Semi-final pool the rest (organized) Flashcards
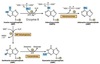
Which amino acid is an activator of N-acetyl-glutamate synthase?
Select one:
a. glutamine
b. lysine
c. arginine
d. aspartate
e. asparagine
The correct answer is:
c. arginine
In what form is ammonia transported from muscle to the liver?
Select one:
a. asparagine
b. arginine
c. leucine
d. glutamine
e. valine
The correct answer is:
b. glutamine
Which hepatocytes express the highest activity of the ornithine cycle enzymes?
Select one:
a. periportal
b. pericentral
c. perivenous
d. centrolobular
The correct answer is:
a. periportal
Which amino acid contributes to the increase in the activity of sirtuins?
Select one:
a. tryptophan
b. phenylalanine
c. tyrosine
d. valine
e. glutamine
The correct answer is:
a. tryptophan
What is the effect of acidosis on the activity of glutamine synthesis in the liver?
Select one:
a. increase in the periportal hepatocytes
b. increase in the pericentral hepatocytes
c. decrease in the perivenous hepatocytes
d. decrease in all regions of the lobules
answer:
b. increase in the pericentral hepatocytes
Which amino acid does NOT contribute to the formation of pyruvate in the course of its degradation?
Select one:
a. Alanine
b. Glutamine
c. Tyrosine
d. Leucine
e. spartateAAspartate
The correct answer is:
d. Leucine
Which amino acid can NOT provide any C-atom for the synthesis of glucose in humans?
Select one:
a. Glutamate
b. Isoleucine
c. Leucine
d. Phenylalanine
e. Tryptophan
The correct answer is:
c. Leucine
Which pair of amino acids are released at the highest concentration from skeletal muscle in the fasting state?
Select one:
a. Glutamate, aspartate
b. Glutamine, asparagine
c. Alanine, glutamine
d. Alanine, leucine
e. Valine, leucine
The correct answer is:
c. Alanine, glutamine
What happens in the course of glutaminolysis?
Select one:
a. Glutamine is converted to aspartate
b. Glutamine is converted to asparagine
c. Glutamine is completely oxidized to CO2 and water
d. Glutamine is converted to glucose
The correct answer is:
a. Glutamine is converted to aspartate
Which amino acid is the most common source of the 1C-groups transferred by tetrahydrofolate?
Select one:
a. Alanine
b. Serine
c. Threonine
d. Isoleucine
e. Methionine
The correct answer is:
b. Serine
Deficiency of which vitamin would cause enhanced excretion of methylmalonate in the urine?
Select one:
a. B1
b. B2
c. biotin
d. B12
e. D
The correct answer is:
d. B12
Which amino acids should be enriched in the diet of a patient with phenylketonuria?
Select one:
a. Phe, Gln
b. Arg, Lys
c. Trp, Tyr
d. Asp, Glu
e. Ala, Glu
The correct answer is:
c. Trp, Tyr
Which interconversion includes glutamic semialdehyde as an intermediate?
Select one:
a. Arginine to Proline
b. Glutamate to Glutamine
c. Glutamate to α-ketoglutarate
d. Methionine to Threonine
The correct answer is:
a. Arginine to Proline
Which vitamin is a co-factor in the synthesis of hydroxyproline?
Select one:
a. B1
b. B2
c. B6
d. B12
e. C
The correct answer is:
e. C
What is the role of Se in the function of the thyroid gland?
Select one:
a. Se participates in the structure of thyroxine
b. Se participates in the structure of thyroglobulin
c. Se participate in the structure of deiodinase
d. Se forms a complex with iodine to activate it for thyroxine synthesis
The correct answer is:
c. Se participate in the structure of deiodinase
How is the nitrogen balance changed, if the food is depleted of Leu, but all other amino acids are doubled?
Select one:
a. no change
b. negative N-balance
c. positive N-balance
d. positive N-balance only in children
e. positive N-balance only in adults
The correct answer is:
b. negative N-balance
How is the nitrogen balance changed, if the food is depleted of Glu, but all other amino acids are doubled?
Select one:
a. no change
b. negative N-balance
c. positive N-balance
d. negative only in children
e. positive N-balance only in adults
The correct answer is:
a. no change
Dietary supplementation with which amino acid could counteract the sleep-promoting effect of serotonin?
Select one:
a. Glu
b. Trp
c. Leu
d. Lys
e. Arg
The correct answer is:
c. Leu
Which one is a metalloprotease?
Select one:
a. pepsin
b. trypsin
c. elastase
d. carboxypeptidase
e. chymotrypsin
The correct answer is:
d. carboxypeptidase
Which zymogen does not need another protease for its activation?
Select one:
a. trypsinogen
b. pepsinogen
c. chymotrypsinogen
d. proelastase
The correct answer is:
b. pepsinogen
Which amino acid is present in the active site of the proteasome proteases?
Select one:
a. Aspartate
b. Tyrosine
c. Lysine
d. Threonine
e. Trpyptophan
The correct answer is:
d. Threonine
Which metal ion is present in the active site of the matrix metalloproteases?
Select one:
a. Zn2+
b. Fe2+
c. Fe3+
d. Cu2+
e. Ca2+
The correct answer is:
a. Zn2+
Which amino acid acts as a signal to suppress autophagy?
Select one:
a. Glycine
b. Leucine
c. Glutamate
d. Glutamine
e. Arginine
The correct answer is:
b. Leucine
Which compound is the first N-free intermediate released in the indirect deamination of aspartate?
Select one:
a. pyruvate
b. oxaloacetate
c. fumarate
d. α-ketoglutarate
e. methylmalonate
The correct answer is:
c. fumarate
Which protein kinase is activated to transmit the anabolic signal of insulin?
Select one:
a. PKA
b. AMPK
c. PKC
d. mTOR
The correct answer is:
d. mTOR
Where is hepcidin produced?
Select one:
a. liver
b. spleen
c. intestine
d. adrenal gland
e. pancreas
The correct answer is:
a. liver
What is the normal degree of transferrin saturation with iron?
Select one:
a. 10 %
b. 30 %
c. 60 %
d. 80 %
e. 100-120 %
The correct answer is:
b. 30 %
Which intermediate is elevated in blood in lead poisoning?
Select one:
a. δ-aminolevulinate
b. protoporphyrin
c. haem
d. bilirubin
e. biliverdin
The correct answer is:
a. δ-aminolevulinate
Which factor regulates the activity of aminolevulinate synthase 1 (ALAS1)?
Select one:
a. ferroportin
b. transferrin receptor 2
c. haem
d. iron response element binding protein 1
e. ferritin
The correct answer is:
c. haem
(*heme)
Which factor regulates the activity of aminolevulinate synthase 2 (ALAS2)?
Select one:
a. protoporphyrin
b. hemoglobin
c. haem
d. iron response element binding protein 1
e. ferroportin
The correct answer is:
d. iron response element binding protein 1
Which compound is a substrate of haem oxygenase?
Select one:
a. O2
b. CO
c. CO2
d. HCO3-
The correct answer is:
a. O2
Which compound is a product of haem oxygenase?
Select one:
a. CO
b. O2
c. CO2
d. HCO3-
e. NADPH
The correct answer is:
a. CO
Why is blue light used to treat neonatal icterus?
Select one:
a. blue light promotes the conjugation of bilirubin
b. blue light activates the haem oxygenase in the skin
c. blue light generates lipid-soluble photoisomers of bilirubin
d. blue light generates photoisomers of bilirubin with higher water solubility
The correct answer is:
d. blue light generates photoisomers of bilirubin with higher water solubility
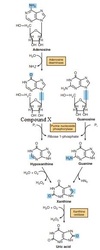
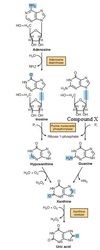
In what form do the dietary purine bases enter the blood circulation?
Select one:
a. nucleotide
b. nucleoside
c. free base
d. uric acid
answer:
d. The correct answer is: uric acid
Which enzyme is needed for the salvage of purine bases?
Select one:
a. phosphoribosyl-pyrophosphate synthetase
b. xanthine oxidase
c. xanthine dehydrogenase
d. AMP deaminase
The correct answer is:
a. phosphoribosyl-pyrophosphate synthetase
Which two amino acids contribute with 2 N-atoms each to the de novo synthesis of one adenine?
Select one:
a. Asparagine, Glutamine
b. Aspartate, Glutamine
c. Asparagine, Glutamate
d. Aspartate, Glutamate
The correct answer is:
b. Aspartate, Glutamine
Which amino acid contributes with both C- and N-atoms to the de novo synthesis of adenine?
Select one:
a. Glycine
b. Glutamine
c. Aspartate
d. Tryptophan
The correct answer is:
a. Glycine
The degradation of which nucleotide generates propionyl-CoA?
Select one:
a. AMP
b. GMP
c. UMP
d. TMP
The correct answer is:
d.TMP
Which amino acid contributes with 4 atoms to the de novo synthesis of one pyrimidine ring?
Select one:
a. Glycine
b. Proline
c. Aspartate
d. Proline
The correct answer is:
c. Aspartate
Which compound is a substrate of the ribonucleotide reductase?
Select one:
a. AMP
b. ADP
c. ATP
d. phosphoribosyl-pyrophosphate
The correct answer is:
b. ADP
Select all valid statements!
Select one or more:
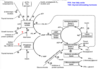
a. In the course of the urea cycle fumarate is produced
b. Enzymes of the urea cycle participate in the de novo synthesis of arginine
c. The amide group of glutamine serves as nitrogen source for the N-acetylglutamate-activated carbamoylphosphate synthetase
d. Ornithine can be synthesized from glutamate
The correct answers are:
a. In the course of the urea cycle fumarate is produced.
b. Enzymes of the urea cycle participate in the de novo synthesis of arginine
d. Ornithine can be synthesized from glutamate
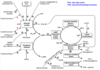
Select all valid statements!
Select one or more:
a. Citrullin is an intermediate of the urea cycle
b. Citrullin is a precursor of the de novo arginine biosynthesis
c. Urea may be produced by the kidney
d. Arginine may be produced by the kidney
The correct answers are:
a. Citrullin is an intermediate of the urea cycle
b. Citrullin is a precursor of the de novo arginine biosynthesis
d. Arginine may be produced by the kidney
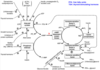
Select the false statement!
Select one:
a. Urea can be produced by the kidney
b. The nitrogen atoms present in urea are derived from free ammonium ion and from aspartate
c. The de novo synthesis of arginine requires ornithine synthesis
d. Ornithine is synthesized from glutamate
e. Arginine may be produced in the kidney
The correct answer is:
a. Urea can be produced by the kidney
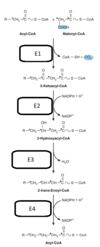
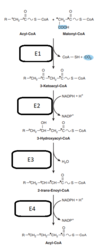
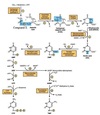
A part of the carbon skeleton of which amino acids may enter the citric acid cycle in the form of succinyl-CoA?
Select one or more:
a. Isoleucine
b. Leucine
c. Tyrosine
d. Proline
e. Valine
The correct answers are:
a. Isoleucine
e. Valine
A part of the carbon skeleton of which amino acids may enter the citric acid cycle in the form of a-ketoglutarate?
Select one or more:
a. Proline
b. Glutamine
c. Arginine
d. Cysteine
e. Phenylalanine
The correct answers are:
a. Proline
b. Glutamine
c. Arginine
A part of the carbon skeleton of which amino acids may enter the citric acid cycle?
Select one or more:
a. Leucine
b. Asparagine
c. Phenylalanine
d. Tyrosine
The correct answers are:
a. Asparagine
b. Phenylalanine
c. Tyrosine
Which of the following answer(s) complete(s) the sentence correctly? Glutamate is reduced to glutamic semialdehyde in the course of the formation of……..
Select one or more:
a. Ornithine.
b. Proline.
c. Glutamine.
d. Glutathione.
e. g-aminobutyrate.
The correct answers are:
a. Ornithine
b. Proline.
Select all valid statements!
Select one or more:
a. Formation of tyrosine is an essential step in the physiological degradation of phenylalanine
b. Degradation of phenylalanine starts with removal of the amino group by phenylalanine a-ketoglutarate transaminase
c. The carbon skeleton of phenylalanine yields acetoacetate
The correct answers are:
a. Formation of tyrosine is an essential step in the physiological degradation of phenylalanine
c. The carbon skeleton of phenylalanine yields acetoacetate
Select all valid statements!
Select one or more:
a. Formation of tyrosine is an essential step in the physiological degradation of phenylalanine
b. Phenylalanine may loose its amino group by a phenylalanine a-ketoglutarate transaminase under pathological conditions
c. Carbon skeleton of phenylalanine yields acetoacetate
The correct answers are:
a. Formation of tyrosine is an essential step in the physiological degradation of phenylalanine
b. Phenylalanine may loose its amino group by a phenylalanine a-ketoglutarate transaminase under pathological conditions
c. Carbon skeleton of phenylalanine yields acetoacetate
Select all valid statements!
Select one or more:
a. Folic acid should be reduced in order to serve as a one carbon carrier
b. S-adenosylmethionine is a methyl-group donor
c. Regeneration of S-adenosylmethionine from S-adenosylhomocystein requires B12 vitamin
d. One carbon units carried by the derivative of folic acid are derived from S-adenosylmethionine
The correct answers are:
a. Folic acid should be reduced in order to serve as a one carbon carrier
b. S-adenosylmethionine is a methyl-group donor
c. Regeneration of S-adenosylmethionine from S-adenosylhomocystein requires B12 vitamin
Select all valid statements!
Select one or more:
a. One carbon units carried by tetrahydrofolic acid may be derived from serine, glycine, tryptophan or histidine
b. All one carbon units bound by tetrahydrofolic acid can be transformed into each other
c. The methyl group carried by tetrahydrofolic acid is derived from methionine
The correct answer is:
a. One carbon units carried by tetrahydrofolic acid may be derived from serine, glycine, tryptophan or histidine
Which of the following amino acids are nutritionally essential for the human organism?
Select one or more:
a. Proline
b. Valine
c. Phenylalanine
d. Methionine
e. Cysteine
The correct answers are:
b. Valine
c. Phenylalanine
d. Methionine
Which of the following amino acids are nutritionally non-essential for the human organism?
Select one or more:
a. Proline
b. Valine
c. Tyrosine
d. Methionine
e. Cysteine
The correct answers are:
a. Proline
c. Tyrosine
e. Cysteine
Which of the following amino acids are nutritionally essential for the human organism?
Select one or more:
a. Isoleucine
b. Serine
c. Cysteine
d. Phenylalanine
e. Tryptophan
The correct answers are:
a. Isoleucine
d. Phenylalanine
e. Tryptophan
Select those enzymes which can catalyse directly the release of ammonia!
Select one or more:
a. Glutaminase
b. Glutamate dehydrogenase
c. Isoleucine-a-ketoglutarate aminotransferase
d. Arginase
e. Mitochondrial carbamoylphosphate synthetase
The correct answers are:
a. Glutaminase
b. Glutamate dehydrogenase
Select those enzymes which can incorporate free ammonia (from ammonium ion) into organic compounds!
