Anatomy Pre-Practical Lecture Flashcards
study this diagram:

the transpyloric plane is in line with what vertebra?
L1
what is found along the transpyloric plane?
- Pylorus of stomach
- Neck of pancreas
- 2nd part of duodenum, duodenojejunal flexure
- Hilus of kidney
- Origin of portal vein
- Start of SMA (superior mesenteric artery)
- Termination of the spinal cord

do the kidneys move with respiration or are they static?
they move
what kidney is lower and why?
right due to the liver pushing down on it
what do the fascial coverings do for the kidneys?
afford it proteciton

what are the layers of the surrounding layers of the kidneys?
- Fibrous renal capsule
- fatty renal capsule = peri-renal fat
- renal fascia – fibro-fatty tissue = gerotas or peri-renal fascia
- pararenal fatty tissue – mainly on the posterior aspects of the kidney

how are the kidneys peritonised?
retroperitoneal
what are the anterior relations of the kidney?

what are the posterior relations of the kidneys?
superiorly - diaphragm
inferiorly and medially - psoas major
inferorly and laterally - quadratus lumborum

what is a horseshoe kidney?
- Inferior pole fused. Isthmus made up of fibrous tissue/functioning parenchyma
- Can have abnormal position, abnormal insertion of ureter
- More prone to hydronephrosis (kidney swells due to urine failing to properly drain), infection, stone formation, tumours

what is shown here and what is it and what problems does it cause?

Duplicated ureter
Formed due to duplication of ureteric bud from the mesonephric duct
Can be entirely asymptomatic
Can result in vesicoureteric reflux and UTI
may be incidental finding and cause no problems or may cause increased predisposition to things like UTI
a

renal cortex
b

renal medulla
c
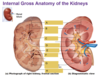
major calyx (2 or 3 og these)
d

renal pelvis
e

minor calyx
f

ureter
g

renal cloumn (projects from cortex)
h

fibrous capsule
are the renal veins or arteries more anteiror
renal vein rome anterior as would get squashed at the back

what is the functional unit of the kidney?
The nephron, the functional unit of the kidney, is responsible for removing waste from the body. Each kidney is composed of over one million nephrons that dot the renal cortex, giving it a granular appearance when sectioned sagittally
a

cortex
b

medulla
c

capsule
d

proximal convaluted tubule
e

renal corpuscle
f

distal convoluted tubule
g

collecting tubule
h

loop of henle
i

colelcting duct
j

bowmans space
a

renal corpuscles
b

convoluted tubules
c

bowmans capsule
d

arterioles
e

space within bowmans capsule
what are the sites of constriction of the ureter?

what can commonly happen at the sites of constriction of the ureter?
ureter calculi/stones
Stanes can cause……..
Stones cause back pressure so the ureter above the calculus dilates
each of the following can be used to look for what?
CT KUB
MRI renal
CT KUB – ureteric calculus
MRI renal – renal cyst


