Skin and Systematic Disease Flashcards
skin signs of GI disease
what are GI genetic conditions causing skin manifestations?
Hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia
Ehlers danlos (collagen) – poor collagen in blood vessel = likely to burst and bleed
Pseudo xanthoma elasticum (elastic)
Blue rubber bleb naevus
-> GI haemorrhage

What GI Inflammatory/Autoimmune cause skin manifestions?
Malignant atrophic papulosis (degos disease) – GI haemorrhage
Erythema nodosum
Pyoderma gangrenosum
> IBD

what vitamin deficiencies cause skin manifestations?
Scurvy/Beriberi

Skin signs of endocrine disease
what skin manifestations does diabetes cause?
- Acanthosis nigricans
- Diabetic bullae
- Diabetic dermopathy
- Eruptive xanthomas
- Necrobiosis lipoidica

what skin manifestations does thyroid disorders cause?
- Hyperthyroid - Thyroid acropachy
- Hypothyroid - Pre-tibial Myxoedema

what are autoimmune conditions cause skin manifestations?
Cutaneous lupus
Cutaneous vasculitis
Alopecia
Vitiligo
how does cutaneous lupus present?
Lupus has different types of presentations
Cutaneous – Butterfly rash
- Plaques with clear margins
- Photosensitivity
- Negative antibodies
may be drug related

what causes Vasculitic rashes?
Small vessel vasculitis (commonest)
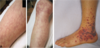
what is alopecia and what are some differnetial diagnosis?
Alopecia areata
T-lymphocyte, cytokine rejection of hair
Totalis - total hair loss
Universalis
Differential dx:
- Scarring alopecia
- Androgenic alopecia
what is Vitiligo?
Segmental
Generalised
Destruction of melanocytes
Associated with other autoimmune conditions

do skin conditions have an association with an underlying malignancy?
Some skin conditions have stronger associations with underlying malignancy, while others have less strong association
there may be an underlying malignancy in most cases in what diseases?
Carcinoid Syndrome
Ectopic ACTH
Pagets disease
Paraneoplastic pemphigus
Acquired hypertrichosis
Erythema Gyratum Repens
Bazex Syndrome
Leser Trelat
what is Carcinoid Syndrome?
- Episodic flushing, mins -hours - No sweating (unlike menopause)
- Facial telangiectasia
- GI carcinoid = liver mets
- Bronchial, ovarian = can occur with no liver mets

what is Ectopic ACTH syndrome?
- Tumour production of ACTH leads to generalised hyperpigmentation
- ACTH -> Inc. MSH -> release of melanin from melanocytes

what is Pagets & Extra-Mammary Pagets
Paget’s Disease
- Eczematous Plaque (nipple/Areola)
- Extension of underlying ductal adenocarcinoma
Extra-Mammary Pagets
- Usually axilla or ano-genital areas
- Intraepithelial adenoca in ¾ cases
what is Paraneoplastic Pemphigus?
Erosive stomatitis, rash
Auto-antibodies driven
Non-hodgkins, Castlemans disease
Pemphigus – autoimmune blistering condition
Haemorrhagic erosions on lips and inside the mouth

what is Acquired hypertrichosis lanuginosa?
Acute onset of lanugo hairs at face & body
Colorectal ca > lung > breast, usually advanced
very rare

what is Erythema Gyratum Repens?
Concentric erythematous lesions
Associated with Lung ca > Oesophageal,Breast
Very rarely with -Mycobacteial infection, Pregnancy

what is Bazex Syndrome?
- Symmetrical hyperkeratosis of extremities - Acrokeratosis neoplastica
- Resembles psoriasis, non-specific fx on skin biopsy
- SCC: Bronchial, oropharyngeal, Gastric, colon, biliary adenocarcinomas

what is Leser-Trelat?
Eruptive seborrhoeic keratosis
GI adenocarcinomas

what are conditions associated with cancer?
Acanthosis Nigricans
Dermatomyositis
what is Acanthosis Nigricans?
Can preceed malignancy (gastric adenocarcinoma). ?related to by-products. Concern if:
Older patient, rapid onset
Involves lips
Weight loss