Select one or more:
a. Glutamine synthetase
b. Glutamate dehydrogenase
c. Mitochondrial carbamoylphosphate synthetase
d. Argininosuccinate lyase
e. Asparagine synthetase
The correct answers are:
a. Glutamine synthetase
b. Glutamate dehydrogenase
c. Mitochondrial carbamoylphosphate synthetase
Select the false statement!
Select one:
a. Aspartate is a nitrogen donor in the course of urea formation
b. One of the nitrogen atoms of urea is derived from free ammonia
c. The amide group of glutamine is removed by glutamate dehydrogenase
d. The amino group of alanine may be released as free ammonia in a series of two consecutive reactions
e. The transaminase reactions require pyridoxal phosphate
The correct answer is:
c. The amide group of glutamine is removed by glutamate dehydrogenase
Which of the following reactions, enzymes or compounds participate in the urea cycle?
Select one or more:
a. synthesis of carbamoyl phosphate
b. aspartate
c. formation of argininosuccinate
d. ornithine
e. arginase
The correct answers are:
a. synthesis of carbamoyl phosphate
b. aspartate
c. formation of argininosuccinate
d. ornithine
e. arginase
Phenylketonuria can be a consequence of:
Select one or more:
a. dihydrobiopterin reductase deficiency
b. vitamin B6 deficiency
c. phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency
d. defective synthesis of biopterin
e. vitamin C deficiency
The correct answers are:
a. dihydrobiopterin reductase deficiency
c. phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency
d. defective synthesis of biopterin
Which of the urea cycle enzymes are not localized in the cytosol?
Select one or more:
a. carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I
b. ornithine transcarbamoylase
c. argininosuccinate lyase
d. argininosuccinate synthetase
e. arginase
The correct answers are:
a. carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I
b. ornithine transcarbamoylase
What is the fate of the exocytosed glutamic acid localized in the synaptic cleft?
Select one or more:
a. Glutamate can enter into the postsynaptic neuron by ionotropic receptors
b. Glutamate dehydrogenase splits the molecule in the synaptic cleft, the formed alfa-ketoglutarate is taken up by the postsynaptic neuron
c. Most of glutamate is taken up by astrocytes at the expense of Na+ gradient.
d. Glutamate is transformed into glutamine in astrocytes
e. Released glutamate will be recycled to the neurons in the form of glutamine
The correct answers are:
c. Most of glutamate is taken up by astrocytes at the expense of Na+ gradient.
d. Glutamate is transformed into glutamine in astrocytes
e. Released glutamate will be recycled to the neurons in the form of glutamine
Which of the following statements is/are true for the digestive enzymes?
Select one or more:
a. The carboxypeptidase is a carboxyl protease
b. Elastase and pepsin are thiolproteases
c. No Zn2+ protease can be found in the gastrointestinal tract
d. Both trypsin and chymotrypsin are serine proteases.
The correct answer is:
d. Both trypsin and chymotrypsin are serine proteases.
Which of the following agents and enzymes are required for the synthesis of cystein?
Select one or more:
a. methionine
b. adenosylhomocysteinase
c. serine
d. cystathionine synthase
e. cystathionase
The correct answers are:
a. methionine
b. adenosylhomocysteinase
c. serine
d. cystathionine synthase
e. cystathionase
Which of the following statements are valid for transamination?
Select one or more:
a. It is a reversible reaction
b. The coenzyme of transaminases is a noncovalently bound cobalamin
c. In the first step of catalysis ketoacids are attached to the lysine residue of the enzyme forming a Schiff base
d. The Schiff base linkage is in tautomeric equilibrium between an aldimine and a ketimine.
The correct answers are:
a. It is a reversible reaction
d. The Schiff base linkage is in tautomeric equilibrium between an aldimine and a ketimine.
Tetrahydrofolate has the following one-carbon derivatives:
Select one or more:
a. methyl H4folate
b. methylene H4folate
c. methenyl H4folate
d. carboxyl H4folate
The correct answers are:
a. methyl H4folate
b. methylene H4folate
c. methenyl H4folate
S Adenosylmethionine (SAM) is the methyl donor in the synthesis of
Select one or more:
a. carnitine
b. epinephrine
c. choline
d. norepinephrine
The correct answers are:
a. carnitine
b. epinephrine
c. choline
S Adenosylmethionine (SAM) is the methyl donor in the synthesis of
Select one or more:
a. urea
b. methyl-malonyl-CoA
c. choline
d. epinephrine
The correct answers are:
c. choline
d. epinephrine
Transamination of the following amino acids results in formation of citric acid cycle intermediates
Select one or more:
a. lysine
b. aspartate
c. leucine
d. glutamate
The correct answers are:
b. aspartate
d. glutamate
Degradation of the following amino acids results in formation of citric acid cycle intermediates
Select one or more:
a. valine
b. leucine
c. isoleucine
d. tryptophan
The correct answers are:
a. valine
c. isoleucine
Which of the following amino acids are ketoplastic?
Select one or more:
a. serine
b. leucine
c. cysteine
d. lysine
The correct answers are:
b. leucine
d. lysine
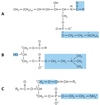
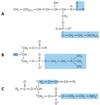
The reaction catalysed by the mitochondrial carbamoyl phosphate synthetase
Select one or more:
a. uses 2 ATP molecules
b. uses glutamine as a substrate
c. inhibited by N-acetylglutamate
d. activated by N-acetylglutamate
The correct answers are:
a. uses 2 ATP molecules
d. activated by N-acetylglutamate
Which of the following statements are true for the urea cycle?
Select one or more:
a. A citric acid cycle intermediate is formed in the cycle
b. The enzymes of the cycle are located either in the cytosol or in the mitochondria
c. Condensation of citrulline and glutamate requires hydrolysis of ATP
d. Synthesis of one urea molecule consumes energy equivalent to three high group transfer potential bonds
The correct answers are:
a. A citric acid cycle intermediate is formed in the cycle
b. The enzymes of the cycle are located either in the cytosol or in the mitochondria
Synthesis of tyrosine requires
Select one or more:
a. dietary phenylalanine
b. phenylalanine hydroxylase
c. tetrahydrobiopterin
d. dihydrobiopteridine reductase
e. transamination of phenylalanine
The correct answers are:
a. dietary phenylalanine
b. phenylalanine hydroxylase
c. tetrahydrobiopterin
d. dihydrobiopteridine reductase
Synthesis of proline involves
Select one or more:
a. glutamate
b. N-methyllysine
c. pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase
d. glutamic semialdehyde
e. pyrroline-5-carboxylate
The correct answers are:
a. glutamate
c. pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase
d. glutamic semialdehyde
e. pyrroline-5-carboxylate
Tryptophan can be the precursor of the following compounds:
Select one or more:
a. Lysine
b. acetoacetyl-CoA
c. nicotinamide
d. alanine
e. serotonin
The correct answers are:
b. acetoacetyl-CoA
c. nicotinamide
d. alanine
e. serotonin
Which of the following enzymes are regulated by N-acetylglutamate?
Select one:
a. N-acetylglutamate synthase
b. Ornithine transcarbamoylase
c. Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I
d. Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II
e. Arginase
The correct answer is:
c. Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I
Which of the following parameters are suitable to differentiate the deficiency of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I and ornithine transcarbamoylase ?
Select one:
a. Determination of blood pH
b. Determination of citrulline level in blood
c. Determination of arginine level in plasma
d. Determination of orotic acid level in urine
e. Determination of ammonia level in blood
The correct answer is:
d. Determination of orotic acid level in urine
Patients with deficiency of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I and ornithine transcarbamoylase are treated with sodium benzoate and sodium phenylacetate. What is the rationale of this treatment?
Select one or more:
a. Benzoate conjugates with Gly and removes 1 N atom
b. Phenylacetate conjugates with hippurate and removes 1 N atom
c. Benzoate and phenylacetate activate the enzymes of urea cycle
d. Phenylacetate conjugates with glutamine and removes 2 N atoms
e. N- containing conjugation products of benzoate and phenylacetate are released in the urine
The correct answers are:
b. Benzoate conjugates with Gly and removes 1 N atom
d. Phenylacetate conjugates with glutamine and removes 2 N atoms
e. N- containing conjugation products of benzoate and phenylacetate are released in the urine
Which of the following intermediates can be converted to serine in a single step reaction?
Select one:
a. Pyruvate
b. Some citric acid cycle intermediates
c. Some ornithine cycle intermediates
d. Glycine
e. Choline
The correct answer is:
d. Glycine
Which of the following amino acids are non-essential for an adult human?
Select one or more:
a. Phe
b. Tyr
c. Met
d. Cys
e. Glu
The correct answers are:
b. Tyr
d. Cys
e. Glu
Which of the following proteases is/are involved in the activation of pancreatic proenzymes?
Select one or more:
a. Carboxypeptidase A
b. Enteropeptidase
c. Trypsin
d. Chymotrypsin
e. Elastase
The correct answers are:
b. Enteropeptidase
c. Trypsin
Which of the following statements are valid for aminotransferases (AT)? The AT needs:
Select one or more:
a. Efficient amount of Vitamin B6
b. The presence of free aminoacids
c. The presence of free ketoacids
d. The formation of Schiff base between the amino group of the aminoacid and aldehyde group of pyridoxal phosphate
e. The presence of AT in blood circulation
The correct answers are:
a. Efficient amount of Vitamin B6
b. The presence of free aminoacids
c. The presence of free ketoacids
d. The formation of Schiff base between the amino group of the aminoacid and aldehyde group of pyridoxal phosphate
Which of the following statements are valid for the S-adenosylmethionine cycle?
Select one or more:
a. Met + ATP forms S-adenosylmethionine
b. Stable covalent bond exists between one C atom of Met and 5’C atom of adenosine
c. S-adenosylmethionine is converted to homocysteine + H2O
d. Homocysteine+ N5-Methyl FH4 form Met + FH4
e. Homocysteine methyltranferase uses a vitamin B12 derived cofactor
The correct answers are:
a. Met + ATP forms S-adenosylmethionine
d. Homocysteine+ N5-Methyl FH4 form Met + FH4
e. Homocysteine methyltranferase uses a vitamin B12 derived cofacto
Which of the following amino acids have their alpha-amino groups removed by dehydratases?
Select one or more:
a. Histidine
b. Tryptophan
c. Serine
d. Glutamine
e. Threonine
The correct answers are:
c. Serine
e. Threonine
Which of the following amino acids are derived from alpha-ketoglutarate ?
Select one or more:
a. Glutamate
b. Cysteine
c. Aspartate
d. Proline
e. Serine
The correct answers are:
a. Glutamate
d. Proline
Which of the following statements are valid for N-acetyl-glutamate?
Select one or more:
a. its concentration depends on the concentration of arginine
b. its concentration depends on the concentration of ornithine
c. it is an activator of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I
d. it is an inhibitor of argininosuccinate lyase
e. it is an activator of ornithine transcarbamoylase
The correct answers are:
a. its concentration depends on the concentration of arginine
c. it is an activator of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I
Hyperhomocysteinemia can be the consequence of:
Select one or more:
a. cystathionine -synthase defficiency
b. methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase deficiency
c. folate deficiency
d. B12 deficiency
e. methionine deficiency
The correct answers are:
a. cystathionine -synthase defficiency
b. methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase deficiency
c. folate deficiency
d. B12 deficiency
High citrulline levels are characteristic in the following enzyme deficiencies:
Select one or more:
a. carbamoyl phosphate synthetase
b. arginino succinate synthetase
c. arginino succinase
d. ornithine transcarbamoylase
The correct answers are:
b. arginino succinate synthetase
c. arginino succinase
Which enzyme is critical in the activation of zymogens for the digestion of proteins in the small intestine?
Select one:
a. enteropeptidase
b. hexokinase
c. papain
d. pepsin
e. secretin
The correct answer is:
a. enteropeptidase
Which of these is NOT an intestinal protease?
Select one:
a. chymotrypsin
b. elastase
c. enteropeptidase
d. pepsin
e. trypsin
The correct answer is:
d. pepsin
Which of the following is a zymogen that can be converted to an endopeptidase that hydrolyzes peptide bonds adjacent to Lys and Arg residues?
Select one:
a. chymotrypsinogen
b. pepsin
c. pepsinogen
d. proelastase
e. trypsinogen
The correct answer is:
e. trypsinogen
In amino acid catabolism, the first reaction for many amino acids is a:
Select one:
a. decarboxylation requiring thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP).
b. hydroxylation requiring NADPH and O2.
c. oxidative deamination requiring NAD+.
d. reduction requiring pyridoxal phosphate (PLP).
e. transamination requiring pyridoxal phosphate
The correct answer is:
e. transamination requiring pyridoxal phosphate.
The cofactor required for all transaminations is derived from:
Select one:
a. niacin.
b. pyridoxine (vitamin B6).
c. riboflavin
d. thiamin.
e. vitamin B12
The correct answer is:
b. pyridoxine (vitamin B6).
The cofactor involved in a transaminase reaction is:
Select one:
a. biotin phosphate.
b. lipoic acid.
c. nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP+).
d. pyridoxal phosphate (PLP)
e. thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP)
The correct answer is:
d. pyridoxal phosphate (PLP)
Transamination of alanine to alpha-ketoglutarate requires the cofactor:
Select one:
a. thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP).
b. pyridoxal phosphate (PLP).
c. No coenzyme is involved.
d. NADH.
e. biotin.
The correct answer is:
b. pyridoxal phosphate (PLP).
Pyridoxal phosphate is a cofactor in this class of reactions:
Select one:
a. transamination.
b. reduction.
c. methylation.
d. desulfuration.
e. acetylation.
The correct answer is:
a. transamination.
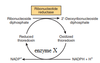
Which of the following is not true for the reaction catalyzed by glutamate dehydrogenase?
Select one:
a. The reaction is similar to transamination in that it involves the coenzyme pyridoxal phosphate (PLP).
b. The enzyme is specific for glutamate.
c. The enzyme can use either NAD+ or NADP+ as a cofactor.
d. NH4+ is produced.
e. alpha-ketoglutarate is produced
The correct answer is:
a. The reaction is similar to transamination in that it involves the coenzyme pyridoxal phosphate (PLP).
Glutamate is metabolically converted to alpha-ketoglutarate and NH4+ by a process described as:
Select one:
a. transamination.
b. reductive deamination.
c. hydrolysis.
d. deamidation
e. oxidative deamination
The correct answer is:
e. oxidative deamination
The conversion of glutamate to an alpha-ketoacid and NH4+:
Select one:
a. does not require any cofactors.
b. is a reductive deamination.
c. is accompanied by ATP hydrolysis catalyzed by the same enzyme.
d. is catalyzed by glutamate dehydrogenase.
e. requires ATP.
The correct answer is:
d. is catalyzed by glutamate dehydrogenase.
Which substance is NOT involved in the production of urea from NH4+ via the urea cycle?
