Superficial back week 1 Flashcards
The spine of the scapula is at the level of which vertebrae?
T3
The inferior angle of the scapula is at the level of which vertebrae?
T7
The ileac crest is at the level of which vertebrae?
L4
Surface anatomy: identify the landmarks of this picture. Include the landmarks that may be used to estimate what level of the spine you are at in a physical exam.


How many vertebrae are there in each section of the vertebral column?
7 cervical
12 thoracic
5 lumbar
5 fused sacral
3-4 fussed coccygeal (coccyx)

Identify the junctions of the vertebral column.
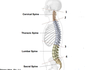
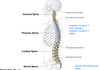
What is the shape of the spine in newborns? In adults? Why are their differences?
- newborns have a kyphotic spine
- adults have thoracic and sacral kyphosis (primary curvature) and cervical and lumbar lordosis (secondary curvature)
- the shape of the spine in adults brings the center of gravity into a vertical line and allows body weight to be balanced over the spine for energy efficent ambulation.

Identify the anatomical landmarks of the scapula and note where it attaches to other bone as well as muscles.

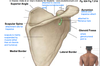
Define what muscles are considered extrinsic vs intrinsic, if they are innervated by anterior (ventral) rami or posterior (dorsal rami), and what their general functions are.
Extrinsic: innervated by anterior (ventral) rami
- Superficial layer: function in movements of the scapula and upper limbs
- trapezius (exception, is also innervated by CN, accessory nerve)
- levator scapulae
- rhomboid major and minor (diff muscles that share actions)
- latissimus dorsi
- Intermediate layer: function to move ribs, aid in respiration. so thin that they stick to superficial muscles
- serratus posterior superior
- serratus posterior inferior
Intrinsic muscles: innervated by posterior (dorsal) rami. function in related movements of the vertebral column
Identify the landmarked back muscles.
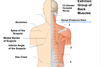

Identify the landmarked structures.
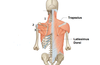

Identify the landmarked structures.


Identify the landmarked structures.
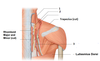

Identify the landmarked structures of the back.


What are the movements of the scapula?
protraction (abduction)/retraction (adduction)
elevation/depression
upward and downward rotation

What is are the origins, insertions, functions, and innervations of the trapezius?
origins: posterior aspects of skull, spinous processes of C7-T12 vertebrae, ligamentum nuchae
insertions: clavicle, arcromion process, spine of scapula
function:
- upper part: elevates and retracts scapula
- middle part: retracts scapula
- lower part: depresses and retracts scapula
- lower and upper parts upwardly rotate the scapula
__innervation: accessory nerve and cervical nerves 3 & 4

What are the origins, insertions, functions, and innervations of the rhomboid major and minor?
origins: spinous processes of C7-T5, ligamentum nuchae
insertion: medial border of the scapula
functions: retracts and downwardly rotates the scapula
innervation: dorsal scapular nerve
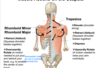
What are the origins, insertions, functions, and innervation of the levator scapulae?
origin: transverse processes of C1-C4 vertebrae
insertion: medial border of the scapula superior to the scapular spine
functions: elevates and downwardly rotates the scapula
innervation: dorsal scapular nerve and cervical nerves 3 & 4
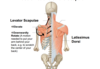
What are the origins, insertions, functions, and innervation of the latissimus dorsi?
origins: spinous processes of T6-T12, crest of ilium, inferior 3rd or 4th ribs, throracolumbar fascia, scapula (variable from person to person)
insertion: humerus
functions: depresses the scapula. adducts, medially rotates, and extends the arm at the glenohumeral joint
innervation: thoracodorsal nerve


