SNS/PNS drugs Flashcards
Used for post op Ileus;, neurogenic ileus and urinary retention via Activating bowel and bladder smooth muscles.
Bethanechol
Direct Ach Agonists or Cholomimetic
Bethany activates your Bowels and Bladder
What drug can we use for Gluacoma because it cause pupillayr contriction and provides relief of introcular pressure?
Carbachol
= Carbon copy of acetycholine
Used to treat people with Open angle and Closed angle glaucoma but causes stimulation of sweat, tears and saliva
Pilocarpine
Ach Direct agonist; contracts ciliary mucle of the eye (for open angle)
in closed angle is causes pupillary CONSTRICTION
You cry, sweat, and drool on your PILlow
Stimulates the muscarinic receptors in airway when inhaled
used to dx asthma
Methacholine
Drug used post-operatively for neurogenic ileus and urinary retention.
Helps with mysethenia gravis
What is it’s mechanism?
Neostigmine
Indirect agnosist or Achecholinesterase Inhibitor
What is the MOA of Neostigmine?
When do we use it?
What are it’s limitiation?
Neostigmine = Acetylcholinesterase inhibitor thus INCREASE endogenous Ach
Uses: Post op ileus and to Tx urinary retention, Myasthenis Gravis
Neo or NO ≠CNS penetration
If you wanted to give someone medication for Myasthenia Gravis that they didn’t have to take often, what would it be?
MOA?
Pryidostigmine (long acting)
Acetlcholinesterase inhibitor, Increase Ach and increase pts Strength
PyRIDostiGMine gets RID of Myasthenia Gravis
What NT is low in Alzeihmers? How can help with this?
Alzeihmers have Low Ach: give acetycholinesterase inhibitor
Donepezil, Rivastigmine, Galatamine
Old man comes in after working outside. He’s flushed, red and very aggitated. He has dry oral mucosal membranes and cycloplegia (loss of ability to accomidate with ciliary musl).
What could he have been exposed to while outiside to cause symptoms?
What is the treatement and why?
Think Jimsonweed = alkaloid which causes ATROPINE overdose
Give pts PHysiostigmine
Physiostigmine, phyxes atropine OD (it’ an acetlycholinesterase inhibitor)
When do we use PHysiostigmine?
What’s it’s mechanism of action?
Used for Anticholinergic toxicity (like atropine overdose)
Acetycholinesterase inhibitor
will cross the BBB
may be used for glaucoma
What once use to dx Myasthenia Gravis?
What the MOA?
Edrophoinum
short acting acetycholinesterase inhibitor to increase endogenouch Ach
What is the clinical applicaiton of Doneprizil?
Used for Alzheihmers: it’s and Acetycholinesterase inhibitor
What is a side affect we need to be aware of when prescribing Acetycholinesterase inhibitors?
Exacerbation of COPD, asthma and Peptic ulcers
” most end in imine”
Neostigmine, Pyridostigmine, Physostigmine, Edrophinium and Donepezil, rvastigmine, galantamine
Pt comes in with Diarrhea, cough, excessive sweating and his eyes are tearing
HR: 55 but he feels very jittery.
What did he OD on?
What do you rx?
DUMBELLS for too much Ach: seen in organophosphate poisoning = acetycholinesterase inhibitor
Tx = Atropine (competitive inhibitor) + Pralidoxime (regenerates AchE if given early)
What two meds do we rx for pt with Acetycholinesterase inhibitor poisoning?
Give atropine (muscarininc antagonist) which is a competitive inhibitor
*Atropine will not correct skeletal muscle excitation)
And Pralidoxine which can regenerate AchE (this will correct skeletal muscle excitation)
What is the action you see with Atropine, Homotropoine and Tropicamide?
What receptor do they act on?
Used as eye drops to cause Mydriasis or pupil dialation
Blocks binding of Ach to the Muscarinic receptor thus NO pupil constriction
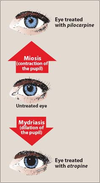
What different actions does pilocarpine and atropine have on the eye?
Pilocarpine is a cholimimetic or Ach drug. Binds to M3 to cause pupil cnx
Atropine is an muscarininic competitive antagonist; blocks site where Ach thus INHIBITING the pupil constriction
When would you give a patient Benztropine?
What is it’s mechanism of action?
Benztropine is used in Parkinosns
muscarining antagonist on the GABA receptor
“Park my Benz”
When would we prescribe Scopolamine?
How does it work?
Scopolamine is motion sickness pathc
muscarinic antagonist (targets M1 in CNS)
Why would we prescribe Ipratropium or Tiotriupium to asthmatic patient?
Ipratropium and Tiotropium are muscarinic antagonists
compete at M3 receptor = Bronsoconstriciton which asthmatics don’t like
What is teh clincal application of Oxybutynin?
What is it’s MOA?
Oxybutynin is muscarinig antagonist
Used to tx OVERACTIVE bladder (when Ach binds M3 receptores = bladder cnx)
Oxybutynin is competitive antagonist to inhibit binding
Oxybutynin = OxybuTOILET

What drugs are used to treat Spastic bladder?
How do they work?
Oxybutynin, Tolterodine, Darfenacin and Trospium
= On The Darn Toilet
musc. antagonist at the M3 receptors to decreased bladder tone.