Select one:
a. ornithine
b. malate
c. carbamoyl phosphate
d. ATP
e. aspartate
The correct answer is:
b. malate
A nitrogen atom of which compound is incorporated in the urea by an enzyme of the urea cycle?
Select one:
a. ornithine
b. glutamate
c. carnitine
d. aspartate
e. adenine
The correct answer is:
e. aspartate
Conversion of ornithine to citrulline is a step in the synthesis of:
Select one:
a. urea.
b. tyrosine.
c. pyruvate.
d. carnitine.
e. aspartate.
The correct answer is:
a. urea.
In the urea cycle, ornithine transcarbamoylase catalyzes:
Select one:
a. cleavage of urea to ammonia.
b. formation of citrulline from ornithine and another reactant.
c. formation of ornithine from citrulline and another reactant.
d. formation of urea from arginine.
e. transamination of arginine.
The correct answer is:
b. formation of citrulline from ornithine and another reactant.
The amino acids serine, alanine, and cysteine can be catabolized to yield:
Select one:
a. succinate.
b. pyruvate.
c. oxaloacetate
d. fumarate.
e. alpha-ketoglutarate.
The correct answer is:
b. pyruvate.
Serine or cysteine may enter the citric acid cycle as acetyl-CoA after conversion to:
Select one:
a. oxaloacetate.
b. propionate.
c. pyruvate.
d. succinate.
e. succinyl-CoA.
The correct answer is:
c. pyruvate.
The human genetic disease phenylketonuria (PKU) can result from:
Select one:
a. inability to convert phenylalanine to tyrosine.
b. deficiency of protein in the diet.
c. inability to catabolize ketone bodies.
d. inability to synthesize phenylalanine.
e. production of enzymes containing no phenylalanine.
The correct answer is:
a. inability to convert phenylalanine to tyrosine.
Nonessential amino acids:
Select one:
a. may be substituted with other amino acids in proteins.
b. can be synthesized in humans.
c. are synthesized by plants and bacteria, but not by humans.
d. are not utilized in mammalian proteins.
e. cannot be converted to intermediates of the citric acid cycle
The correct answer is:
b. can be synthesized in humans.
Glutamine, arginine, and proline:
Select one:
a. do not have a common precursor in their synthesis
b. may all be derived from a citric acid cycle intermediate.
c. may all be derived from a glycolytic intermediate.
d. may all be derived from an urea cycle intermediate.
The correct answer is:
b. may all be derived from a citric acid cycle intermediate.
Delta-aminolevulinic acid is formed from succinyl-CoA and __________ and is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of _________.
Select one:
a. serine; sphingosine
b. serine; heme
c. acetyl-CoA; long chain fatty acids
d. alpha-ketoglutarate; glutamate and proline
e. glycine; porphyrin
The correct answer is:
e. glycine; porphyrin
Glutathione is a:
Select one:
a. product of glutamate and methionine.
b. tripeptide of glycine, glutamate, and cysteine.
c. enzyme essential in the synthesis of glutamate.
d. methyl-group donor in many biosynthetic pathways.
The correct answer is:
b. tripeptide of glycine, glutamate, and cysteine.
Which amino acid is not directly involved in the purine biosynthetic pathway?
Select one:
a. alanine.
b. aspartate.
c. glutamine.
d. glycine.
The correct answer is:
a. alanine.
What is not true among the following statements concerning biotransformation
Select one or more:
a. biotransformation results in formation of ATP
b. biotransformation is an intermediary metabolism process
c. biotransformation is often called drug metabolism
d. biotransformation processes usually require cofactors
The correct answers are:
a. biotransformation results in formation of ATP
b. biotransformation is an intermediary metabolism process
What is true among the following statements concerning the possible fates of xenobiotics
Select one or more:
a. they can be converted by enzymes
b. they can be eliminated without chemical reactions
c. they can be converted spontaneously
d. they can be accumulated
The correct answers are:
a. they can be converted by enzymes
b. they can be eliminated without chemical reactions
c. they can be converted spontaneously
d. they can be accumulated
What is/are not true among the following statements concerning drug metabolism
Select one:
a. conjugation is a first phase reaction in biotransformation
b. usually fat soluble substrates become water soluble
c. in the preparatory phase usually reactive intermediates are formed
d. the conjugated derivatives are usually inactivated
The correct answer is:
a. conjugation is a first phase reaction in biotransformation
What is true among the following statements: In the cytochrome P450 system
Select one or more:
a. NADPH is required
b. electrons are transferred in two steps
c. flavoproteins are involved
d. superoxide anions can be formed
The correct answers are:
a. NADPH is required
b. electrons are transferred in two steps
c. flavoproteins are involved
d. superoxide anions can be formed
Cytochrome P450 enzymes can be expressed
Select one or more:
a. only in the liver
b. in several cell types
c. mainly in the liver but also in other tissues
d. in the cytosol
The correct answers are:
b. in several cell types
c. mainly in the liver but also in other tissues
Drugs can be conjugated
Select one or more:
a. by glucuronidation
b. by acetylation
c. with glutathion
d. by sulfation
The correct answers are:
a. by glucuronidation
b. by acetylation
c. with glutathion
d. by sulfation
What is true among the following statements concerning cytochrome P450 inducers
Select one or more:
a. polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons can be inducers
b. dioxin is a powerful carcinogen
c. nitrosamine derivatives can cause chemical carcinogenesis
d. can stimulate proliferation of endoplasmic reticulum
e. cannot be drug metabolism substrates
The correct answers are:
a. polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons can be inducers,
b. dioxin is a powerful carcinogen,
c. nitrosamine derivatives can cause chemical carcinogenesis,
d. can stimulate proliferation of endoplasmic reticulum
The straight glucose chains of glycogen molecules are broken down initially to
Select one:
a. glucose
b. glucose- 6- phosphate
c. glucose-1- phosphate
d. fructose diphosphate
e. UDP-glucose
The correct answer is:
c. glucose-1- phosphate
The branch points of glycogen are broken down to
Select one:
a. fructose diphosphate
b. glucose
c. glucose- 1- phosphate
d. glucose -6- phosphate
e. UDP-glucose
The correct answer is:
b. glucose
The straight chains of glycogen molecules are broken down by
Select one:
a. adenylate cyclase
b. glycogen glicosidase
c. glycogen phosphorylase
d. glycogen-glycosidase
e. protein kinase
The correct answer is:
c. glycogen phosphorylase
The debranching enzyme possesses the following activity(ies)
Select one:
a. A transferase activity
b. Both debranching and a transferase activity
c. Debranching activity
d. Elongase activity
e. Neither a debranching and a transferase activity
The correct answer is:
b. Both debranching and a transferase activity
Glucagon
Select one:
a. inhibits the formation of glycogen and stimulates the breakdown of glycogen
b. simultaneously inhibits the formation of glycogen and glycogen breakdown
c. simultaneously stimulates the formation of glycogen and glycogen breakdown
d. simultaneously stimulates the formation of glycogen and ketone bodies
e. stimulates the formation of glycogen and inhibits the breakdown of glycogen
The correct answer is:
a. inhibits the formation of glycogen and stimulates the breakdown of glycogen
Epinephrine
Select one:
a. stimulates the formation of glycogen and inhibits the breakdown of glycogen
b. simultaneously stimulates the formation of glycogen and ketone bodies
c. simultaneously stimulates the formation of glycogen and glycogen breakdown
d. simultaneously inhibits the formation of glycogen and glycogen breakdown
e. inhibits the formation of glycogen and stimulates the breakdown of glycogen
The correct answer is:
e. inhibits the formation of glycogen and stimulates the breakdown of glycogen
Insulin
Select one:
a. stimulates the formation of glycogen and inhibits the breakdown of glycogen
b. simultaneously stimulates the formation of glycogen and ketone bodies
c. simultaneously stimulates the formation of glycogen and glycogen breakdown
d. simultaneously inhibits the formation of glycogen and glycogen breakdown
e. inhibits the formation of glycogen and stimulates the breakdown of glycogen
The correct answer is:
a. stimulates the formation of glycogen and inhibits the breakdown of glycogen
Glucagon
Select one:
a. activates glycogen phosphorylase and increases the rate of glycogen synthesis
b. activates glycogen phosphorylase and increases the rate of glycogen breakdown
c. activates phosphofruktokinase 1 and increases the rate of gluconeogenesis
d. deactivates glycogen phosphorylase and decreases the rate of glycogen synthesis
e. deactivates glycogen phosphorylase and increases the rate of glycogen synthesis
The correct answer is:
b. activates glycogen phosphorylase and increases the rate of glycogen breakdown
Insulin
Select one:
a. activates phosphofruktokinase 2 and increases the rate of gluconeogenesis
b. decreases the activity of glycogen synthase and decreases the rate of glycogen synthesis
c. decreases the activity of glycogen synthase and increases the rate of glycogen synthesis
d. increases the activity of glycogen synthase and decreases the rate of glycogen synthesis
e. increases the activity of glycogen synthase and increases the rate of glycogen synthesis
The correct answer is:
e. increases the activity of glycogen synthase and increases the rate of glycogen synthesis
The binding of epinephrine to a receptor
Select one:
a. deactivates protein kinase A
b. deactivates adenylate cyclase
c. causes the breakdown of cyclic AMP to ATP
d. activates phosphodiesterase
e. activates adenylate cyclase
The correct answer is:
e. activates adenylate cyclase
The binding of glucagon to its receptor
Select one:
a. deactivates protein kinase
b. deactivates adenylate cyclase
c. causes the breakdown of cyclic AMP to ATP
d. activates adenylate cyclase
e. activates phosphodiesterase
The correct answer is:
d. activates adenylate cyclase
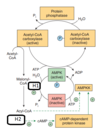
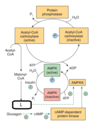
Protein kinase A
Select one:
a. removes a phosphate molecule from glycogen synthase
b. removes a phosphate molecule from cAMP
c. adds a phosphate to fructose-6-phosphate
d. adds a phosphate molecule to glycogen synthase
e. adds a phosphate molecule to cAMP
The correct answer is:
d. adds a phosphate molecule to glycogen synthase
Protein kinase A
Select one:
a. adds a phosphate molecule to phosphorylase kinase
b. adds a phosphate molecule to glycogen phosphorylase
c. adds a phosphate to glucokinase
d. removes a phosphate molecule from glycogen phosphorylase
e. removes a phosphate molecule from phosphorylase kinase
The correct answer is:
a. adds a phosphate molecule to phosphorylase kinase
Protein kinase A
Select one:
a. Directly activates glycogen phosphorilase
b. activates glycogen synthase
c. converts ATP to cAMP
d. converts cAMP to ATP
e. deactivates glycogen synthase
The correct answer is:
e. deactivates glycogen synthase
In glycogenesis, the enzyme (i)________ uses a molecule of (ii)_________ to lengthen the glycogen chain
Select one:
a. (i) glycogen synthase (ii) glucose
b. (i)glycogen phosphorylase (ii) glucose
c. (i) glycogen phosphorylase (ii) UDP-glucose
d. (i) glycogen synthase (ii) UDP-glucose
e. (i) glycogenin (ii) glucose-1-phosphate
The correct answer is:
d. (i) glycogen synthase (ii) UDP-glucose
A person is suffering from a disease which is caused by a defective glucose-6-phosphatase. Such a person
Select one:
a. can breakdown glycogen completely to glucose
b. can convert pyruvate to glucose
c. can dephosphorylate glucose-6-phosphate
d. can convert glycogen to pyruvate
e. can convert acetyl-CoA to glucose
The correct answer is:
b. can convert glycogen to pyruvate
A person is suffering from a disease in which is caused by a defective glucose-6-phosphatase. Such a person
Select one:
a. can convert acetyl-CoA to glucose
b. cannot breakdown glycogen completely to glucose
c. cannot convert acetyl-CoA to citric acid
d. cannot convert glycogen to pyruvate
e. would suffer no ill-effects from this defect
The correct answer is:
b. cannot breakdown glycogen completely to glucose
In glycogenolysis, the enzyme (i)________ breaks an (ii) _______ bond to release a molecule of (iii)_________.
Select one:
a. (i) glycogen synthase (ii) alpha 1-4 (iii) glucose
b. (i) glycogen synthase (ii) alpha 1-4 (iii) UDP-glucose
c. (i) glycogen phosphorylase (ii) alpha 1-4 (iii) glucose-1-phosphate
d. (i) glycogen phosphorylase (ii) alpha 1-6 (iii) glucose-6-phosphate
e. (i) debranching enzyme (ii) alpha 1-6 (iii) glucose-1-phosphate
The correct answer is:
c. (i) glycogen phosphorylase (ii) alpha 1-4 (iii) glucose-1-phosphate
Which enzyme catalyzes the first ATP producing step of glycolysis?
Select one:
a. phosphofructokinase 1
b. hexokinase
c. pyruvate kinase
d. phosphoglycerate mutase
e. phosphoglycerate kinase
The correct answer is:
e. phosphoglycerate kinase
Which enzyme catalyzes the second ATP producing step of glycolysis?
Select one:
a. phosphofructokinase 1
b. hexokinase
c. pyruvate kinase
d. phosphoglycerate mutase
e. phosphoglycerate kinase
The correct answer is:
c. pyruvate kinase
Upon phosphorylation of phosphofructokinase 2 by protein kinase A in liver:
Select one:
a. it becomes active.
b. it becomes inactive.
c. phosphatase function is activated, kinase function is inactivated.
d. kinase function is activated, phosphatase function is inactivated.
e. phosphofructokinase 2 is not covalently regulated.
The correct answer is:
c. phosphatase function is activated, kinase function is inactivated.
The allosteric activator of pyruvate carboxylase is:
Select one:
a. oxaloacetate
b. NADH
c. CoA
d. ATP
e. acetyl-coA
The correct answer is:
e. acetyl-coA
When is the glycogen pool of the liver depleted during fasting?
Select one:
a. in 6 hours
b. in 1 hour
c. in 24 hours
d. in 3 days
e. in a week
The correct answer is:
c. in 24 hours
Choose the enzyme, the lack of which leads to fructose intolerance
Select one:
a. aldolase A (fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase)
b. aldolase B (fructose 1-phosphate aldolase)
c. fructokinase
d. hexokinase
e. phosphofructokinase
The correct answer is:
b. aldolase B (fructose 1-phosphate aldolase)
Glycolysis in the erythrocyte produces pyruvate that is further metabolized to:
Select one:
a. CO2.
b. lactate.
c. glucose.
d. hemoglobin.
e. ethanol.
The correct answer is:
b. lactate.
The conversion of 1 mol of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate to 2 mol of pyruvate by the glycolytic pathway results in a net formation of:
Select one:
a. 2 mol of NADH and 4 mol of ATP.
b. 2 mol of NADH and 2 mol of ATP.
c. 2 mol of NAD+ and 4 mol of ATP.
d. 1 mol of NADH and 1 mol of ATP.
e. 1 mol of NAD+ and 2 mol of ATP.
The correct answer is:
a. 2 mol of NADH and 4 mol of ATP.
