Section 7 - Reproduction and Inheritance 2 Flashcards
What are sperm, where are they made and when (3)
- Male gametes
- Made in the testes
- All the time after puberty
Sperm mix with a liquid to form …. , which is ejaculated from the …….. to the ………. of the female during sexual intercourse
semen
penis
vagina


What is 1 and what is its purpose (2)
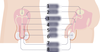
- Bladder
- Stores urine
What is 2 and what is its purpose (2)

- Glands
- Produce the liquid that’s added to sperm to make semen
What is 3 and what is its purpose (3)

- Sperm duct (vas deferens)
- Muscular tube
- Carries sperm from testis towards the urethra
What is 4 and what is its purpose (3)

- Urethra
- Tube which carries sperm through the penis during ejaculation
- Urine also passes through the urethra before leaving the body
What is 6 and what is its purpose (2)

- Testis
- Where sperm is made
What is 8 and what is its purpose (2)

- Scrotal sac/scrotum
- Hangs behind the penis and contains the testis
What is erectile tissue (1)
- Swells when filled with blood, making the penis erect


What are female gametes (1)
- Ova
How and when is an ovum produced (2)
- Every 28 days
- From one of the two ovaries
What happens once an ovum is produced (2)
- Passes into the fallopian tube
- Might meet sperm that have entered the vagina during sex
What happens if an ovum isn’t fertilised by sperm (2)
- Ovum will break up
- And pass out of the vagina
What happens if the ovum is fertilised (2)
- Ovum starts to divide
- New cells will travel down the Fallopian tube to the uterus
- Attaches tp endometrium (uterus lining)
- Fertilised ovum develops into an embryo


What is 1 and what is its purpose (2)

- Ovaduct (Fallopian tube)
- Muscular tube that carries the ovum from the ovary to the uterus
What is 2 and what is its purpose (2)

- Ovary
- The organ that produces ova and sex hormones
What is 3 and what is its purpose (2)

- Uterus (womb)
- The organ where an embryo grows
What is 4 and what is its purpose (2)

- Cervix
- Neck of the uterus
What is 5 and what is its purpose (2)

- Bladder
- Stores urine
What is 6 and what is its purpose (2)

- Urethra
- Organ where an embryo grows
What is 7 and what is its purpose (2)
- Vagina
- Where sperm are deposited
What are the sex hormones in men and women (2)
Men - testosterone
Women - oestrogen
What 4 things does oestrogen in women cause (4)
- Extra hair on underarms and pubic area
- Hips to widen
- Development of breasts
- Ovum release and start of periods
What 5 things does testosterone in men cause (5)
- Extra hair on face and body
- Muscles to develop
- Penis and testicles to enlarge
- Sperm production
- Deepening of voice
What are stages 1 and 2 of the menstrual cycle (4)
- S1 : Day 1 is when bleeding starts
- Uterus lining breaks down for about four days
- S2 : The uterus lining builds up again
- From day 4 to 14, devleops into a thick spongy layer of blood vessels ready to recieve a fertilised ovum
What are stages 3 and 4 of the menstrual cycle (4)
- S3 : An ovum develops and is released
- Released from the ovary at day 14
- S4 : The wall is maintained for about 14 days until day 28
- If no fertilised ovum has landed on the uterus wall by day 28, spongy lining starts to break down and cycle starts again


Where are oestrogen and progesterone produced (1)
- Ovaries
What does oestrogen do (2)
- Causes the lining of the uterus to thicken and grow
- Oestrogen stimulates the production of LH, which stimulates the release of an ovum at day 14
What does progesterone do (2)
- Maintains the lining of the uterus
- When the level of progesterone falls, the lining breaks down
How do progesterone levels change if the women is pregnant (3)
- Progesterone levels stay high
- Instead of falling
- To maintain the lining of the uterus during pregnancy


What is the term for when a baby starts to look human in the later stages of pregnancy (1)
- Fetus
When does the placenta develop and what does it do (2)
- Once the embryo has imolanted in the uterus
- Lets the blood of the embryo and mother come very close to allow the exchange of food, oxygen and waste
Where is amniotic fluid found and what does it do (2)
- Found in the amnion membrane, which surronds the embryo
- Protects the embryo against bumps and knocks
What 3 factors aren’t affected by enviornment (3)
- Eye and hair colour
- Inherited disorders
- Blood group
What is the theory of evolution (1)
- Life began as simple organisms from which more complex organisms evolved
Explain the process of natural selection (6)
- Resources living things need to survive are limited
- Individuals compete for resources to survive, only some surviving
- Some varieties of a particular species will have a better chance of survival
- Those varieties will then have an increased chance of breeding and passing on genes
- A greater proportion of individuals in the next generation have beter alleles, better characteristics for survival
- Over many generations, species become better able to survive. ‘Best’ features are naturally selected and species adapt
What are mutations (1)
- rare, random changes to the genetic code
Give two ways mutations can be harmful (2)
- If a mutation occurs in reproductive cells, offspring might abnormally develop, or die
- If a muation occurs in body cells, mutant cells may multiply in an uncontrolled way, causing cancer
Give two ways the chance of mutation is increased (2)
- Ionising radiation, e.g X rays
- Chemicals called mutagens, e.g chemicals in tobacco
How can mutations be beneficial (3)
- Give an organism a survival advantage
- Organism can live on in conditions where the others die
- Natural selection
How can bacteria evolve and become antibiotic-resistant (5)
- Bacteria develop random mutation in DNA
- Sometimes, means a bacterium is less affected by a particular anti biotic
- Therefore lives for longer and reproduces many more times
- Leads to natural selection
- Problem for those who are affected bu the bacteria, as it is no longer easy to get rid of


