Spinal Cord 1 Flashcards
(35 cards)
embryologically, what are alternative names for the dorsal an ventral horns?
alar- dorsal (sensory) basal- ventral (motor)
what structure in the central canal divides the alar and basal plates?
sulcus limitans
how does the central canal change in the caudal medulla?
expands to become the 4th ventricle
where are the visceral motor and sensation nuclei located in the caudal medulla?
immediately medial and lateral to sulcus limitans
reticular formation
an expansion of the interneurons in the caudal medulla that serve feeding, breathing, eye way protection, swallowing, etc. reflexes
most lateral nuclei in brainstem do what?
receive somatic afferent (chief sensory nucleus of the trigeminal nerve) and special somatic senses (vestibular, cochlear)
what nuclei are immediately lateral to the sulcus limitans
visceral sensation (solitary nucleus, gustatury nuclei)
chief sensory nucleus of trigeminal
in pons, somatic sensory input from trigeminal
spinal nucleus of trigeminal
in medulla, somatic sensory input from trigeminal, vagus, facial, glossopharyngeal
solitary nucleus
vagal sensory from thorax/abdomen glossopharyngeal sensory carotid body/sinus
nuclei immediately medial to sulcus limitans
visceral motor nuclei dorsal motor nuclei of vagus salivatory nuclei
dorsal motor nuclei of vagus
parasympathetics of upper thoracis and abdomen
salivatory nuclei
parasympathetics to salivary and lacrimal glands
medialmost cranial nerve nuclei
somatic motor hypoglossal, abducens. trochlear, and oculomotor nuclei
location of motor nuclei to pharyngeal arches
medial and ventral of sulcus limitans
nucleus ambiguus
located in medulla, pharyngeal arch nuclei muscles of the larnyx, pharynx, and soft palate
facial nucleus
pharyngeal arch nuclei innervate muscles of facial expression
motor trigeminal nucleus
pharyngeal arch nuclei, muscles of masticatino mid medulla




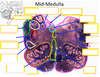


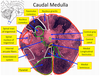

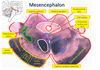
damage to the vestibular nerve causes what?
disrupts balance and causes vertigo and nytsagmus


