SLE Flashcards
What is systemic Lupus erythematosus?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0junqD4BLH4
A multisystemic autimmune disease in which auto-antibodies are made against a variety of autoantigens. It presents as a multi-system inflammatory disease with a wide range of clinical manifestations. Most of these manifestations can be explained on the basis of excess production of pathogenic autoantibodies.
What are the four key pathological processes that underlie the autoimmune rheumatic diseases?
- Inflammation
- Fibrosis or scarring
- Vasospasm
- Vascular thrombosis
What is the prevalence of SLE?
1/4000
Which sex is more affected by SLE?
Females - 9:1
What age does SLE most commonly affect?
Can present at any age, but peak age at onset:
- Late third – early fourth decade of life
- Second peak in the sixth decade
What is thought to cause SLE?
Unknown, however risk factors include:
- UV light exposure
- Female sex hormones
- Certain drugs, e.g. chlorpromazine, hydralazine and isoniazid.
- Smoking
What types of hypersensitivity reactions are thought to occur in SLE?
Type II and Type III
What are the diagnostic criteria for lupus?
Use SOAP BRAIN DRAM - Diagnose if >/= 4 criteria
- Serositis
- Oral Ulcers
- Arthritis - non erosive
- Photosensitivity
- Blood disorders
- Renal disorder
- ANA positive
- Immunological Disorder
- Neuro disorders
- Discoid rash
- Raynauds
- Alopecia
- Malar Rash

What is serositis?
Inflammation of serous membranes
What serous membranes can become inflammed in SLE?
- Pleura - Pleuritis
- Pericardium - Pericarditis
What is the following?

Malar Rash
Fixed erythema, flat or raised, over the malar eminences, tending to spare the nasolabial folds
What is thought to be the mechanism behind malar rash?
Immune complex deposition caused by various factors

What are features of pleuritis caused by SLE?
- Pleural friction rub
- Chest pain - pleural
- Pleural effusion
What are features of pericarditis caused by SLE?
- Chest pain
- Pericardial friction rub
- Pericardial effusion
- ECG changes
What is the following?
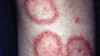
Discoid Rash
Erythematous raised pathces with adherent keratoric scales and follicular clugging +/- atrophic scarring. It has 3 stages:
- Erythema
- Pigmented hyperkeratotic oedematous papules
- Atrophic depressed lesions
Where are discoid rashes most commonly found in SLE?
- Ears
- Cheeks
- Scalp
- Forehead
- Chest
What are features of renal disorder in SLE?
- Persistent Proteinuria > 0.5g/day
- Cellular casts - red cell, granuar, mixed
What are features of CNS disorder in SLE?
In absence of drugs or metabolic imbalance
- Seizure
- Psychosis
What are features of haematological disorder in SLE?
- Leucopenia
- Haemolytic anaemia
- Thrombocytopenia
- Lymphopenia
What are features of immunological disorder in SLE?
- ANA
- Anti-dsDNA antibody
- Anti-Sm antibody
- Antiphospholipid antibody - either IgG or IgM anticardiolipin OR a positive lupus anticoagulant OR a biological false-positive test for syphilis
- Low complement
- Direct coombs test positive
What type of arthrtis most commonly presents in SLE?
Non-erosive small joint symmetrical polyarticular arthritis
What is jaccoud’s arthropathy?
A reversible deforming arthropathy causing capular/ligametnous laxity, causing deformities similar to those seen in rheumatoid arthritis

What are non-specific constitutional symptoms of systemic upset seen in SLE?
- Malaise
- Fatigue
- Myalgia
- Fever
- Weight loss
Why are people with SLE at increasedd risk of thromboembolism?
The propensity to thrombosis is related to the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies, which reflect a pro-coagulant state. In addition, blood vessel inflammation can impair the normal anticoagulant properties of the endothelium. As a result, patients with SLE are at increased risk of VTE, arterial thrombosis and adverse pregnancy outcomes
Besides features outlined in the diagnostic criteria for lupus, what other features can be present?
- Lymphadenopathy
- Alopecia
- Nail-fold infarcts
- Libman Sacks Syndrome - Non-infective endocarditis
- Raynaud’s
- Migraine
- Stroke
- Retinal exudates
Why is infection a common complication in SLE?
Active disease is associated with complement consumption, relative hyposplenism, neutropenia and lymphopenia. In addition to low absolute counts, leucocyte function is also impaired.
Drugs such as corticosteroids and immunosuppressive agents increase the propensity to infection.
It is also not unusual for infection to coexist with a flare-up of the underlying inflammatory disease and, therefore, sepsis needs to be considered carefully in most clinical settings
What is raynaud’s phenomenon?
Raynaud’s syndrome/phenomenon occurs in the digits from various stimuli, resulting in peripheral hypoperfusion followed by hyperaemia.