Which substrates are necessary for the synthesis of bile salts?
Select one or more:
a. NADPH2
b. NADH2
c. ATP
d. O2
e. H2O
The correct answers are:
a. NADPH2,
c. ATP,
d. O2
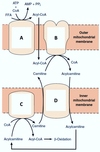
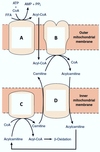
What is the subcellular localization of the side chain cleavage enzyme in adrenal fascicular cells?
Select one:
a. Golgi membranes
b. mitochondria
c. nuclear membrane
d. plasma membrane
e. rough endoplasmic reticulum
The correct answer is:
b. mitochondria
What is the weakly androgenic steroid that is synthesized in the fascicular zone of the adrenal gland?
Select one:
a. testosterone
b. progesterone
c. pregnenolone
d. dehydroepiandrosterone
e. corticosterone
The correct answer is:
d. dehydroepiandrosterone
Select the statements valid for the lipoproteins
Select one or more:
a. Their density increases in parallel with their protein content
b. Their density is reciprocally proportional to their lipid content
c. The core non-polar lipids are surrounded by polar lipids
d. All of them contain phospholipids
e. Non-polar interactions bind together the lipids in their structure
The correct answers are:
a. Their density increases in parallel with their protein content,
b. Their density is reciprocally proportional to their lipid content,
c. The core non-polar lipids are surrounded by polar lipids,
d. All of them contain phospholipids,
e. Non-polar interactions bind together the lipids in their structure
Which of the following statements are valid for the apolipoprotein B-100?
Select one or more:
a. It is synthesized in the liver
b. It is recognized by the LDL-receptor
c. It is not present in the structure of VLDL
d. It participates in the liver uptake of chylomicron remnants
e. It is found in the structure of IDL
The correct answers are:
a. It is synthesized in the liver,
b. It is recognized by the LDL-receptor,
e. It is found in the structure of IDL
Which of the following lipoproteins does not contain triacylglycerols?
Select one:
a. Chylomicron
b. HDL3
c. IDL
d. Nascent VLDL
e. VLDL
The correct answer is:
b. HDL3
Which of the following statements is not valid for the lipoprotein lipase?
Select one:
a. An isoenzyme with a low KM is present in the mammary gland
b. It degrades the majority of plasma triacylglycerols
c. It is bound to the luminal surface of the capillary endothelial cells
d. Its activity increases in the fasting state
e. VLDL carries its cofactor
The correct answer is:
d. Its activity increases in the fasting state
Which of the following statements are valid?
Select one or more:
a. The nascent VLDL is formed in the intestinal epithelial cells
b. The VLDL is converted to IDL in the circulation
c. The cells recognize the apo B-100 in the structure of VLDL and take up the lipoprotein through it
d. The lipoprotein lipase reduces the triacylglycerol content of VLDL
e. The apo B-100 of LDL is derived from VLDL
The correct answers are:
b. The VLDL is converted to IDL in the circulation,
d. The lipoprotein lipase reduces the triacylglycerol content of VLDL,
e. The apo B-100 of LDL is derived from VLDL
Which of the following statements is not valid?
Select one:
a. Cholesterol overload inhibits the expression of LDL-receptors
b. Cholesterol overload inhibits the HMG-CoA reductase in the cells
c. In case of cholesterol overproduction cholesteryl esters are formed in the cells as a result of the action of LCAT enzyme
d. The LDL-derived cholesterol affects the cholesterol synthesis in the cells
e. The LDL-receptor recognizes the apo B-100
The correct answer is:
c. In case of cholesterol overproduction cholesteryl esters are formed in the cells as a result of the action of LCAT enzyme
Select the statements valid for the bile acids
Select one or more:
a. The bile acids are synthesized in the intestine
b. In the course of synthesis the polar character of the molecules increases
c. Bile acids are necessary for the solubilization of cholesterol in water phase
d. Deoxycholic acid is one of the primary bile acids
e. Lack of bile acids results in steatorrhea
The correct answers are:
b. In the course of synthesis the polar character of the molecules increases,
c. Bile acids are necessary for the solubilization of cholesterol in water phase,
e. Lack of bile acids results in steatorrhea
Which is the committed step of the cholesterol biosynthesis?
Select one:
a. Mevalonate to 5-phosphomevalonate
b. Acetyl-CoA to acetoacetyl-CoA
c. Acetoacetyl-CoA to 3-hydroxi-3-methyl glutaryl-CoA
d. 5-phosphomevalonate to 5-pyrophosphomevalonate
e. 3-hydroxi-3-methyl glutaryl-CoA to Mevalonate
The correct answer is:
e. 3-hydroxi-3-methyl glutaryl-CoA to Mevalonate
Select the correct statements
Select one or more:
a. The nascent HDL does not contain cholesteryl esters
b. Triacylglycerols are transferred from VLDL to HDL
c. Cholesteryl esters are transferred from VLDL to HDL
d. The hepatic lipase degrades the triacylglycerols in HDL2
e. The HDL-derived cholesterol is taken up by the liver in part in the form of LDL
The correct answers are:
a. The nascent HDL does not contain cholesteryl esters,
b. Triacylglycerols are transferred from VLDL to HDL,
d. The hepatic lipase degrades the triacylglycerols in HDL2,
e. The HDL-derived cholesterol is taken up by the liver in part in the form of LDL
Select the wrong statement
Select one:
a. HDL carries ACAT (acyl-CoA cholesterol acyltransferase)
b. HDL takes up triacylglycerols with the help of cholesteryl ester transfer protein
c. HDL2 delivers cholesterol to the liver
d. The HDL contains apo-A1
e. The triacylglycerol content of HDL2 is higher than that of HDL3
The correct answer is:
a. HDL carries ACAT (acyl-CoA cholesterol acyltransferase)
At least how many glucose molecules are necessary to provide the carbon atoms for the biosynthesis of one cholesterol molecule in mammalian tissues?
Select one:
a. 7
b. 8
c. 9
d. 6
e. 5
The correct answer is:
c. 9
Which of the following statements are valid for the ABCA1 transporter?
Select one or more:
a. It is the major transporter of bile salts
b. Its deficiency causes atherosclerosis because of the elevated levels of LDL-cholesterol
c. High intracellular cholesterol content stimulates its transcription
d. It is necessary for the efflux of cholesterol from the cells
e. It is a scavenger receptor for LDL
f. HDL binds to it
The correct answers are:
c. High intracellular cholesterol content stimulates its transcription,
d. It is necessary for the efflux of cholesterol from the cells,
f. HDL binds to it
Which processes are modulated by the amount of intracellular free cholesterol?
Select one or more:
a. synthesis of bile acids
b. down-regulation of LDL-receptors in the membrane
c. transfer of cholesterol from the membrane into HDL
d. cholesterol synthesis
e. synthesis of cholesterol esters
The correct answers are:
a. synthesis of bile acids,
b. down-regulation of LDL-receptors in the membrane,
c. transfer of cholesterol from the membrane into HDL,
d. cholesterol synthesis,
e. synthesis of cholesterol esters
Which carbon atom carries the hydroxylic group in cholesterol?
Select one:
a. C-3
b. C-7
c. C-10
d. C-21
e. C-27
The correct answer is:
a. C-3
Which statements are true?
Select one or more:
a. Cholesterol is formed from HMG-CoA synthesized in the mitochondria
b. Cholesterol is formed from HMG-CoA synthesized in the cytosol
c. Mevalonate is formed from HMG-CoA by decarboxylation
d. NADPH is needed for mevalonate synthesis
e. Acetyl-CoA for cholesterol synthesis originates from mitochondria
The correct answers are:
b. Cholesterol is formed from HMG-CoA synthesized in the cytosol,
d. NADPH is needed for mevalonate synthesis,
e. Acetyl-CoA for cholesterol synthesis originates from mitochondria
Cholesterol is synthesized from:
Select one:
a. oxalate.
b. malate.
c. lipoic acid.
d. choline.
e. acetyl-CoA.
The correct answer is:
e. acetyl-CoA.
Which of these statements about the regulation of cholesterol synthesis is not true?
Select one:
a. Cholesterol acquired in the diet has essentially no effect on the synthesis of cholesterol in the liver.
b. Failure to regulate cholesterol synthesis predisposes humans to atherosclerosis.
c. High intracellular cholesterol stimulates formation of cholesterol esters.
d. Insulin stimulates HMG-CoA reductase.
e. Cholesterol exerts a negative feedback effect on HMG-CoA reductase.
The correct answer is:
a. Cholesterol acquired in the diet has essentially no effect on the synthesis of cholesterol in the liver.
Where is acyl-CoA cholesterol-transferase (ACAT) localized?
Select one:
a. endoplasmic reticulum membrane
b. cytosol
c. mitochondrium matrix
d. inner mitochondrial membrane
The correct answer is:
a. endoplasmic reticulum membrane
Which process is inhibited, if MTP (microsomal TG transfer protein) inhibitor is used as a drug?
Select one:
a. TG (triglyceride) transfer into adipocytes
b. TG (triglyceride) transfer into hepatocytes
c. cholesteryl ester transfer into lipid droplets
d. cholesteryl ester transfer into chylomicrons
The correct answer is:
d. cholesteryl ester transfer into chylomicrons
How many Acetyl-CoA molecules are needed for the synthesis of one molecule of cholesterol?
Select one:
a. 10
b. 18
c. 20
d. 25
The correct answer is:
b. 18
Where is the SREBP regulator domain localized if there is excess cholesterol in the cell?
Select one:
a. cytosol
b. endoplasmic reticulum
c. Golgi
d. nucleus
The correct answer is:
b. endoplasmic reticulum
Which protein of the SREBP-dependent signalling binds directly cholesterol?
Select one:
a. SCAP
b. SREBP
c. INSIG
d. SREBP-cleavage protease
The correct answer is:
a. SCAP
What is the consequence of increased release of PCSK9?
Select one:
a. enhanced LDL uptake in hepatocytes
b. increased number of LDL receptors in hepatocytes
c. lower blood plasma LDL level
d. higher blood plasma LDL level
The correct answer is:
d. higher blood plasma LDL level
What is the consequence of enhanced IDOL production in the liver?
Select one:
a. enhanced LDL uptake in the liver
b. higher number of LDL-receptors in the hepatocytes
c. higher blood plasma LDL level
d. lower blood plasma LDL level
The correct answer is:
c. higher blood plasma LDL level
What is the function of the cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP)?
Select one:
a. transfers cholesteryl esters from extrahepatic cells to HDL
b. transfers cholesteryl esters from HDL to VLDL
c. transfers cholesteryl esters from the intestine to HDL
d. transfers cholesteryl esters from HDL to the liver
The correct answer is:
b. transfers cholesteryl esters from HDL to VLDL
What is the function of scavenger receptor B1 (SR-B1)?
Select one:
a. LDL endocytosis
b. HDL endocytosis
c. selective uptake of LDL-cholesterol
d. selective uptake of HDL-cholesterol
The correct answer is:
d. selective uptake of HDL-cholesterol
What chemical changes occur when primary bile acids are converted to secondary bile acids?
Select one:
a. removal of carboxylic groups
b. reduction of the double bond at 3C
c. removal of the 3C-hydroxylic group
d. removal of the 7C-hydroxylic group
The correct answer is:
d. removal of the 7C-hydroxylic group
Which value approaches most closely the daily rate of cholesterol synthesis in the liver (X) and in the extrahepatic tissues (Y) in adults (70 kg body weight)? Numbers are in mg cholesterol synthesized per kg organ mass.
Select one:
a. X=10; Y=1000
b. X=100; Y=100
c. X=250; Y=10
d. X=500; Y=1
e. X=1000; Y=0
The correct answer is:
c. X=250; Y=10
Which proteins are needed for the transfer of dietary cholesterol to extrahepatic tissues?
Select one or more:
a. apoB48
b. apoB100
c. lipoprotein lipase
d. acyl-CoA cholesterol acyl transferase
e. lecithin cholesterol acyl transferase
The correct answers are:
a. apoB48,
b. apoB100,
c. lipoprotein lipase,
d. acyl-CoA cholesterol acyl transferase
Which statements are true concerning proprotein convertase subtilisin-like/kexin type 9 (PCSK9)?
Select one or more:
a. it contributes to the intracellular processing of LDL receptors prior their exposure in the membrane
b. it stimulates the degradation of LDL receptors
c. it triggers the endocytosis of LDL-receptor
d. it binds to LDL receptors
e. it is a protease that degrades LDL receptors
The correct answers are:
b. it stimulates the degradation of LDL receptors,
c. it triggers the endocytosis of LDL-receptor,
d. it binds to LDL receptors
Which statements are true concerning Idol (inducer of degradation of LDL receptor)?
Select one or more:
a. it is a transcription factor controlling PCSK9 (proprotein convertase subtilisin-like/kexin type 9)
b. it is a protease that degrades LDL receptor
c. it binds LDL receptors extracellularly
d. it is under the control of LXR (liver X receptor)
e. it stimulates the ubiquitination of LDL receptor
The correct answers are:
d. it is under the control of LXR (liver X receptor),
e. it stimulates the ubiquitination of LDL receptor
Which statements are true concerning FXR (farnesoid X receptor)?
Select one or more:
a. it operates in fibroblasts, hepatocytes and intestinal epithelial cells
b. its ligands are bile acids
c. in fibroblasts it induces FGF19 (fibroblast growth factor 19)
d. in hepatocytes it induces 7a-hydoxylase
e. in intestinal epithelial cells it induces IBAT (ileal bile acid transporter)
The correct answers are:
b. its ligands are bile acids,
e. in intestinal epithelial cells it induces IBAT (ileal bile acid transporter)
Which statements are true concerning miR-33 microRNA?
Select one or more:
a. its level increases in cholesterol depletion
b. its level increases in cholesterol overload
c. it stimulates the translation of ABCA1 (ATP binding cassette A 1 transporter)
d. it stimulates the transcription of NPC1 (Nieman-Pick type C 1 protein)
e. it suppresses the translation of ABCA1 (ATP binding cassette A 1 transporter)
The correct answers are:
a. its level increases in cholesterol depletion,
e. it suppresses the translation of ABCA1 (ATP binding cassette A 1 transporter)
Select the factors that cause increase of the plasma LDL-cholesterol level
Select one or more:
a. LDL-receptor deficiency
b. Apo-B100 deficiency
c. lipoprotein lipase deficiency
d. PCSK9 (proprotein convertase subtilisin-like/kexin type 9) deficiency
e. Idol (inducer of degradation of LDL receptor) deficiency
The correct answers are:
a. LDL-receptor deficiency,
b. Apo-B100 deficiency
What is the biological role of bile acids?
Select one or more:
a. they contribute to the interfacial activation of pancreatic lipase in the intestine
b. their micelles are essential for cholesterol absorption in the intestine
c. they are ligands of FXR (farnesoid X receptor)
d. their micelles are essential for cholesterol disposal in the intestine
e. they are ligands of LXR (liver X receptor)
The correct answers are:
a. they contribute to the interfacial activation of pancreatic lipase in the intestine,
b. their micelles are essential for cholesterol absorption in the intestine,
c. they are ligands of FXR (farnesoid X receptor),
d. their micelles are essential for cholesterol disposal in the intestine
Which reactions participate in the bile acid synthesis?
