to-deliver obligation - the payoff on which the CDS is based



