S11) Pharmacology of Airway Control Flashcards
Describe the autonomic innervation of the airway smooth muscle
- Parasympathetic (dominant) – bronchoconstriction, vascular dilatation, increased secretion from mucus glands
- Sympathetic – innervates vascular smooth muscle & glands (doesn’t affect airway, but β-adrenoreceptors found in airway smooth muscle)
What does asthma control mean?
- Minimal symptoms during day and night
- Minimal need for reliever medication
- No exacerbations
- No limitation of physical activity
- Normal lung function (FEV1 and/or PEF >80% predicted or best)
Outline the stepwise treatment approach for asthma
- Step 1 – short acting β2 agonists, consider low dose ICS
- Step 2 – regular low dose ICS
- Step 3
A. LABA + low dose ICS
B. LABA + ↑ dose ICS / stop LABA if no effect
- Step 4 – LABA + high dose ICS (can add LTRA/aminophylline)
- Step 5 – daily oral steroid + high dose ICS + consider others
What is used to treat mild intermittent asthma in Step 1 of asthma control?
Mild intermittent asthma – short-acting β2-agonists e.g. salbutamol, terbutaline
Describe the Step 1 treatment aims in asthma control
- Symptom relief through reversal of bronchoconstriction
- Used on an as-required basis (not regularly)
Describe the site and/or mechanism of action of β2 agonists in Step 1 of asthma control
- Acts predominantly on airway smooth muscle
- Potentially inhibits mast cell degranulation (if used intermittently)
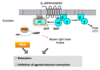
Illustrate the β2 receptor function in airway smooth muscle
Classify the different inhaled β2 agonists in terms of the speed of onset and the duration of action

Identify some side effects of β2 agonists
Adrenergic i.e. tachycardia, palpitations, tremor
What is used as regular preventer therapy in Step 2 of asthma control?
Regular preventer therapy – inhaled corticosteroids
What are the four conditions one must consider before starting Step 2 in the asthma control for a patient?
- Using β2 agonist ≥ 3 times/week
- Symptoms ≥ 3times/week
- Waking ≥ 1time/week
- Exacerbation requiring oral steroids in last 2 years
What are the aims of Step 2 treatment in asthma control?
- Improve symptoms
- Improve lung function
- Reduce exacerbations
- Prevent death
Illustrate the systemic availability of inhaled drugs

Provide some examples of inhaled corticosteroids
- Budesonide
- Beclomethasone
- Fluticasone
Provide an example of a combined LABA and steroid
Symbicort
Provide an example of a leukotriene receptor antagonists
Montelukast
What are some ADRs for leukotriene receptor antagonists?
- Angioedema
- Dry mouth
- Anaphylaxis
- Arthralgia
- Fever
Describe the mechanism of action for LTRAs
- LTRAs lock the effect of cysteinyl leukotrienes in the airways at the CysLT1 receptor
- Leukotrienes are released by mast cells/eosinophils, induce bronchoconstriction, mucus secretion and mucosal oedema and promote inflammatory cell recruitment
Provide some examples of methylxanthines
- Theophylline
- Aminophylline
Describe the mechanism of action for methylxanthines
- Antagonise adenosine receptors
- Inhibit phosphodiesterase
- Increase cAMP
What are the ADRs for methylxanthines?
- Common – nausea, headache, reflux
- Potentially life-threatening toxic complications – arrhythmias, fits
What possible drug interactions might methylxanthines have?
Levels increased by CYP450 inhibitors e.g. erythromycin, ciprofloxacin
Provide some examples of long acting anticholinergics
- Tiotropium bromide
- Glycopyrronium
What are the indications for LAMAs?
- COPD
- Severe asthma
Describe the mechanism of action for long acting anticholinergics
LAMAs bind to M3 muscarinic receptor and block it’s action (prevent bronchoconstriction)

What are the ADRs of LAMAs?
Anticholinergic – dry mouth, urinary retention, glaucoma
Describe the mechanism of action of omalizumab (anti-IgE)
Biological therapies:
- Prevents IgE binding to high affinity IgE receptor
- Cannot bind to IgE already bound to receptor, so cannot cross-link IgE and activate mast cells
Describe the mechanism of action of reslizumab (Anti IL-5)
Biological therapies:
- Reduce peripheral blood and airway eosinophil numbers
- Most effective at reducing rate of severe asthma exacerbations