Select one or more:
a. 7alfa hydroxylation
b. 7beta hydroxylation
c. 12alfa hydroxylation
d. glycine conjugation
e. glutamine conjugation
The correct answers are:
a. 7alfa hydroxylation,
c. 12alfa hydroxylation,
d. glycine conjugation
What is the recommended daily allowance of cholesterol in normal mixed-type diet of adults?
Select one:
a. 0.5 g
b. 1 g
c. 2 g
d. 10 g
e. 100 g
The correct answer is:
a. 0.5 g
In what form are the C-atoms of cholesterol released from the human body?
Select one or more:
a. CO2
b. free cholesterol
c. cholesteryl esters
d. cholate
e. bilirubin
The correct answers are:
a. CO2,
b. free cholesterol,
d. cholate
In what form is cholesterol released by the liver?
Select one:
a. chylomicron
b. VLDL
c. LDL
d. IDL
e. in complex with albumin
The correct answer is:
b. VLDL
In what form is cholesterol taken up by the liver?
Select one or more:
a. chylomicron
b. chylomicron remnant
c. HDL
d. LDL
e. VLDL
The correct answers are:
b. chylomicron remnant,
c. HDL,
d. LDL
Select the correct order of enzymes or transporters operating in the disposal of excess cholesterol from the human body?
Select one:
a. ABCA1 / LCAT / LDL / IDL / BSEP
b. ABCA1 / LCAT / LDL / VLDL / BSEP
c. ACAT / ABCA1 / HDL / LDL / BSEP
d. ABCA1 / LCAT / HDL / CETP / LDL
e. ABCA1 / ACAT / LCAT / HDL / LDL
The correct answer is:
d. ABCA1 / LCAT / HDL / CETP / LDL
Which cells express FXR?
Select one or more:
a. hepatocytes
b. enterocytes
c. macrophages
d. adipocytes
e. smooth muscle cells
The correct answers are:
a. hepatocytes,
b. enterocytes
Which cells express LXR?
Select one or more:
a. hepatocytes
b. enterocytes
c. macrophages
d. adipocytes
e. smooth muscle cells
The correct answers are:
a. hepatocytes,
b. enterocytes,
c. macrophages,
d. adipocytes,
e. smooth muscle cells
Which statements are true regarding the lecithin cholesterol acyl transferase?
Select one or more:
a. It is one of the enzymes of cholesterol synthesis.
b. It forms cholesteryl esters.
c. It is localized in the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum.
d. Apo AI is its activator.
e. It is active in phosphorylated state.
The correct answers are:
b. It forms cholesteryl esters.
d. Apo AI is its activator.
Which statements are true regarding the synthesis of cholesterol in mammalians?
Select one or more:
a. Cholesterol is synthesized only in the liver.
b. The rate of cholesterol synthesis is constant.
c. Cholesterol inhibits the activity of 3-hydroxy 3-methyl glutaryl-CoA reductase
d. Cholesterol inhibits the transcription of 3-hydroxy 3-methyl glutaryl-CoA reductase
e. Cholesterol inhibits the degradation of 3-hydroxy 3-methyl glutaryl-CoA reductase
The correct answers are:
c. Cholesterol inhibits the activity of 3-hydroxy 3-methyl glutaryl-CoA reductase,
d. Cholesterol inhibits the transcription of 3-hydroxy 3-methyl glutaryl-CoA reductase
Which metabolic pathway uses the reaction catalyzed by 3-hydroxy 3-methyl glutaryl-CoA reductase?
Select one:
a. glycolysis
b. synthesis of ketone bodies
c. oxidation of fatty acids
d. synthesis of fatty acids
e. synthesis of cholesterol
The correct answer is:
e. synthesis of cholesterol
Where is the 3-hydroxy 3-methyl glutaryl-CoA reductase localized within the cell?
Select one:
a. cytosol
b. membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum
c. matrix of mitochondria
d. the inner membrane of mitochondria
e. the outer membrane of mitochondria
The correct answer is:
b. membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum
De novo synthesis of purine nucleotides utilizes:
Select one or more:
a. glutamine.
b. components of the tetrahydrofolate one-carbon pool.
c. aspartate.
d. glycine.
The correct answers are:
a. glutamine.
b. components of the tetrahydrofolate one-carbon pool.
c. aspartate.
d. glycine.
The conversion of cholesterol to pregnenolone is a common reaction in the synthesis of adrenal steroid hormones. Which statements are true for the enzyme catalyzing this reaction?
Select one or more:
a. The enzyme uses biotin as a prosthetic group, which temporarily binds the side chain of cholesterol
b. The enzyme is called ``side-chain cleavage enzyme’’, and is a member of the family of cytochrom P450 isoenzymes
c. The enzyme is localized to the cytosol, where it can easily access its substrate, cholesterol
d. Cholesterol needs to be transported into the mitochondria for the reaction to take place
e. The complete deficiency of this enzyme is lethal
The correct answers are:
b. The enzyme is called ``side-chain cleavage enzyme’’, and is a member of the family of cytochrom P450 isoenzymes,
d. Cholesterol needs to be transported into the mitochondria for the reaction to take place,
e. The complete deficiency of this enzyme is lethal
What is the role of StAR (Steroidogenic Acute Regulatory Protein) in the synthesis of steroid hormones?
Select one or more:
a. It is a protein required for the transport of cholesterol from the cytosol into the mitochondria
b. Congenital lipoid adrenal hyperplasia is a lethal disease, where the mutations are localized to the StAR gene
c. It is a protein required for the transport of cholesterol from the mitochondria to the cytosol, where cholesterol can be converted to pregnenolone
d. In the adrenal cortex ACTH induces the synthesis of StAR, which is necessary for cortisol production
e. In the adrenal cortex angiotensin II induces the synthesis of StAR, which is necessary for aldosterone production
The correct answers are:
a. It is a protein required for the transport of cholesterol from the cytosol into the mitochondria,
b. Congenital lipoid adrenal hyperplasia is a lethal disease, where the mutations are localized to the StAR gene,
d. In the adrenal cortex ACTH induces the synthesis of StAR, which is necessary for cortisol production,
e. In the adrenal cortex angiotensin II induces the synthesis of StAR, which is necessary for aldosterone production
Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate is required for:
Select one or more:
a. the salvage of adenine
b. the salvage of uridine
c. conversion of purines to uric acid
d. de novo synthesis of purine nucleotides
The correct answers are:
a. the salvage of adenine,
d. de novo synthesis of purine nucleotides
Select the cytochrom P450 isoenzymes!
Select one or more:
a. Side chain cleavage enzyme
b. 21-Hydroxylase
c. 11beta-hydroxy-steroid dehydrogenase
d. 17-Hydroxylase
e. 17-hydroxy-steroid dehydrogenase
The correct answers are:
a. Side chain cleavage enzyme,
b. 21-Hydroxylase,
d. 17-Hydroxylase
Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase is an enzyme:
Select one:
a. for conversion of hypoxanthine to guanine
b. for conversion of guanine to hypoxanthine
c. required to convert hypoxanthine and guanine to urate
d. participating in the synthesis of the purine ring
e. required for the salvage of purine bases
The correct answer is:
e. required for the salvage of purine bases
Select the correct statements regarding steroid hormone synthesis in the adrenal gland!
Select one or more:
a. Aldosterone is produced in the zona fasciculata cells
b. Cortisol is produced in the zona fasciculata cells
c. Testosterone is produced from estradiol by the aromatase enzyme
d. The major products in the zona glomerulosa cells are the weak androgens
e. The three layers of the adrenal cortex are specialized for the production of mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids and estrogens
The correct answer is:
a. Cortisol is produced in the zona fasciculata cells
In tissues where the de novo purine synthesis is not active, adenine nucleotides could be supplied by:
Select one or more:
a. adenine phosphoribosyl transferase
b. ATP uptake from the blood
c. nucleoside phosphorylase
d. hypoxanthine-guanine phosphorybosyl transferase
The correct answers are:
a. adenine phosphoribosyl transferase,
d. hypoxanthine-guanine phosphorybosyl transferase
What are the signs of aldosterone deficiency?
Select one or more:
a. hypertension (elevated blood pressure)
b. salt loss and dehydration
c. elevated K+ concentration in blood
d. loss of K+ with the urine
e. red bumps on the toes
The correct answers are:
b. salt loss and dehydration,
c. elevated K+ concentration in blood
Thioredoxin is involved in the conversion of:
Select one:
a. hypoxantin to ATP.
b. dUMP to dTMP.
c. UTP to CTP.
d. hypoxanthine and guanine to urate
e. ribonucleotides to deoxyribonucleotides
The correct answer is:
e. ribonucleotides to deoxyribonucleotides
Select the correct order of the enzymes in the de novo synthesis of orotic acid:
Select one:
a. Carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase/Asp transcarbamoylase/Dihydroorotase/Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase
Dihydroorotase
Dihydroorotase
b. Dihydroorotase/Carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase/Asp transcarbamoylase/Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase
c. Asp transcarbamoylase/Carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase/Dihydroorotase/Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase
d. Dihydroorotase/Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase/Asp transcarbamoylase/Carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase/
The correct answer is:
a. Carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase/Asp transcarbamoylase/Dihydroorotase/Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase
Dihydroorotase
Dihydroorotase
What is the role of the 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase enzyme in the mineralocorticoid target cells?
Select one:
a. The enzyme inactivates cortisol
b. The enzyme activates aldosterone
c. The enzyme inactivates DOC (11-deoxycorticosterone)
d. The enzyme activates DOC (11-deoxycorticosterone)
e. The enzyme activates corticosterone
The correct answer is:
a. The enzyme inactivates cortisol
What are the effects of aldosterone?
Select one or more:
a. Increases Na+-reabsorption in the kidney
b. Increases K+-excretion in the kidney
c. Promotes salt and water retention
d. Promotes salt and water loss
e. Induces the gene expression of Na+/K+-ATPase, as well as Na+-, and K+-channels in the kidney tubular cells
The correct answers are:
a. Increases Na+-reabsorption in the kidney,
b. Increases K+-excretion in the kidney,
c. Promotes salt and water retention,
e. Induces the gene expression of Na+/K+-ATPase, as well as Na+-, and K+-channels in the kidney tubular cells
The formation of dATP occurs primarily by:
Select one:
a. salvaging deoxyadenylate by a phosphoribosyltransferase
b. salvaging deoxyadenosine by a phosphoribosyltransferase.
c. converting ATP to dATP using NADH.
d. converting ADP to dADP using thioredoxin.
e. converting dIMP to dAMP using 5,10-methylene THF
The correct answer is:
d. converting ADP to dADP using thioredoxin.
What are the correct statements regarding cortisol synthesis?
Select one or more:
a. Cortisol is synthesized exclusively in the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex
b. Cortisol is synthesized in the adrenal medulla
c. Cortisol synthesis does not require the action of 17-hydroxylase
d. The last step of cortisol synthesis is catalyzed by 11-hydroxylase
e. Cortisol is synthesized from cholesterol
The correct answers are:
d. The last step of cortisol synthesis is catalyzed by 11-hydroxylase,
e. Cortisol is synthesized from cholesterol
Which of the following reactions will be inhibited by dihydrofolate analogues, such as methotrexates:
Select one or more:
a. de novo synthesis of UMP
b. conversion of dUMP to dTMP.
c. conversion of IMP to GMP
d. de novo synthesis of IMP
The correct answers are:
b. conversion of dUMP to dTMP.
d. de novo synthesis of IMP
Aspartate is involved as a N-donor in:
Select one or more:
a. conversion of UTP to CTP.
b. synthesis of AMP from IMP
c. synthesis of GMP from IMP
d. de novo synthesis of IMP
The correct answers are:
b. synthesis of AMP from IMP,
d. de novo synthesis of IMP
Which enzymes are not required for the synthesis of estrogens starting from cholesterol?
Select one or more:
a. 17-hydroxylase
b. 21-hydroxylase
c. 11-hydroxylase
d. aromatase
e. side chain cleavage enzyme
The correct answers are:
b. 21-hydroxylase,
c. 11-hydroxylase
Select the correct statements regarding the production of female sex steroids!
Select one or more:
a. The major site of estrogen production is the adrenal cortex
b. Testosterone is converted to estradiol by aromatase, a cytochrome P450 isoenzyme
c. The ovaries produce estradiol and progesterone
d. In the placenta estradiol is synthesized from the weak androgen, DHEA provided by the maternal or fetal adrenal gland
e. In the placenta estradiol is synthesized from LDL-cholesterol
The correct answers are:
b. Testosterone is converted to estradiol by aromatase, a cytochrome P450 isoenzyme,
c. The ovaries produce estradiol and progesterone,
d. In the placenta estradiol is synthesized from the weak androgen, DHEA provided by the maternal or fetal adrenal gland
Select the correct statements regarding the production and inactivation of sex steroids!
Select one or more:
a. Leydig cells produce testosterone
b. Testosterone can be reduced to dihydrotestosterone by a cytochrome P450 isoenzyme
c. In the ovaries granulosa cells produce progesterone only in the luteal phase, after ovulation
d. In the ovaries two cell types, the granulosa cell and the theca interna cell have to cooperate for the production of estradiol
e. In the placenta the maternal steroid hormones are inactivated by a cytochrom P450 isoenzyme
The correct answers are:
a. Leydig cells produce testosterone,
c. In the ovaries granulosa cells produce progesterone only in the luteal phase, after ovulation,
d. In the ovaries two cell types, the granulosa cell and the theca interna cell have to cooperate for the production of estradiol
If a cell has an adequate supply of adenine nucleotides but requires more guanine nucleotides:
Select one or more:
a. Glutamine-PRPP amidotransferase will not be fully inhibited.
b. AMP will be a feedback inhibitor of the condensation of IMP with aspartate.
c. ATP will stimulate the production of GMP from IMP.
d. ATP will inhibit IMP dehydrogenase.
The correct answers are:
a. Glutamine-PRPP amidotransferase will not be fully inhibited.
b. AMP will be a feedback inhibitor of the condensation of IMP with aspartate.
c. ATP will stimulate the production of GMP from IMP.
Select the correct statements regarding the synthesis of prostaglandins and thromboxanes!
Select one or more:
a. Arachidonic acid is an essential fatty acid, frequently found in membrane phospholipids
b. Arachidonic acid is released from membrane phospholipids by phospholipase A2
c. PGH-synthase is a homodimer containing two different types of catalytic sites
d. Arachidonic acid is converted to PGG2 by a peroxidase
e. Platelets synthesize exclusively PGI2 from arachidonic acid
The correct answers are:
b. Arachidonic acid is released from membrane phospholipids by phospholipase A2,
c. PGH-synthase is a homodimer containing two different types of catalytic sites
Regulation of de novo AMP synthesis involves:
Select one or more:
a. allosteric activation by GMP
b. allosteric inhibition by AMP
c. availability of PRPP
The correct answers are:
b. allosteric inhibition by AMP,
c. availability of PRPP
Select the correct statements regarding the biological effects of prostaglandins and thromboxanes!
