S1) Embryology of the Musculoskeletal System Flashcards
When do the limb buds appear?
The limb buds first appear as small projections on the lateral body wall during the fourth week of development
Describe the structure of the limb buds
- The buds consist of a mass of mesenchyme covered by a layer of ectoderm
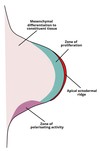
- At the tip of the bud the ectodermal cells divide to form an apical ectodermal ridge

Which limb develops first?
Upper limb buds develops a few days before the lower limb buds
What drives limb elongation?
Proliferation of mesenchyme (induced by AER)
As the limbs elongate, they rotate.
Describe the rotation of the upper and lower limbs
- The upper limb rotates laterally through 90° so extensor muscles lie on the posterior aspects of the limb
- The lower limb rotates medially through almost 90° so extensor muscles lie on the anterior aspects of the limb
Identify the three spatial axes in limb development
- Proximal-distal axis
- Dorsal-ventral axis
- Anterior-posterior axis
Identify the controllers of axial specification in limb development
- Zone of Polarising Activity controls anterior-posterior axis
- Apical Ectodermal Ridge controls proximal-distal axis
- Ectoderm controls dorsal-ventral axis
What does the AER do?
AER lies immediately above the mesenchyme and orchestrates limb development from proximal to distal then regresses
Describe how the proximal-distal axis is generated by the AER
- AER exerts an inductive influence on mesenchyme so it remains undifferentiated
- Proximal mesenchyme begins to differentiate into constituent tissues
- AER induces development of the digits within the hand/foot plates

What is the Zone of Polarising Activity and what does it do?
- ZPA is a signalling centre located at the posterior base of the limb bud
- It controls maintains the AER and generates the asymmetry of the limbs (anterior – posterior axis determination)

What are the digital rays?
- Mesenchyme condensations within plates
- Cartilaginous models of the digital bones
Describe how apoptosis sculpts the digits of the upper and lower limbs
- AER breaks up and is maintained only over the tips of the digital rays
- Interdigital spaces are progressively sculpted by programmed cell death

Describe the innervation of the upper and lower limb buds
- Upper limb buds appear opposite the caudal & cervical spinal segments
- Lower limb buds appear opposite the lumbar & sacral spinal segments
Describe the development of limb compartments
- Myogenic precursors migrate into limbs from somites (body segments)
- They coalesce into 2 common muscle masses around the newly formed skeletal elements
Identify the two compartments in the limbs
- Flexor compartment (ventral)
- Extensor compartment (dorsal)
Identify and describe 3 underlying problems in morphogenesis
- Malformation – intrinsic error in coordination of morphogenesis
- Deformation – constriction bands
- Disruption – external agent e.g. thalidomide
What is syndactyly?
Syndactyly is the fusion of digits (connective tissue / bones)

What is polydactyly?
Polydactyly is an autosomal recessive trait resulting in extra digits

What is amelia?
Amelia is the complete absence of a limb

What is meromelia?
Meromelia is the partial absence of one or more limb structures

segmental elements
makes building the body more efficient
hox genes
gives location for different segments in the body


