S4) The Thigh Flashcards
What is the femur?
The femur is the only bone in the thigh and acts to transmit forces from the tibia to the hip joint

Identify the structures visible in the proximal area of the femur

Describe the structure and function of the head in the proximal area of the femur

- Structure: smooth surface with a depression on the medial aspect (ligament of head of femur attaches)
- Function: articulates with the acetabulum of the pelvis to form the hip joint

Describe the structure and function of the neck in the proximal area of the femur

- Structure: cylindrical, projecting in a superior and medial direction
- Function: connects the head of the femur with the shaft

Describe the structure and function of the greater trochanter in the proximal area of the femur

- Structure: bony projection angled superiorly and posteriorly, lateral to the neck
- Function: attachment site for many of the muscles in the gluteal region

Describe the structure and function of the lesser trochanter in the proximal area of the femur

- Structure: smaller bony projection, on the posteromedial side of the femur, inferior to the neck-shaft junction
- Function: attachment site for the psoas major and iliacus muscles

Describe the structure and function of the intertrochanteric line in the proximal area of the femur

- Structure: a ridge of bone running inferomedially on the anterior surface of the femur, connecting the two trochanters
- Function: attachment site for the iliofemoral ligament

Describe the structure and function of the intertrochanteric crest in the proximal area of the femur

- Structure: ridge of bone that connects the two trochanters on the posterior surface of the femur
- Function: attachment site for quadratus femoris (quadrate tubercle)

What is the pectineal line?

The pectineal line is the line formed when the intertrochanteric line passes the lesser trochanter on the posterior surface of the proximal femur

What are linea aspera?
Linea aspera are roughened ridges of bone found on the posterior surface of the femoral shaft

Describe the features of the linea aspera in the proximal region of the posterior femur
- Pectineal line → medial border of the linea aspera
- Gluteal tuberosity → lateral border of the linea aspera

Describe the features of the linea aspera in the distal region of the posterior femur
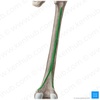
- Linea aspera widens and forms the floor of the popliteal fossa
- The medial and lateral borders form the medial and lateral supracondylar lines

Identify the structures visible on the anterior surface of the distal femur

Identify the structures visible on the posterior surface of the distal femur

Describe the articulations of the medial and lateral condyles of the distal femur
- Posterior & inferior surfaces articulate with the tibia and menisci
- Anterior surface articulates with the patella

Describe the structure and function of the intercondylar fossa in the distal femur
- Structure: a depression on the posterior surface of the femur, between the two condyles
- Function: contains two facets for attachment of internal knee ligaments

Where do the posterior and anterior cruciate ligaments of the knee attach to on the distal femur?
- Facet for attachment of the posterior cruciate ligament – found on the medial wall of the intercondylar fossa (large, rounded, flat)
- Facet for attachment of anterior cruciate ligament – found on the lateral wall of the intercondylar fossa (smaller)
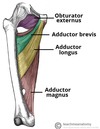
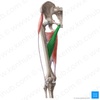
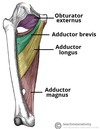
Identify the 4 muscles found in the anterior thigh
- Pectineus
- Sartorius
- Quadriceps femoris muscles
- Iliopsoas
Which two individual muscles compose the illiopsoas muscle?
- Psoas major
- Illiacus

Describe the structure, function and innervation of the psoas major muscle

- Structure: insert as the same tendon with the illiacus
- Function: hip flexion, lateral rotation (both muscles)
- Innervation: anterior rami of L1-3

State the origin and attachment of the psoas major

- Origin: lumbar vertebrae
- Attachment: lesser trochanter of the femur (with illiacus)

Describe the structure, function and innervation of the illiacus muscle

- Structure: insert as the same tendon with the psoas major
- Function: hip flexion, lateral rotation (both muscles)
- Innervation: femoral nerve

State the origin and attachment of the illiacus muscle

- Origin: iliac fossa of the pelvis
- Attachment: lesser trochanter of the femur (with psoas major)

Which 4 muscles compose the quadriceps femoris?
- Rectus femoris
- Vastus medialis
- Vastus intermedius
- Vastus lateralis