Select one or more:
a. TXA2 promotes platelet aggregation
b. PGE2 promotes platelet aggregation
c. PGE2 protects gastric mucosa cells from the erosive effects of gastric juice
d. PGI2 inhibits platelet aggregation
e. PGE2 and PGF2a play a role in the regulation of uterus contractility
The correct answers are:
a. TXA2 promotes platelet aggregation,
c. PGE2 protects gastric mucosa cells from the erosive effects of gastric juice,
d. PGI2 inhibits platelet aggregation,
e. PGE2 and PGF2a play a role in the regulation of uterus contractility
Orotic aciduria might be caused by the deficiency of:
Select one or more:
a. hypoxanthine-guanosine phosphoribosyl transferase
b. UMP synthase
c. adenosine deaminase
d. Ornithine transcarbamoylase
The correct answers are:
b. UMP synthase,
d. Ornithine transcarbamoylase
How do the non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) interfere with the synthesis of eicosanoids?
Select one or more:
a. Aspirin is a competitive inhibitor of the cyclooxygenase, COX-1 isoenzyme
b. The cyclooxygenase, COX-1 isoenzyme is completely blocked after acetylation of a Ser residue in its substrate-binding pocket
c. Aspirin prevents stroke in the elderly because it irreversibly acetylates the thromboxane synthase enzyme of platelets
d. NSAIDs decrease the inflammatory reactions by reversibly blocking the conversion of LTA4 to LTB4
e. The selective blockage of the cyclooxygenase, COX-2 isoenzyme could be a good strategy for pain relief without the side effect of gastric bleeding
The correct answers are:
b. The cyclooxygenase, COX-1 isoenzyme is completely blocked after acetylation of a Ser residue in its substrate-binding pocket,
e. The selective blockage of the cyclooxygenase, COX-2 isoenzyme could be a good strategy for pain relief without the side effect of gastric bleeding
What are the correct statements regarding leukotrienes?
Select one or more:
a. The cysteinyl leukotrienes include LTC4, LTD4 and LTE4
b. LTA4 and LTB4 together form the ``slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis’’ that plays a major role in the pathogenesis of asthma bronchiale
c. Montelukast (Singulair) and zafirlukast (Accolate) block the receptor for cysteinyl leukotrienes
d. Leukotrienes are named after their capability to absorbe white light
e. LTB4 is a chemotactic factor for neutrophil granulocytes
The correct answers are:
a. The cysteinyl leukotrienes include LTC4, LTD4 and LTE4,
c. Montelukast (Singulair) and zafirlukast (Accolate) block the receptor for cysteinyl leukotrienes,
e. LTB4 is a chemotactic factor for neutrophil granulocytes
Which of the following conditions out of A-D can cause gout?
Select one or more:
a. mutation at the allosteric site of PRPP synthase
b. glucose-6-phosphatase deficiency
c. hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase deficiency
d. fructose intolerance
e.
The correct answers are:
a. mutation at the allosteric site of PRPP synthase,
b. glucose-6-phosphatase deficiency,
c. hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase deficiency,
d. fructose intolerance
Administration of allopurinol to a patient with gout, who has a normal HG-PRT level, would lead to all of the following EXCEPT:
Select one:
a. Decreased de novo synthesis of IMP.
b. Decreased urate in the urine.
c. An increase of hypoxanthine in the blood.
d. Increased levels of PRPP .
e. Increased xanthine in the blood.
The correct answer is:
d. Increased levels of PRPP .
Which statements are true for the cyclooxygenase enzymes?
Select one or more:
a. the enzyme is also called PGH-synthase
b. cyclooxygenases belong to the family of cytochrome P 450 isoenzymes
c. arachidonate is a substrate for the enzyme
d. aspirine inhibits cyclooxygenase activity
e. in addition to the cyclooxygenase activity, the enzyme also exhibits epoxidase activity
The correct answers are:
a. the enzyme is also called PGH-synthase,
c. arachidonate is a substrate for the enzyme,
d. aspirine inhibits cyclooxygenase activity
How many cyclooxygenase isoenzymes are known?
Select one:
a. 4
b. 3
c. 2
d. there are no isoforms of this enzyme
e. there are no isoforms but the enzyme can exist in phosphorylated form
The correct answer is:
c. 2
Which of the following statements is not true?
Select one:
a. The active form of cyclooxygenase is monomeric
b. a serine residue of cyclooxygenase can be acetylated by aspirin
c. aspirin blocks cyclooxygenase-1 by irreversible covalent modification
d. Cyclooxygenase is a membrane-bound homodimeric enzyme
e. each cyclooxygenase monomer contains two different active centers
The correct answer is:
a. The active form of cyclooxygenase is monomeric
Which statements are valid for arachidonic acid?
Select one or more:
a. It can be released from phospholipids
b. Phospholipase C catalyzes its release from the plasma membrane
c. Prostaglandins are produced from arachidonic acid
d. Cyclooxygenase catalyzes the synthesis of leukotrienes
The correct answers are:
a. It can be released from phospholipids,
c. Prostaglandins are produced from arachidonic acid
Prerequisites for thromboxane synthesis are:
Select one or more:
a. availability of phospholipid containing arachidonate for phospholipase A2
b. active lipoxygenase
c. functional cyclooxygenase
d. corticosteroids do not inhibit cyclooxygenase
The correct answers are:
a. availability of phospholipid containing arachidonate for phospholipase A2,
c. functional cyclooxygenase,
d. corticosteroids do not inhibit cyclooxygenase
Which of these can be synthesized by plants but not by humans?
Select one:
a. linoleate [18:2(D9,12)]
b. palmitate (16:0)
c. phosphatidylcholine
d. pyruvate
e. stearate (18:0)
The correct answer is:
a. linoleate [18:2(D9,12)]
Which of these statements about eicosanoid synthesis is true?
Select one:
a. An early step in the path to thromboxanes is blocked by aspirin
b. Aspirin acts by blocking the synthesis of arachidonate.
c. Plants can synthesize leukotrienes, but humans cannot.
d. Thromboxanes are produced from arachidonate via the “lipoxygenase” path.
The correct answer is:
a. An early step in the path to thromboxanes is blocked by aspirin
Which of the following is a definition of glycemic index?
Select one:
a. The decrease in the blood concentration of glucagon after consuming the food compared with an equivalent amount
of white bread.
b. The increase in the blood concentration of glucose after
consuming the food.
c. The increase in the blood concentration of glucose after
consuming the food compared with an equivalent amount of white bread.
d. The increase in the blood concentration of insulin after
consuming the food.
e. The increase in the blood concentration of insulin after
consuming the food compared with an equivalent amount of white bread.
The correct answer is:
c. The increase in the blood concentration of glucose after consuming the food compared with an equivalent amount of white bread.
Which of the following will have the lowest glycemic index?
Select one:
a. baked apple
b. A baked potato
c. An uncooked apple
d. An uncooked potato
e. Apple juice
The correct answer is:
d. An uncooked potato
Which of the following will have the highest glycaemic index?
Select one:
a. A baked apple
b. A baked potato
c. An uncooked apple
d. An uncooked potato
e. Apple juice
The correct answer is:
e. Apple juice
A blood sample is taken from a 50-year-old woman after an overnight fast. Which one of the following will be at a higher concentration than after she had eaten a meal?
Select one:
a. Glucose
b. Insulin
c. Ketone bodies
d. Nonesterified fatty acids
e. Triacylglycerol
The correct answer is:
d. Nonesterified fatty acids
A blood sample is taken from a 25-year-old man after he has eaten three slices of toast and a boiled egg. Which one of the following will be at a higher concentration than if the blood sample had been taken after an overnight fast?
Select one:
a. Alanine
b. Glucagon
c. Glucose
d. Ketone bodies
e. Nonesterified fatty acids
The correct answer is:
c. Glucose
A blood sample is taken from a40-year-old man has been fasting completely for a week, drinking only water. Which of the following will be at a higher concentration than after a normal overnight fast?
Select one:
a. Glucose
b. Insulin
c. Ketone bodies
d. Nonesterified fatty acids
e. Triacylglycerol
The correct answer is:
c. Ketone bodies
Which one of following statements about the fed and fasting metabolic states is correct?
Select one:
a. In the fasting state glucagon acts to increase the activity of lipoprotein lipase in adipose tissue.
b. In the fasting state, glucagon acts to increase the synthesis of glycogen from glucose.
c. In the fed state insulin acts to increase the breakdown of glycogen to maintain blood glucose.
d. Ketone bodies are synthesized in liver in the fasting state, and the amount synthesized increase as fasting extends into starvation.
e. In the fed state there is decreased secretion of insulin in response to increased glucose in the portal blood.
The correct answer is:
d. Ketone bodies are synthesized in liver in the fasting state, and the amount synthesized increase as fasting extends into starvation.
Which one of following statements about the fed and fasting metabolic states is correct?
Select one:
a. In the fed state muscle can take up glucose for use as a metabolic fuel because glucose transport in muscle is stimulated in response to glucagon.
b. In the fed state there is decreased secretion of glucagon in response to increased glucose in the portal blood.
c. In the fed state, glucagon acts to increase the synthesis of glycogen from glucose.
d. Plasma glucose is maintained in starvation and prolonged fasting by gluconeogenesis from ketone bodies.
e. There is an increase in metabolic rate in the fasting state.
The correct answer is:
b. In the fed state there is decreased secretion of glucagon in response to increased glucose in the portal blood.
Which one of following statements about the fed and fasting metabolic states is correct?
Select one:
a. In the fasting state muscle synthesizes glucose from amino acids.
b. In the fed state adipose tissue can take up glucose for synthesis of triacylglycerol because glucose transport in adipose tissue is stimulated in response to insulin.
c. Ketone bodies are synthesized in muscle in the fasting state, and the amount synthesized increases as fasting extends into starvation.
d. Ketone bodies provide an alternative fuel for red blood cells in the fasting state.
e. Plasma glucose is maintained in starvation and prolonged fasting by gluconeogenesis from fatty acids.
The correct answer is:
b. In the fed state adipose tissue can take up glucose for synthesis of triacylglycerol because glucose transport in adipose tissue is stimulated in response to insulin.
Which one of following statements about the fed and fasting metabolic states is correct?
Select one:
a. In the fasting state adipose tissue synthesizes glucose from
the glycerol released by the breakdown of triacylglycerol.
b. In the fasting state adipose tissue synthesizes ketone bodies.
c. In the fasting state the main fuel for red blood cells is fatty
acids released from adipose tissue.
d. Ketone bodies provide the main fuel for the central nervous
system in the fasting state.
e. Plasma glucose is maintained in starvation and prolonged fasting by gluconeogenesis in the liver from the amino acids released by the breakdown of muscle protein.
The correct answer is:
e. Plasma glucose is maintained in starvation and prolonged fasting by gluconeogenesis in the liver from the amino acids released by the breakdown of muscle protein.
Which one of following statements about the fed and fasting metabolic states is correct?
Select one:
a. Fatty acids and triacylglycerol are synthesized in the liver in
the fasting state.
b. In the fasting state the main fuel for the central nervous
system is fatty acids released from adipose tissue.
c. In the fasting state the main metabolic fuel for most tissues
comes from fatty acids released from adipose tissue.
d. In the fed state muscle cannot take up glucose for use as a
metabolic fuel because glucose transport in muscle is
stimulated in response to glucagon.
e. Plasma glucose is maintained in starvation and prolonged
fasting by gluconeogenesis in adipose tissue from the glycerol released from triacylglycerol.
The correct answer is:
c. In the fasting state the main metabolic fuel for most tissues comes from fatty acids released from adipose tissue.
A 25-year-old man visits his GP complaining of abdominal cramps and diarrhea after drinking milk. What is the most likely cause of his problem?
Select one:
a. Bacterial and yeast overgrowth in the large intestine
b. Infection with the intestinal parasite Giardia lamblia
c. Lack of pancreatic amylase
d. Lack of small intestinal lactase
e. Lack of small intestinal sucrase-isomaltase
The correct answer is:
d. Lack of small intestinal lactase
Which one of following statements about glycolysis and gluconeogenesis is correct?
Select one:
a. All the reactions of glycolysis are freely reversible for
gluconeogenesis.
b. Fructose cannot be used for gluconeogenesis in the liver
because it cannot be phosphorylated to fructose-6-
phosphate.
c. Glycolysis can proceed in the absence of oxygen only if
pyruvate is formed from lactate in muscle.
d. Red blood cells only metabolize glucose by anaerobic
glycolysis (and the pentose phosphate pathway).
e. The reverse of glycolysis is the pathway for gluconeogenesis
in skeletal muscle.
The correct answer is:
d. Red blood cells only metabolize glucose by anaerobic glycolysis (and the pentose phosphate pathway).
Which one of following statements about the step in glycolysis catalyzed by hexokinase and in gluconeogenesis by glucose 6-phosphatase is correct?
Select one:
a. Because hexokinase has a low Km its activity in liver
increases as the concentration of glucose in the portal
blood increases.
b. Glucose-6-phosphatase is mainly active in muscle in the
fasting state.
c. If hexokinase and glucose-6-phosphatase are both equally
active at the same time there is net formation of ATP from
ADP and phosphate.
d. Liver contains an isoenzyme of hexokinase, glucokinase,
which is especially important in the fed state
e. Muscle can release glucose into the circulation from its
glycogen reserves in the fasting state.
The correct answer is:
d. Liver contains an isoenzyme of hexokinase, glucokinase, which is especially important in the fed state
Which one of following statements about this step in glycolysis catalyzed by phosphofructokinase and in gluconeogenesis by fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase is correct?
Select one:
a. Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase is mainly active in the liver in the fed state.
b. If phosphofructokinase and fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase are both equally active at the same time, there is a net formation of ATP from ADP and phosphate.
c. Phosphofructokinase is inhibited more or less completely by physiological concentrations of ATP.
d. Phosphofructokinase is mainly active in the liver in the fasting state.
The correct answer is:
c. Phosphofructokinase is inhibited more or less completely by physiological concentrations of ATP.
Which one of the following statements about glucose metabolism in maximum exertion is correct?
Select one:
a. Gluconeogenesis from lactate requires less ATP than is formed during anerobic glycolysis.
b. In maximum exertion pyruvate is oxidized to lactate in muscle.
c. Oxygen debt is caused by the need to exhale carbon dioxide produced in response to acidosis.
d. Oxygen debt reflects the need to replace oxygen that has been used in muscle during vigorous exercise.
e. There is metabolic acidosis as a result of vigorous exercise
The correct answer is:
e. There is metabolic acidosis as a result of vigorous exercise
Which one of following statements about glycogen metabolism is correct?
