Sport's Medicine Flashcards
(85 cards)
Specific Injuries based on anatomic site
- Shoulder? 4
- Elbow? 2
- Knee? 4
- Foot and Ankle sprains? 1
- Shoulder
- Rotator cuff disease
- Degeneration
- Instability
- Biceps and SLAP Lesions - Elbow
- Medial pain issues
- Lateral pain Issues - Knee
- ACL
- Meniscal Injuries
- Articular Cartilage
- Anterior Knee pain - Foot and Ankle
- sprains
Who’s at risk for rotator cuff injuries? 2
- Trauma
- Repetitive overuse
- What kind of population sufferes from degenerative tenon?
- Describe the process?
- Many sports played competitively into 60’s, 70’s and 80’s
2.
- Tendons undergo normal aging and degeneration
- Sport further stress on tendon complex
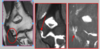
Describe whats going on in the pictures below?

- Supraspinatus- No sign of white, which is good. no fat
- More white streaks, pretty substantial tear in a younger individual. fatty white streaks
- Probably not reconstructable and have to start thinking replacable.
What is our goal for nonoperative treatment?
What are these? 6
- Reduce Inflammation
2.
- Time
- Activity shutdown
- NSAID’s
- Subacromial injection
- Modalities
- PT: ROM and Strength
Supraspinatus exercise?

Infra/Teres Strengthening?

Subscapularis Strengthening?

What is the surgical option for a Full thickness rotato cuff tear?
3
- Open Repair
- Mini-Open Repair
- Arthroscopic Repair

Describe the Open Repair for RC

Describe Mini-Open Repair for RC?

Describe the Arthroscopic repair for RC?

Post-op Course for RC surgery?
6
- Sling for 6 weeks
- Rehab for 3 mos
- Golf 4 to 5 mos
- Tennis 6 mos
- Swimming 7 to 8 mos
- Full recovery 1 year
Shoulder Arthritis:
1. Early/Moderate Tx? 5
- Severe? 1
1.
- Activity Modification
- NSAIDS
- Steroid Injections
- PT
- Arthroscopy
2. Shoulder Replacement
What is going on in the following pictures?

Osteophyte off the humerus itself. They almost always wear out posteriorly. This is best treated with a replacement.

TSR results
- Failure rate?
- Advantages? 2
- 3% failure
2.
- Predictable pain relief
- Excellent function
What is often a sign of shoulder instability?

Treatment of 1st Dislocation
- Have to determine what?
- Tx Options? 3
- Whats your biggest issue with stability?
- Anterior vs. Posterior
2.
- Reduction: X-ray
- Immediate: ER Brace
- Surgical
3. Labral tear
Instability Treatment
Open Repair
- Pros? 3
- Cons? 2
- Pro’s:
- Higher success rate
- Better in ligamentously lax
- Glenoid reconstruciton possible - Con’s:
- Risk of over tightening
- Painful post-op
What does neer test?
Biceps Disease
Neer: Outlet Impingement
What contributes to bicep dz?
3
- Acromion shape and slope
- AC joint enlargement
- Cuff and biceps problems
Biceps Degeneration/Tendonitis
How would you treat the following:
- Isolated?
- W/ Rotator Cuff Tendonitis?
- W/ Rotator Cuff Tear?
- Non-Operative Management: if failure then surgical tx
- Non-Operative Management: if failure then surgical Tx
- Surgical Tx
What tests would we do for Bicep pathology?
4

Tests for Subscap?
2
Stomach compression test
Lift off test