Rheumatoid Arthritis Flashcards
What Is rheumatoid arthritis? (i.e the defintion of the disease)
- Chronic auto immune systemic illness - Symmetrical destructive peripheral polyarthritis and other systemic features
- Predisposition for the hands, particularly the IP, MCP and wrist joints, but can affect any synovial joint.
What is the general Prevalence of RA?
Prevalence - 1%
What is the pathogenesis and pathology of RA?
- No clear antigen identified
- Whatever the trigger ⇒ evidence of both innate and adaptive immune responses → Pro-inflammatory melieu dominated by cytokines such as TNF and IL-6.
- Pathologically, the picture is of (see image)
- Inflammed synovial membrane
- Pannus formation - abnormal layer of fibrovascular tissue or granulation tissue. Pannus basically refers to the hypertrophied synovium
- Synovial fluid containing neutrophils (Major cell type - there are others!!)

What is the diagnostic classficiation system used for diagnosing RA?

American college of Rheumatology/European Union League Against Rheumatism classification criteria
What is the typical presentation of RA?
- Progressive, symmetrical peripheral polyarthritis of hands and feet
- Worse in the morning
- Eased by movement
- Can fluctuate
- Can have extra-articular signs
What are the late SIGNS of RA?
- Ulnar deviation
- Dorsal Wrist Subluxation
- Bouttonieres
- Swan neck deformities
- Z-deformity of the thumb
- Ruptured hand extensor tendons
- Large joints
- Wasting of interossei

Think basic…
What are the general SYMPTOMS of RA?
- Pain
- Stiffness
- Immobility
- Poor function
- Systemic Symptoms
What are the early SIGNS of RA?
- Swelling
- Joint effusions
- Tenderness
- Limitation of Movement
- (Redness)
- (Heat)
What are the non-specific extra-articular Signs/Symptoms?
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
- Anaemia
How is disease activity assessed?
(Specifically describe the scoring system and the cut-offs for differing levels of disease activity)
DAS 28 Score
- “An objective method for measuring disease activity”
- >5.1 = Active disease
- <3.2 = low disease activity
- <2.6 = Remission
PLUS - CRP/ESR + Global Health assessment

What are the Eye symptoms that can be seen in RA?
- Sicca syndrome
- Scleritis/episcleritis
What other possible diagnoses could there be for a presentation similar to RA? (i.e. differential diagnosis?)
- Post-viral arthritis: rubella, hepatitis B or erythrovirus
- Seronegative spondyloarthropathies
- Polymyalgia rheumatica
- Acute nodal osteoarthritis (PIPs and DIPs involved)
What investigations would you perform to diagnose RA?
- FBC, ESR, CRP
- RF
- Anti CCP, ACPA
- Joint aspiration - If effusion is present
- X-rays
- US/MRI
How is RA managed?
Analgesia
- NSAIDS
DMARDS - 1st line; should ideally be started within 3 months of persistent symtpoms. Can take 6-12 weeks for symptomatic benefit. Examples include:
- Methotrexate
- Sulfasalazine
Biologics - Idicated in active disease defined by DAS > 5.1. Adequate therapeutic trial of at least 2 standard DMARDs (including methotrexate) without improvement.
- Anti-TNF - Entaracept, Infliximab, Adalimumab
- IL-1, IL-6 - Tocilizumab
- B-cells - Rituximab
- T-cells - Abatacept
Steroids - used in acute flares to rapidly reduce symptoms and inflammation
Physio and OT input
What are poor prognostic markers of RA?
- Age
- Female sex
- Symmetrical small joint involvement
- Morning stiffness >30 min
- >4 swollen joints
- CRP >20
- Positive RF and ACPA
- X-rays with early erosive damage (note: ultrasound and MRI can show cartilage and bone damage prior to conventional X-rays).
Which gender does RA more commonly affect?
Females>Males - 3:1
When is the peak age of onset?
Peak age - 4th-5th decade
What is the cause of RA?
Unknown
What risk factors are associated with the development of RA
- HLA DR4/DR1
- Cigarette smoking
- Chronic Infection (e.g. periodontal disease)
What is Rheumatoid Factor?
- Circulating autoantibodies - Fc portion of IgG as their antigen
- Transient production an essential part of the body’s normal mechanism for removing immune complexes
- In RA, RF shows higher affinity for immune complexes, production is persistent and it occurs in the joints
- Approx. 70% of people with polyarticular RA have serum IgM RF
What are Anti-cyclic citrullinated antibodies (Anti-CCP, ACPA)?
- Citrullination - post-translation modification of the amino acid arginine to citrulline in a protein ⇒ changes both peptide sequence and charge ⇒ can escape conventional tolerance mechanisms.
- Bacterial citrullination of self proteins in inflammation can also cause the same effect
- ACPA present in RA along with RF - Highly specific for RA together
Which joints are most commonly affected in RA?
- MCP
- PIP
- DIP
- Wrist
- MTP
Is the arthritis seen in RA symmetrical or asymmetrical?
Symmetrical
What are the different components to the diagnostic classification system for RA?
- Joint involvement
- Serology
- Acute phase reactants
- Duration of symptoms