Select one:
a. Glycogen is synthesized in the liver in the fed state, then exported to other tissues in low density lipoproteins.
b. Glycogen reserves in liver and muscle will meet energy requirements for several days in prolonged fasting.
c. Liver synthesizes more glycogen when the hepatic portal blood concentration of glucose is high because of the activity of glucokinase in the liver.
d. Muscle synthesizes glycogen in the fed state because glycogen phosphorylase is activated in response to insulin.
e. The plasma concentration of glycogen increases in the fed state.
The correct answer is:
c. Liver synthesizes more glycogen when the hepatic portal blood concentration of glucose is high because of the activity of glucokinase in the liver.
Which one of following statements about glucose metabolism is correct?
Select one:
a. Glucagon increases the rate of glycolysis.
b. Glycolysis requires NADP+.
c. In glycolysis, glucose is cleaved into two three carbon compounds.
d. Substrate level phosphorylation takes place in the electron transport system.
e. The main product of glycolysis in red blood cells is pyruvate.
The correct answer is:
c. In glycolysis, glucose is cleaved into two three carbon compounds.
Which one of following statements about glycogen metabolism is correct?
Select one:
a. Glycogen synthase activity is increased by glucagon.
b. Glycogen phosphorylase is an enzyme that can be activated by phosphorylation of serine residues.
c. Glycogen phosphorylase cannot be activated by calcium ions.
d. cAMP activates glycogen synthesis.
e. Glycogen phosphorylase breaks the α1-4 glycosidic bonds by hydrolysis.
The correct answer is:
b. Glycogen phosphorylase is an enzyme that can be activated by phosphorylation of serine residues.
The proton motive force is the sum of:
Select one:
a. Proton gradient and electrical potential difference across the outer mitochondrial membrane
b. Proton gradient and ATP gradient across the outer mitochondrial membrane
c. Proton gradient and electrical potential difference across the inner mitochondrial membrane
d. Proton gradient and ATP gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane
e. Electrical potential difference and ATP gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane
The correct answer is:
c. Proton gradient and electrical potential difference across the inner mitochondrial membrane
Which statement is false?
Select one:
a. Trypsin can cleave the peptide bond formed by the carboxyl group of a basic amino acid.
b. Trypsin can cleave the peptide bond formed by the amino group of a basic amino acid.
c. Chymotrypsin can cleave the peptide bond formed by the carboxyl group of aromatic amino acids.
d. Chymotrypsin can cleave the peptide bond near tyrosine.
e. Trypsin can cleave the peptide bond near lysine.
The correct answer is:
b. Trypsin can cleave the peptide bond formed by the amino group of a basic amino acid.
Which of the following enzyme is not the component of the reagent for triglyceride determination?
Select one:
a. Peroxidase
b. Glycerol kinase
c. ACAT
d. Glycerol-3-phosphate oxidase
e. Lipoprotein lipase
The correct answer is:
c. ACAT
Select the correct statement from the sentences below:
Select one:
a. Higher HDL-cholesterol level is accompanied with higher risk for myocardial infarct.
b. Determination of LDL-cholesterol level is important for patients with familial and secondary hypercholesterinaemia.
c. Cholesterol is only present in LDL and HDL liporpoteins.
d. Hyperlipoproteinaemia is protective against cardiovascular diseases.
e. Dyslipidaemia is an essential risk factor in bone diasesas.
The correct answer is:
b. Determination of LDL-cholesterol level is important for patients with familial and secondary hypercholesterinaemia.
Which of the following enzymes is present in the reagent for cholesterol determination?
Select one:
a. Cholesterol esterase
b. HMG-CoA-reductase
c. LCAT
d. Glycerol-3-phosphate oxidase
e. Malate-dehydrogenase
The correct answer is:
a. Cholesterol esterase
Select the correct statement for the determination of serum cholesterol!
Select one:
a. LDL-cholesterol level is determinded directly from the plasma-supernatant after precipitation of other lipoproteins.
b. HDL-cholesterol level is determinded directly from the plasma-supernatant after precipitation of other lipoproteins.
c. In the first step of cholesterol level determination, cholesterol-esthers will be hydrolised by cholesterol peroxidase.
d. VLDL-cholesterol level is determinded directly from the plasma-supernatant after precipitation of other lipoproteins.
e. Cholesterol determination is performed by the Biuret-reaction.
The correct answer is:
b. HDL-cholesterol level is determinded directly from the plasma-supernatant after precipitation of other lipoproteins.
Which statement is false?
Select one:
a. Enzymatic hydrolysis of cholesteryl esters is needed for determination of HDL-cholesterol.
b. Determination of HDL-cholesterol is needed for determination of LDL-cholesterol.
c. Determination of HDL-cholesterol is needed for determination of total serum cholesterol.
d. Determination of serum triglyceride is needed for determination of LDL-cholesterol.
e. Precipitation and sedimentation of VLDL and LDL is needed for determination of HDL-cholesterol.
The correct answer is:
c. Determination of HDL-cholesterol is needed for determination of total serum cholesterol.
Which statement is false?
The enzymatic reactions involved in determination of LDL-cholesterol include:
Select one:
a. hydrolysis of cholesteryl esters by cholesteryl esterase
b. hydrolysis of cholesteryl esters by cholesteryl esterase
c. oxidation of cholesterol by cholesterol oxidase
d. oxidation of glycerol by glycerol oxidase
e. reduction of hydrogen peroxide by peroxidase
The correct answer is:
d. oxidation of glycerol by glycerol oxidase
Which statement is false?
Enzymatic determination of serum cholesterol and serum triglyceride both involve:
Select one:
a. hydrolysis of ester bonds
b. phosphorylation on the expense of ATP
c. oxidation by molecular oxygen
d. production of hydrogen peroxide
e. oxidation by hydrogen peroxide
The correct answer is:
b. phosphorylation on the expense of ATP
Which statement is true?
Enzymatic determination of serum triglyceride does but determination of serum cholesterol does not involve:
Select one:
a. phosphorylation on the expense of ATP
b. hydrolysis of ester bonds
c. oxidation by molecular oxygen
d. dehydrogenation by using NAD+
e. oxidation by hydrogen peroxide
The correct answer is:
a. phosphorylation on the expense of ATP
Which statement is true regarding the enzymatic determination of serum lipids?
Select one:
a. The assay procedure starts with precipitation of chylomicrons by trichloroacetic acid (TCA).
b. Lipoprotein lipase is needed to liberate fatty acids and cholesterol from the lipoproteins.
c. Both HDL-cholesterol and LDL-cholesterol are directly determined in different serum fractions.
d. LDL-cholesterol content is estimated as one fifth of the total serum triglyceride.
e. HDL-cholesterol can be determined in blood serum supernatant after precipitation and sedimentation of VLDL and LDL.
The correct answer is:
e. HDL-cholesterol can be determined in blood serum supernatant after precipitation and sedimentation of VLDL and LDL.
An uncoupler is:
Select one:
a. A lipophilic substance or a protein with the ability to transport protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane bypassing the Fo-F1 ATP synthase
b. An inhibitor of the Fo-F1 ATP synthase
c. An inhibitor of cytochrome c oxidase
d. An inhibitor of the adenine nucleotide translocase
e. A lipophilic substance or a protein with the ability to transport NADH across the inner mitochondrial membrane
The correct answer is:
a. A lipophilic substance or a protein with the ability to transport protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane bypassing the Fo-F1 ATP synthase
Which statement is true regarding serine proteases?
Select one:
a. Serine proteases are proteases that have serine and tyrosine bonded at the active site.
b. The serine proteases are the enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of phosphoanhydryl bond.
c. The serine proteases are the enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of ester or amide bond.
d. Serine proteases are proteases that have serine and proline bonded at the active site.
e. Hydrolysis of amide bond involves the reaction of acylation of the carbroxyl group of Asp102.
The correct answer is:
c. The serine proteases are the enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of ester or amide bond.
Which statement is false regarding serine proteases?
Select one:
a. Serine proteases are proteases that have serine bonded at the active site.
b. Serine proteases are the enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of ester or amide bond.
c. Catalytic triad of serine proteases located in the active site of the enzyme consist of three amino acids: His57, Ser195 and Asp102.
d. Many proteases are synthesized and secreted as inactive forms called zymogens and subsequently activated by proteolysis.
e. Catalytic triad of serine proteases located in the active site of the enzyme consist of three amino acids: Lys57, Ser195 and Tyr102.
The correct answer is:
e. Catalytic triad of serine proteases located in the active site of the enzyme consist of three amino acids: Lys57, Ser195 and Tyr102.
Which statement is true regarding serine proteases?
Select one:
a. Chymotrypsin is synthesized as active enzyme.
b. Substrate binding pocket of chymotrypsin is more hydrophobic than in trypsin, therefore chymotrypsin prefers medium to large sized hydrophobic residues, such as tyrosine, phenylalanine and tryptophan in binding pocket.
c. Substrate binding pocket of chymotrypsin is less hydrophobic than in trypsin, therefore chymotrypsin prefers Arg or Lys in binding pocket.
d. Chymotrypsin cleave peptide bonds following a negatively charged amino acid serine or histidine.
e. Serine proteases are not sequence specific.
The correct answer is:
b. Substrate binding pocket of chymotrypsin is more hydrophobic than in trypsin, therefore chymotrypsin prefers medium to large sized hydrophobic residues, such as tyrosine, phenylalanine and tryptophan in binding pocket.
Which statement is false regarding serine proteases?
Select one:
a. Bound substrate is attacked by acidophilic Asp195 of chymotripsinogen active site forming transition state complex (tetrahedral intermediate).
b. Serine proteases responsible for digestion can be categorised based on their substrate specificity as either chymotrypsin-like, trypsin-like or elastase-like.
c. Catalysis by serine proteases involves formation of a covalent acyl-enzyme intermediate.
d. Trypsin cleaves peptide bonds following a positively charged amino acid lysine or arginine.
e. Chymotrypsin is synthesized as inactive proenzymes (chymotrypsinogen) and activated subsequently by proteolysis.
The correct answer is:
a. Bound substrate is attacked by acidophilic Asp195 of chymotripsinogen active site forming transition state complex (tetrahedral intermediate).
Which statement is false regarding serine proteases?
Select one:
a. Chymotrypsin is a digestive enzyme synthesized in its inactive form in the pancreas, along with the related enzymes trypsin and elastase belonging to the superfamily of serine proteases.
b. Chymotrypsin is transported to the small intestine in an inactive form. Once the enzyme enters the small intestine, it becomes activated by proteolysis.
c. Serine proteases are inhibited by natural inhibitors called “serpins”. One of the best-studied serpins are antithrombin and alpha 1-antitrypsin.
d. Activation of trypsin is autocatalytic.
e. Zymogens are active forms of serine proteases in which active sites are fully saturated by their substrates.
The correct answer is:
e. Zymogens are active forms of serine proteases in which active sites are fully saturated by their substrates.
The effect of an uncoupler is:
Select one:
a. Dissipation of the proton motive force
b. Inhibition of respiration
c. Increase of mitochondrial ATP synthesis
d. Increase in protein transport to mitochondria
e. None of them
The correct answer is:
a. Dissipation of the proton motive force
2,4-dinitrophenol is:
Select one:
a. An inhibitor of the Fo-F1 ATP synthase
b. An uncoupler
c. An inhibitor of cytochrome c oxidase
d. An inhibitor of the adenine nucleotide translocase
e. None of them
The correct answer is:
b. An uncoupler
Atractyloside is:
Select one:
a. An inhibitor of the adenine nucleotide translocase
b. An inhibitor of the Fo-F1 ATP synthase
c. An inhibitor of cytochrome c oxidase
d. An uncoupler
e. None of them
The correct answer is:
a. An inhibitor of the adenine nucleotide translocase
Respiratory control ratio is:
Select one:
a. The ratio of oxygen consumption of mitochondria in the presence of ADP and substrates divided by the oxygen consumption in the absence of ADP or substrates
b. The ratio of the amount of NADH transported across the inner mitochondrial membrane divided by the amount of oxygen consumed by mitochondria
c. The ratio of the amount of phosphate incorporated to ATP divided by the amount of oxygen consumed by mitochondria
d. The ratio of the amount of oxygen consumed by mitochondria divided by moles of H+ translocated across the inner mitochondrial membrane
e. None of them
The correct answer is:
a. The ratio of oxygen consumption of mitochondria in the presence of ADP and substrates divided by the oxygen consumption in the absence of ADP or substrates
The P/O ratio is:
Select one:
a. The ratio of oxygen consumption of mitochondria in the presence of ADP and substrates divided by the rate of oxygen consumption in the absence of ADP or substrates
b. The ratio of the amount of NADH transported across the inner mitochondrial membrane divided by the amount of oxygen consumed by mitochondria
c. The ratio of the amount of phosphate incorporated to ATP divided by the amount of oxygen consumed by mitochondria
d. The ratio of the amount of oxygen consumed by mitochondria divided by moles of H+ translocated across the inner mitochondrial membrane
e. None of them
The correct answer is:
c. The ratio of the amount of phosphate incorporated to ATP divided by the amount of oxygen consumed by mitochondria
Oligomycin is:
Select one:
a. An inhibitor of the adenine nucleotide translocase
b. An uncoupler
c. An inhibitor of complex I
d. An inhibitor of the Fo-F1 ATP synthase
e. An inhibitor of complex IV
The correct answer is:
d. An inhibitor of the Fo-F1 ATP synthase
Inhibitors of complex IV are:
Select one:
a. Rotenone, antimycin
b. Oligomycin, atractyloside
c. Malonate, 2,4-dinitrophenol
d. CN-, CO, N3-
e. None of them
The correct answer is:
d. CN-, CO, N3-
Mitochondrial succinate dehydrogenase is:
Select one:
a. an FMN-linked dehydrogenase
b. an NADP+-linked dehydrogenase
c. an FAD-linked dehydrogenase
d. an NAD+-linked dehydrogenase
e. a both NAD+ and NADP+-linked dehydrogenase
The correct answer is:
c. an FAD-linked dehydrogenase
Which one of the following is a competitive inhibitor of succinate dehydrogenase?
Select one:
a. rotenone
b. malonate
c. alanine
d. malate
e. ATP
The correct answer is:
b. malonate
Which one of the following statements describes the mechanism of action of malonate?
Select one:
a. Acts as an uncoupler
b. Acts as inhibitor of ATP/ADP transporter
c. Inactivates the ATP synthase complex
d. Inactivates pyruvate kinase
e. Acts as a competitive inhibitor of succcinate dehydrogenase
The correct answer is:
e. Acts as a competitive inhibitor of succcinate dehydrogenase
Which one of the following statements describes the inhibition of succinate dehydrogenase by malonate?
Select one:
a. malonate decreases Km by interfering with the binding of the substrate
b. malonate does not change Km, but decreases Vmax
c. malonate can bind to the free E or to the ES complex as well
d. malonate does not affect Vmax
e. the inhibition by malonate can be enhanced by increasing the concentration of succinate
The correct answer is:
d. malonate does not affect Vmax
Choose the correct answer:
The reaction rate of succinate dehydrogenase was measured in the laboratory practice by detecting the following compound:
Select one:
a. NADH
b. oxidized form of iodonitrotetrazolium chloride
c. FADH2
d. reduced iodonitrotetrazolium formazan
e. amino-4-antipyrine
The correct answer is:
d. reduced iodonitrotetrazolium formazan
Which statement is true regarding the inhibiton of succinate dehydrogenase by malonate?