What are the 3 stages of Raynaud’s phenomenon?
- White – blanching associated with vasoconstriction of the blood vessels
- Blue – cyanosis
- Red – when blood flow is restored and hyperaemia results.
What is the mechanism behind raynauds phenomenon?
Occurs due to an exaggerated vasoconstrictive response causing transient cessation of blood flow to the digits which is thought to be multifactorial.
In secondary raynauds, Structural vascular abnormalities (in addition to the factors outlined above) are thought to play a role.
What percentage of those with SLE develop raynauds?
30-50%
What is Libman-Sacks Syndrome?
A form of nonbacterial endocarditis that is seen in association with systemic lupus erythematosus. It is one of the most common heart-related manifestations of lupus (the most common being inflammation of the fibrous sac surrounding the heart).
What is the following?

Discoid lupus
Discrete areas, associated with scaling, hypo- or hyper-pigmentation and loss of associated skin appendages
Why can people with SLE get alopecia?
If they get discoid lesions on their scalp
What investigations might you do if you suspected SLE?
- Examination
- ECG
- BP
- Bloods - FBC, U+E’s, ESR, CRP, LFTs, complement (C3, C4), ANA, Anti ds-DNA, Anti Ro, Anti-Sm, Anti-La
- Urinalysis
- CXR
What are the 3 best tests to do if you suspect SLE?
- Anti-dsDNA
- Complement
- ESR
When would you think of SLE as a possible diagnosis in a clinical context?
If someone had a multisystem disorder and had an increased ESR but normal CRP. If CRP was elevated, consider:
- Infection
- Serositis
- Arthritis
What drugs can cause lupus?
- Isoniazid
- Hydralazine
- Procainamide
- Quinidine
- Chlorpromazine
- Minocycline
- Phenytoin
What percentage of SLE patients are ANA positive?
95%
What percentage of SLE patients are Anti-dsDNA positive?
60%
What mgiht be seen when looking at complement in SLE?
Decreased C3/C4
What is the prognosis for someone with lupus?
Increased long-term risk of cardiovascular disease, osteoporosis and infection
How would you treat an acute flare of SLE?
IV cyclophosphamide and high dose prednisolone
How you you treat mild non life-threatening SLE?
- Topical therapies - for rashes
- NSAIDs
- General lifestyle advice - avoidance of sun exposure
How would you treat mild-moderate SLE?
- NSAIDs
- Anti-malarials - hydroxychloroquine, Chloroquine, Mepacrine
- Methotrexate
- Leflunomide
- Azathioprine
- Low-dose corticosteroids
How would you treat someone with lupus nephritis?
- Immunosupression - steroids, cychlophosphamide or mycophenalate
- BP control - ACEi, CCB, alpha blockers
- Renal replacement therapy
Most patients switched to azathioprine or mycophenolate once disease is controlled
How would you treat raynaud’s phenomenon?
Vasodilators - Nifedipine, Amlodipine, Prostacylin
Why would you measure BP when investigating SLE?
If they had lupus nephritis - BP changes need to be managed
How would you manage the risk of osteoporosis as a late complication of SLE?
- Calcium
- Vitamin D
- Risedronate
- Alendronate
- Calcitriol
What are features of antiphospholipid syndrome?
- Recurrent miscariage
- Arterial thrombosis
- Recurrent/atypical venous thrombosis
- Pre-eclampsia
- Foetal growth restriction
- Thrombocytopenia
- Arterial thrombosis
How would you investigate for anti-phospholipid syndrome?
Lupus anticoagulant +/- anticardiolipin antibodies