What are the respiratory symptoms seen in those with RA?
- Rheumatoid nodules
- Pleural effusions
- Fibrosing alveolitis
- Pneumoconiosis (Caplans syndrome)
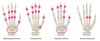
What are the following?

Rheumatoid nodules - image represents common sites for them to develop

What deformity is the following?

Ulnar deviation
What deformity is this?

Boutonniere deformity
What is this deformity?

Swan Neck Deformity
What deformity is this?

Dorsal wrist subluxation
What deformity is this?

Z-Deformity of the thumb
The following scans were taken from someone with RA. What do they show?

Pulmonary Rheumatoid nodules
What are features seen in the nervous system of those with RA?
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Peripheral Neuropathy
What are the features on the skin seen in RA?
Rheumatoid nodules - particularly elbows
What features on an X-ray would indicate RA?
- Soft tissue swelling
- Juxta-articular osteopenia
- Decreased joint space
- Bony erosions
- Subluxation
- Complete carpal destruction
What score on the EULAR/ACR classification criteria is regarded as being diagnostic for RA?
Scores >/= 6/10
What is Caplan’s syndrome?
Combination of RA and pneumoconiosis (occupational lung disease and a restrictive lung disease caused by the inhalation of dust, often in mines and from agriculture)
Presentation - with cough and shortness of breath with RA features
What is koebner phenomenon?
The appearance of skin lesions on lines of trauma. The Koebner phenomenon may result from either a linear exposure or irritation. This explains why rheumatoid nodules grow on the elbows etc.
What is the anatomical abnormality that occurs in a boutonniere’s deformity?
Rupture of the central slip of the extensor mechanism of the finger - Buttonhole deformity
What is the anatomical abnormality that occurs in swan neck deformity?
Rupture of the lateral slip of the extensor mechanism in the finger
What are the main side effects to methotrexate use?
- Pulmonary fibrosis
- Liver toxicity
- Bone marrow suppression
What drugs are contraindicated in someone using methotrexate?
- NSAIDS - excretion is inhibited by nsaids
- Trimethoprim - another folate antagonist
What class of drug is methotrexate?
Folate antagonist
What is the action of sulfasalzine?
Inhibits production of TNF and sytokines
What can be a cause of sudden death in Rheumatoid arthritis?
Atlanto-axial subluxation

How does atlanto axial subluxation occur in rheumatoid arthritis?
Rheumatoid tenosynovitis weakens tendons around odontoid peg - the peg can sublux backwards and compress the spine. This can present in two ways:
- Slow subluxation - spastic tetraparesis
- Acute subluxation - Cardiac arrest due to vagus nerve compressing
What is important to do pre-operatively in someone with rheumatoid arthritis?
Lateral upper cervical spine radiograph in gentle flexion - look for atlanto-axial subluxation
How would you distinguish RA from PA clinically?
DIP joints often spared in RA, whereas PA is mainly DIP joints involved

How would you distinguish RA from OA clinically?
OA does not involve the MCP, whereas RA does
What is impoprtant for those on methotrexate to take?
Folic acid 5 mg
How long are steroids given for in RA?
Until onset of DMARDS