Select one:
a. malonate binds irreversibly to the active site of the enzyme
b. malonate binds reversibly to the active site of the enzyme and therefore not only ES complexes but EI complexes will also be formed
c. Km is decreased in the presence of malonate
d. vmax is decreased in the presence of malonate
e. both the Km and vmax are decreased in the presence of malonate
The correct answer is:
b. malonate binds reversibly to the active site of the enzyme and therefore not only ES complexes but EI complexes will also be formed
We characterized the competitive inhibition of succinate dehydrogenase by malonate in the laboratory practice by plotting the results on a graph. Which one of the following statements is true?
Select one:
a. we plotted malonate concentration versus succinate concentration
b. we plotted 1/v versus 1/[S]
c. the intercept on the Y axis of the graph gave the -1/KM
d. the intercept on the X axis of the graph gave the 1/vmax
e. we plotted the reaction rate versus 1/[S]
The correct answer is:
b. we plotted 1/v versus 1/[S]
Which one of the following parameters did we use to calculate the rate of the succinate dehydrogenase reaction in the laboratory practice?
Select one:
a. the concentration of a reduced redox dye
b. the concentration of an oxidized redox dye
c. the used amount of succinate
d. the produced amount of fumarate
e. the produced amount of FAD
The correct answer is:
a. the concentration of a reduced redox dye
Which one of the following components was not used in the laboratory practice in which succinate dehydrogenase activity was measured?
Select one:
a. phenolphtalein indicator
b. malonate
c. FTF (formate-Triton-formaldehyde solution)
d. INT (iodonitrotetrazolium chloride)
e. mitochondrial membrane
The correct answer is:
a. phenolphtalein indicator
The inhibition of succinate dehydrogenase by malonate can be relieved by adding more of the following chemical to the enzyme system:
Select one:
a. FAD
b. succinate
c. fumarate
d. maleate
e. ubiquinone
The correct answer is:
b. succinate
Which one of the following statements is false regarding succinate dehydrogenase?
Select one:
a. the enzyme oxidizes succinate to fumarate
b. the enzyme is bound to the inner mitochondrial membrane
c. the enzyme contains Fe-S centers and an FAD prosthetic group
d. the enzyme is part of the mitochondrial electron transport chain
e. the enzyme pumps protons out of the matrix into the intermembrane space
The correct answer is:
e. the enzyme pumps protons out of the matrix into the intermembrane space
Which one of the following statements is false?
We can use the enzyme kinetic parameters (Km, vmax, kp) determined by Monte Carlo simulation…
Select one:
a. to identify the rate-limiting step of a metabolic pathway.
b. to find the physiologically relevant substrate of a pathway.
c. to decide which enzyme is saturated in vivo by its substrate (if in vivo [S] is known).
d. to compare the turnover number of two enzymes.
e. to calculate the standard Gibb’s free energy value of a reaction.
The correct answer is:
e. to calculate the standard Gibb’s free energy value of a reaction.
Regarding the effect of pH and temperature on enzyme activity, which one of the following statements is true?
Select one:
a. Increasing the temperature will always lead to a decreased rate of the reaction as a result of protein denaturation.
b. The changes of pH affect only the enzyme molecules, but not the substrates.
c. The effect of temperature on the enzyme molecules is time-independent.
d. The frequency of fruitful collisions of the reactant molecules is determined by their kinetic energy and thus by temperature.
e. The plot v (reaction rate) versus T (temperature) is a linear ascending curve in the range of 0-90°C in the case of human enzymes.
The correct answer is:
d. The frequency of fruitful collisions of the reactant molecules is determined by their kinetic energy and thus by temperature.
Which one of the following Michaelis-Menten assumptions is not correct?
Select one:
a. the [S] is much larger than the [E]
b. the decrease in the [S] is more than 10% of the initial [S]
c. the rate of the P → E+S reaction is negligible
d. the [ES] is constant
e. the increase of the [P] is linear
The correct answer is:
b. the decrease in the [S] is more than 10% of the initial [S]
We identified the rate-limiting step of a metabolic pathway in the biochemistry class using computer simulation. How did we predict the flux-generating (rate-limiting) reaction of the S1 metabolic pathway?
Select one:
a. The in vivo Vmax of this reaction was high, and the in vivo substrate concentration was much greater than the Km.
b. The in vivo Vmax of this reaction was low, and the in vivo substrate concentration was much greater than the Km.
c. The in vivo Vmax of this reaction was high, and the in vivo substrate concentration was much less than the Km.
d. The in vivo Vmax of this reaction was low, and the in vivo substrate concentration was much less than the Km.
The correct answer is:
b. The in vivo Vmax of this reaction was low, and the in vivo substrate concentration was much greater than the Km.
Which statement is true regarding the regulation of pyruvate kinase L and M isoenzymes?
Select one:
a. cAMP dependent phosphorylation increases the affinity of PK-L for the activiting ligands
b. Starvation increases the mRNA level of the PK-M isoenzyme.
c. The PK-L isoenzyme is allosterically inhibited by ADP.
d. Carbohydrate rich diet increases the mRNA level of the PK-M isoenzyme.
e. The PK-M isoenzyme shows no allosteric behavior.
The correct answer is:
e. The PK-M isoenzyme shows no allosteric behavior.
Which statement is false regarding the regulation of pyruvate kinase L and M isoenzymes?
Select one:
a. Carbohydrate rich diet increases the PK-L (liver) isoenzyme mRNA level.
b. The PK-M (muscle) isoenzyme is allosterically inhibited by ATP or alanine.
c. cAMP dependent phosphorylation decreases the affinity of PK-L for the activiting ligands.
d. Starvation decreases the mRNA level of the PK-L isoenzyme.
e. The PK-L isoenzyme is allosterically activated by fructose-1,6-bisphosphate.
The correct answer is:
b. The PK-M (muscle) isoenzyme is allosterically inhibited by ATP or alanine.
Which parameter was measured in the laboratory practice in which we examined the pyruvate kinase (PK) catalyzed reaction?
Select one:
a. The absorbance changes of NADH, which was synthesized by pyruvate-dehydrogenase in a coupled enzyme reaction.
b. The absorbance changes of NADPH, which was produced by hexokinase and glucose-6-phoshate dehydrogenase in a coupled enzyme reaction.
c. The absorbance changes of phosphoenol-pyruvate, which was utilized by the PK catalyzed reaction.
d. The absorbance changes of NADH, which was consumed by lactate-dehydrogenase in a coupled enzyme reaction.
e. The absorbance changes of ATP, which was synthesized by the PK catalyzed reaction.
The correct answer is:
d. The absorbance changes of NADH, which was consumed by lactate-dehydrogenase in a coupled enzyme reaction.
The rate of the reaction catalyzed by pyruvate kinase (PK) increases after….
Select one:
a. pipetting alanine to the PK-L isoenzyme reaction mix.
b. adding fructose-1,6-bisphosphate to the PK-M isoenzyme reaction mix.
c. adding fructose-1,6-bisphosphate to the PK-L isoenzyme reaction mix.
d. pipetting ATP to the PK-M isoenzyme reaction mix.
e. adding alanine to the PK-M reaction mix.
The correct answer is:
c. adding fructose-1,6-bisphosphate to the PK-L isoenzyme reaction mix.
The rate of the reaction catalyzed by pyruvate kinase (PK) decreases after…
Select one:
a. pipetting alanine to the PK-L isoenzyme reaction mix.
b. adding fructose-1,6-bisphosphate to the PK-M isoenzyme reaction mix.
c. adding fructose-1,6-bisphosphate to the PK-L isoenzyme reaction mix.
d. pipetting ATP to the PK-M isoenzyme reaction mix.
e. adding alanine to the PK-M isoenzyme reaction mix.
The correct answer is:
a. pipetting alanine to the PK-L isoenzyme reaction mix.
Which statement is true regarding the measurement of pyruvate kinase activity in the laboratory practice?
Select one:
a. the mitochondrial fractions of liver and muscle were used for the experiments
b. we demonstrated the activating effect of phosphoenolpyruvate on the PK-M isoenzyme
c. the increase in lactate concentration was followed spectrophotometrically
d. we demonstrated the activating effect of fructose-2,6-bisphosphate on the PK-L isoenzyme
e. the reaction was initiated by the addition of ADP
The correct answer is:
e. the reaction was initiated by the addition of ADP
Which statement is false regarding the measurement of pyruvate kinase activity in the laboratory practice?
Select one:
a. the reaction rate was measured using a coupled enzyme assay
b. lactate was oxidized to pyruvate during the experiments
c. the reaction mixture contained Mg2+ ions
d. ATP was formed during the experiments
e. NADH was oxidized during the experiments
The correct answer is:
b. lactate was oxidized to pyruvate during the experiments
Which statement is correct?
Select one:
a. the pancreatic lipase does not need a cofactor for its activity
b. the pancreatic lipase is proteolytically activated in the duodenum
c. bile acids and co-lipase are necessary for the interfacial activation of pancreatic lipase in the duodenum
d. co-lipase is a serine protease, which proteolytically activates pancreatic lipase in the duodenum
e. co-lipase alone can emulsify triglycerides in the duodenum
The correct answer is:
c. bile acids and co-lipase are necessary for the interfacial activation of pancreatic lipase in the duodenum
How did we measure the enzyme activity of pancreatic lipase in the laboratory practice?
Select one:
a. free glycerol generation was measured by complexometry
b. free fatty acid generation was followed by spectrophotometry
c. free fatty acid generation was followed by titration with sodium hydroxide
d. free fatty acid generation was followed by titration with HCl
e. free glycerol generation was followed by spectrophotometry
The correct answer is:
c. free fatty acid generation was followed by titration with sodium hydroxide
Which statement is true for the measurement of pancreatic lipase activity in the laboratory practice?
Select one:
a. we used olive oil as a substrate
b. we used homogenized milk as substrate
c. we excluded co-lipase from the reaction mixture
d. we compared the activity of pancreatic lipase with that of lipoprotein lipase
e. we added apoCII to the reaction mixture
The correct answer is:
b. we used homogenized milk as substrate
Which statement is true for the measurement of pancreatic lipase activity in the laboratory practice?
Select one:
a. we compared pancreatic lipase activities in the absence and presence of milk
b. we compared pancreatic lipase activities in the absence and presence of co-lipase
c. we compared pancreatic lipase activities in the absence and presence of bile
d. we studied the effect of NaOH on the pancreatic lipase activity
e. we used formaldehyde in order to activate pancreatic lipase
The correct answer is:
c. we compared pancreatic lipase activities in the absence and presence of bile
Which statement is true for the results of our laboratory experiments in which pancreatic lipase activity was measured?
Select one:
a. we proved that pancreatic lipase is regulated at the level of gene expression
b. we found that pancreatic lipase was already active in the pancreas tissue
c. we found a higher pancreatic lipase activity in the presence of bile
d. our major conclusion was that formaldehyde stops the reaction
e. the point of the experiments was to prove that phenolphtalein is pink at acidic pH
The correct answer is:
c. we found a higher pancreatic lipase activity in the presence of bile
Which one of the following materials was not used for the laboratory experiment in which pancreatic lipase activity was measured?
Select one:
a. pancreatic extract
b. NaOH
c. phenol red indicator
d. bile
e. 10% formaldehyde solution
The correct answer is:
c. phenol red indicator
Which statement is true regarding the laboratory experiment in which pancreatic lipase activity was measured?
Select one:
a. the triglycerides in the milk were already emulsified
b. the bile used for the experiment contained co-lipase as well
c. a weak base was used to titrate the liberated fatty acids
d. the reaction was started by the addition of bile
e. to evaluate the results we plotted the volume of the used bile versus the incubation time
The correct answer is:
a. the triglycerides in the milk were already emulsified
Which effect of the bile acids was demonstrated in the laboratory experiment in which pancreatic lipase activity was measured?
Select one:
a. bile acids emulsify triglycerides in homogenized milk
b. bile acids activate pro-co-lipase by proteolysis
c. bile acids activate pancreatic lipase by inducing a conformational change
d. bile acids activate co-lipase by inducing a conformational change
e. bile acids activate pancreatic lipase by proteolysis
The correct answer is:
c. bile acids activate pancreatic lipase by inducing a conformational change
Select the correct statements
Select one or more:
a. The acyl-CoA dehydrogenase is a mitochondrial enzyme
b. NAD is the coenzyme of acyl-CoA dehydrogenase
c. The acyl-CoA dehydrogenase generates a trans-double bond
d. No ketone bodies are produced, if the acyl-CoA dehydrogenase is deficient
The correct answers are:
a. The acyl-CoA dehydrogenase is a mitochondrial enzyme,
c. The acyl-CoA dehydrogenase generates a trans-double bond,
d. No ketone bodies are produced, if the acyl-CoA dehydrogenase is deficient
Select the statements valid for the ketone bodies
Select one or more:
a. Produced in the liver
b. Non-soluble in water
c. Only organs expressing the ß-ketoacyl-CoA-transferase enzyme can utilize them
d. Their amount increases in parallel with the increase of b-oxidation of fatty acids in the liver
e. They are not produced under physiological conditions
The correct answers are:
a. Produced in the liver,
c. Only organs expressing the ß-ketoacyl-CoA-transferase enzyme can utilize them,
d. Their amount increases in parallel with the increase of b-oxidation of fatty acids in the liver
Select the statements valid for the synthesis of fatty acids
Select one or more:
a. The activity of acetyl-CoA carboxilase primarily determines the overall rate of the process
b. The acetyl-CoA is transported in the form of citrate to the site of synthesis
c. NADH2 is utilized in the reactions of the process
d. The ATP-citrate-lyase provides the immediate precursor of the synthesis
e. The carnitine carrier is involved in the process
The correct answers are:
a. The activity of acetyl-CoA carboxilase primarily determines the overall rate of the process,
b. The acetyl-CoA is transported in the form of citrate to the site of synthesis,
d. The ATP-citrate-lyase provides the immediate precursor of the synthesis
Select the statements valid for the synthesis of palmitoic acid
Select one or more:
a. The fatty acid synthase is a cytoplasmic enzyme
b. The elongation of the molecule by two carbon atoms is accompanied by the oxidation of two NADPH
c. The fatty acyl-group is attached to ACP in the course of the synthesis
d. Malonyl-CoA loses a carboxyl group during the process
e. Acetyl CoA binds to a SH-group of the condensing enzyme
The correct answers are:
a. The fatty acid synthase is a cytoplasmic enzyme,
b. The elongation of the molecule by two carbon atoms is accompanied by the oxidation of two NADPH,
c. The fatty acyl-group is attached to ACP in the course of the synthesis,
d. Malonyl-CoA loses a carboxyl group during the process,
e. Acetyl CoA binds to a SH-group of the condensing enzyme